
Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Course List)
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305251052
Author: Michael Cummings
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 9, Problem 8QP
The following segment of DNA codes for a protein. The uppercase letters represent exons. The lowercase letters represent introns. The lower strand is the template strand. Draw the primary transcript and the mRNA resulting from this DNA.
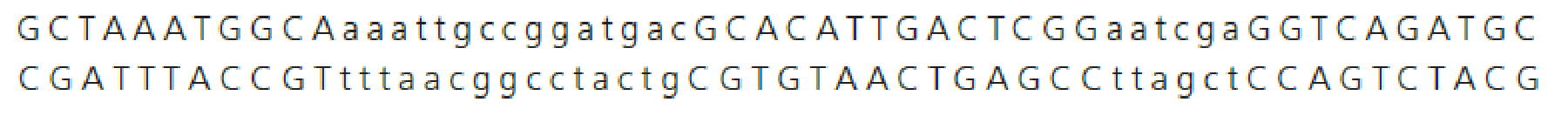
Expert Solution & Answer
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Students have asked these similar questions
This question has multiple parts (A, B & C), and under the subject of Nutrition. Thank you!
Calculate the CFU/ml of a urine sample if 138 E. coli colonies were counted on a Nutrient Agar Plate when0.5 mls were plated on the NA plate from a 10-9 dilution tube. You must highlight and express your answerin scientific notatio
Don't copy off the other answer if there is any
Chapter 9 Solutions
Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Course List)
Ch. 9.6 - Antibiotics and Protein Synthesis Antibiotics are...Ch. 9.6 - Antibiotics and Protein Synthesis Antibiotics are...Ch. 9 - There have been recurring cases of mad-cow disease...Ch. 9 - There have been recurring cases of mad-cow disease...Ch. 9 - There have been recurring cases of mad-cow disease...Ch. 9 - The Link Between Genes and proteins The genetic...Ch. 9 - Define replication, transcription, and...Ch. 9 - If the genetic code used 4 bases at a time, how...Ch. 9 - If the genetic code uses triplets, how many...Ch. 9 - What is the start codon? What are the stop codons?...
Ch. 9 - Is an entire chromosome made into an mRNA during...Ch. 9 - The promoter and terminator regions of genes are...Ch. 9 - The following segment of DNA codes for a protein....Ch. 9 - What are the three modifications made to pre-mRNA...Ch. 9 - The pre-mRNA transcript and protein made by...Ch. 9 - Briefly describe the function of the following in...Ch. 9 - Prob. 12QPCh. 9 - Determine the percent of the following gene that...Ch. 9 - How many kilobases of the DNA strand below will...Ch. 9 - Prob. 15QPCh. 9 - Given the following tRNA anticodon sequence,...Ch. 9 - Given the following mRNA, write the...Ch. 9 - The following is a portion of a protein:...Ch. 9 - Below is the structure of glycine. Draw a...Ch. 9 - Indicate in which category, transcription or...Ch. 9 - Prob. 21QPCh. 9 - Polypeptide folding is often mediated by other...Ch. 9 - Do mutations in DNA alter proteins all the time?Ch. 9 - a. Can a mutation change a proteins tertiary...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Use the following information to answer the question(s) below. Martin Wikelski and L. Michael Romero (Body size, performance and fitness in Galápagos marine iguanas, Integrative and Comparative Biology 43 [2003]:376-86) measured the snout-to-vent (anus) length of Galápagos marine iguanas and observed the percent survival of different-sized animals, all of the same age. The graph shows the log snout-vent length (SVL, a measure of overall body size) plotted against the percent survival of these different size classes for males and females. Survival (%) 100- 80- 60- 40- 20- 0+ 1.9 T 2 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 2.5 2.6 2.7 Log SVL (mm) 19) Examine the figure above. What type of selection for body size appears to be occurring in these marine iguanas? A) directional selection B) stabilizing selection C) disruptive selection D) You cannot determine the type of selection from the above information. 3arrow_forward24) Use the following information to answer the question below. Researchers studying a small milkweed population note that some plants produce a toxin and other plants do not. They identify the gene responsible for toxin production. The dominant allele (T) codes for an enzyme that makes the toxin, and the recessive allele (t) codes for a nonfunctional enzyme that cannot produce the toxin. Heterozygotes produce an intermediate amount of toxin. The genotypes of all individuals in the population are determined (see table) and used to determine the actual allele frequencies in the population. TT 0.49 Tt 0.42 tt 0.09 Refer to the table above. Is this population in Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium? A) Yes. C) No; there are more homozygotes than expected. B) No; there are more heterozygotes than expected. D) It is impossible to tell.arrow_forward30) A B CDEFG Refer to the accompanying figure. Which of the following forms a monophyletic group? A) A, B, C, and D B) C and D C) D, E, and F D) E, F, and Garrow_forward
- Molecular Biology Question. Please help with step solution and explanation. Thank you: The Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) reaction consists of three steps denaturation, hybridization, and elongation. Please describe what occurs in the annealing step of the PCR reaction. (I think annealing step is hybridization). What are the other two steps of PCR, and what are their functions? Next, suppose the Tm for the two primers being used are 54C for Primer A and 67C for Primer B. Regarding annealing step temperature, I have the following choices for the temperature used during the annealing step:(a) 43C (b) 49C (c) 62C (d) 73C Which temperature/temperatures should I choose? What is the corresponding correct explanation, and why would I not use the other temperatures? Have a good day!arrow_forwardUsing the data provided on the mean body mass and horn size of 4-year-old male sheep, draw a scatterplot graph to examine how body mass and horn size changed over time.arrow_forwardPlease write a 500-word report about the intake of saturated fat, sodium, alcoholic beverages, or added sugar in America. Choose ONE of these and write about what is recommended by the Dietary Guidelines for Americans (guideline #4) and why Americans exceed the intake of that nutrient. Explain what we could do as a society and/or individuals to reduce our intake of your chosen nutrient.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...BiologyISBN:9781305117396Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...BiologyISBN:9781305117396Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning Concepts of BiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168116Author:Samantha Fowler, Rebecca Roush, James WisePublisher:OpenStax College
Concepts of BiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168116Author:Samantha Fowler, Rebecca Roush, James WisePublisher:OpenStax College Human Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305112100Author:Cecie Starr, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305112100Author:Cecie Starr, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning

Biology (MindTap Course List)
Biology
ISBN:9781337392938
Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. Berg
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...
Biology
ISBN:9781305117396
Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa Starr
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...
Biology
ISBN:9781305251052
Author:Michael Cummings
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Concepts of Biology
Biology
ISBN:9781938168116
Author:Samantha Fowler, Rebecca Roush, James Wise
Publisher:OpenStax College

Human Biology (MindTap Course List)
Biology
ISBN:9781305112100
Author:Cecie Starr, Beverly McMillan
Publisher:Cengage Learning

QCE Biology: Introduction to Gene Expression; Author: Atomi;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=a7hydUtCIJk;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY