
The hydrogen ion, H+, binds with the enzyme (E−) to activate it in the form EH. The hydrogen ion, H+, also binds with EH to deactivate it by forming
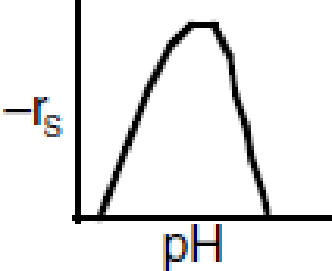
Figure P9-13B Enzyme pH dependence.
where E− and
- (a) Determine if the preceding sequence can explain the optimum in enzyme activity with pH shown in Figure P9-13B.
- (b) List ways you can work this problem incorrectly.
- (c) Apply one or more of the six ideas in Preface Table P-4, page xxviii, to this problem.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 9 Solutions
Elements of Chemical Reaction Engineering (5th Edition) (Prentice Hall International Series in the Physical and Chemical Engineering Sciences)
- Topic: Production of propylene glycol from glycerol derived from palm oil. QUESTION:Estimate capital items, operating costs and economics of the plant. Finally, report the estimatedreturn.The Detailed Factorial Method with approximately 25% accuracy must be used for detailedeconomic evaluation.Plant lifetime is fixed at 15 years.1) Cash Flow AnalysisDevelop a projected cash flow statement for the first 10 years of plant operation, consideringall the costs and revenues. Include working capital, loans, and interest payments if applicable. Use following attached Process Flow Diagram as reference for this question.arrow_forwardTopic: Production of propylene glycol from glycerol derived from palm oil.QUESTION:Estimate capital items, operating costs and economics of the plant. Finally, report the estimatedreturn.The Detailed Factorial Method with approximately 25% accuracy must be used for detailedeconomic evaluation.Plant lifetime is fixed at 15 years.1) Operational Cost AnalysisCalculate the yearly operational costs, including raw materials, labor, utilities, maintenance,and other recurring expenses. Provide a clear explanation of how these costs are derived. Use following attached Process Flow Diagram as reference for this question.arrow_forwardChemical Engineering Questionarrow_forward
- A steam boiler or steam generator is a device used to produce steam by transferring heat to water. In our case, the combustion chamber is fueled with propane (C3H8) at a flowrate of 50.0 mol/h in an excess air of 50%. Assume that both propane and air are fed at 25ºC and the combustion gases leave the chamber at 200ºC. Pressure can be assumed to be atmospheric.* Determine: 1. The heat obtained assuming complete combustion. Compare the results using elements or compounds 2. The steam flowrate that could be generated if the heat is directed to obtain superheated steam at 2 bar and 160ºC from saturated liquid water at this pressure solvearrow_forwardIn a surface coating operation, a polymer (plastic) dissolved in liquid acetone is sprayed on a solid surface and a stream of hot air is then blown over the surface, vaporizing the acetone and leaving a residual polymer film of uniform thickness. Because environmental standards do not allow discharg- ing acetone into the atmosphere, a proposal to incinerate the stream is to be evaluated. The proposed process uses two parallel columns containing beds of solid particles. The air– acetone stream, which contains acetone and oxygen in stoichiometric proportion, enters one of the beds at 1500 mm Hg absolute at a rate of 1410 standard cubic meters per minute. The particles in the bed have been preheated and transfer heat to the gas. The mixture ignites when its temperature reaches 562 C, and combustion takes place rapidly and adiabatically. The combustion products then pass through and heat the particles in the second bed, cooling down to 350 C in the process. Period- ically the flow is…arrow_forwardPropane is burned completely with excess oxygen. The product gas contains 24.5 mole% CO2, 6.10% CO, 40.8% H2O, and 28.6% O2. (a) Calculate the percentage excess O2 fed to the furnace. (b) A student wrote the stoichiometric equation of the combustion of propane to form CO2 and CO as: 2C3H8 + 11O2 → 3CO2 + 3CO + 8H2O According to this equation, CO2 and CO should be in a ratio of 1/1 in the reaction products, but in the product gas of Part (a) they are in a ratio of 24.8/6.12. Is that result possible? (Hint: Yes.) Explain howarrow_forward
- Enumerate the various methods for catalyst preparation and discuss vividly any one of the methodsarrow_forward2. Design a spherical tank, with a wall thickness of 2.5 cm that will ensure that no more than 45 kg of hydrogen will be lost per year. The tank, which will operate at 500 °C, can be made from nickel, aluminum, copper, or iron (BCC). The diffusion coefficient of hydrogen and the cost per pound for each available material is listed in Table 1. Material Do (m2/s) Q (J/mol) Cost ($/kg) Nickel 5.5 x 10-7 37.2 16.09 Aluminium 1.6 x 10-5 43.2 2.66 Copper 1.1 x 10-6 39.3 9.48 Iron (BCC) 1.2 × 10-7 15.1 0.45 Table 1: Diffusion data for hydrogen at 500 °C and the cost of material.arrow_forwardA flash drum at 1.0 atm is separating a feed consisting of methanol and water. If the feed rate is 2000 kg/h and the feed is 45 wt % methanol, what are the values of L (kg/h), V (kg/h), yM, xM (weight fractions), and Tdrum if 35% by weight of the feed is vaporized? VLE data are in Table 2-8.arrow_forward
- Q1.B. Make a comparison between current control PWM rectifier in the abc reference frame and dq reference frame.arrow_forwardstep by steparrow_forwardThe power out of an adiabatic steam turbine is 5 MW and the steam enters turbine at 2 MPa and velocity of 50 m/s, specific enthalpy (h) of 3248 kJ/kg. The elevation of the inlet is 10 m higher than at the datum. The vapor mixture exits at 15 kPa and a velocity of 180 m/s, specific enthalpy (h) of 2361.01 kJ/kg. The elevation of the exit is 6 m higher than at the datum. Let g = 9.81 m/s². Assuming the ideal gas model and R = 0.462 KJ/(kg.K). The steam specific heat ratio is 1.283. Calculate:arrow_forward
 Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynami...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9781259696527Author:J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark SwihartPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynami...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9781259696527Author:J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark SwihartPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY Elements of Chemical Reaction Engineering (5th Ed...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9780133887518Author:H. Scott FoglerPublisher:Prentice Hall
Elements of Chemical Reaction Engineering (5th Ed...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9780133887518Author:H. Scott FoglerPublisher:Prentice Hall
 Industrial Plastics: Theory and ApplicationsChemical EngineeringISBN:9781285061238Author:Lokensgard, ErikPublisher:Delmar Cengage Learning
Industrial Plastics: Theory and ApplicationsChemical EngineeringISBN:9781285061238Author:Lokensgard, ErikPublisher:Delmar Cengage Learning Unit Operations of Chemical EngineeringChemical EngineeringISBN:9780072848236Author:Warren McCabe, Julian C. Smith, Peter HarriottPublisher:McGraw-Hill Companies, The
Unit Operations of Chemical EngineeringChemical EngineeringISBN:9780072848236Author:Warren McCabe, Julian C. Smith, Peter HarriottPublisher:McGraw-Hill Companies, The





