
Statics and Mechanics of Materials (5th Edition)
5th Edition
ISBN: 9780134382593
Author: Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 9, Problem 4RP
Two A992 steel pipes, each having a cross-sectional area of 0.32 in2, are screwed together using a union at B. Originally the assembly is adjusted so that no load is on the pipe. If the union is then tightened so that its screw, having a lead of 0.15 in., undergoes two full turns, determine the average normal stress developed in the pipe. Assume that the union and couplings at A and C are rigid. Neglect the size of the union. Note: The lead would cause the pipe, when unloaded, to shorten 0.15 in. when the union is rotated one revolution.
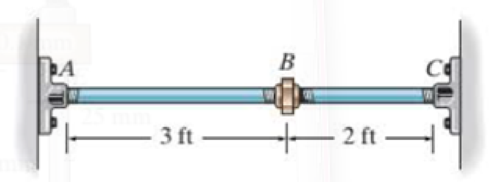
Prob. R9-4
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
5) The bolt has a diameter of 20 mm and passes through a tube with an inner diameter of 50 mm
and an outer diameter of 60 mm. If the bolt and tube are made of A-36 steel, determine the
normal stress in the tube and bolt when a force of 40 kN is applied to the bolt. Assume the end
caps are rigid.
40 kN
160 mm
150 mm
40 kN
The bell-crank mechanism is in equilibrium for an applied load of F1 = 11 kN applied at A. Assume a = 250mm, b = 100mm, c = 90mm, and θ = 40°. Pin B is in a double-shear connection and has a diameter of 29 mm. The bell crank has a thickness of 31 mm. Determine the shear stress in pin B. and the the bearing stress in the bell crank at B.
The compound wooden beam is connected together by a bolt at B. Assuming that the connections at A, B, C, and D exert only vertical forces on the beam, determine the required diameter of the bolt at B and the required outer diameter of its washers if the allowable tensile stress for the bolt is 1st2allow = 150 MPa and the allowable bearing stress for the wood is 1sb2allow = 28 MPa. Assume that the hole in the washers has the same diameter as the bolt.
Chapter 9 Solutions
Statics and Mechanics of Materials (5th Edition)
Ch. 9.2 - In each case, determine the internal normal force...Ch. 9.2 - Determine the internal normal force between...Ch. 9.2 - The post weighs 8 kN/m. Determine the internal...Ch. 9.2 - The rod is subjected to an external axial force of...Ch. 9.2 - The rigid beam supports the load of 60 kN....Ch. 9.2 - The 20-mm-diameter A-36 steel rod is subjected to...Ch. 9.2 - Prob. 2FPCh. 9.2 - The 30-mm-diameter A992 steel rod is subjected to...Ch. 9.2 - Prob. 4FPCh. 9.2 - Prob. 5FP
Ch. 9.2 - The 20-mm-diameter 2014-T6 aluminum rod is...Ch. 9.2 - The A992 steel rod is subjected to the loading...Ch. 9.2 - The copper shaft is subjected to the axial loads...Ch. 9.2 - The composite shaft, consisting of aluminum,...Ch. 9.2 - The composite shaft, consisting of aluminum,...Ch. 9.2 - The 2014-T6 aluminum rod has a diameter of 30 mm...Ch. 9.2 - The A-36 steel drill shaft of an oil well extends...Ch. 9.2 - The truss is made of three A-36 steel members,...Ch. 9.2 - The truss is made of three A-36 steel members,...Ch. 9.2 - The assembly consists of two 10-mm diameter red...Ch. 9.2 - The assembly consists of two 10-mm diameter red...Ch. 9.2 - The load is supported by the four 304 stainless...Ch. 9.2 - The load is supported by the four 304 stainless...Ch. 9.2 - The rigid bur is supported by the pin-connected...Ch. 9.2 - The post is made of Douglas fir and has a diameter...Ch. 9.2 - The post is made of Douglas fir and has a diameter...Ch. 9.2 - The coupling rod is subjected to a force of 5 kip....Ch. 9.2 - Prob. 17PCh. 9.2 - The linkage is made of three pin-connected A992...Ch. 9.2 - The linkage is made of three pin-connected A992...Ch. 9.2 - The assembly consists of three titanium...Ch. 9.2 - The rigid beam is supported at its ends by two...Ch. 9.2 - Prob. 22PCh. 9.2 - The steel bar has the original dimensions shown in...Ch. 9.2 - Determine the relative displacement of one end of...Ch. 9.2 - Prob. 25PCh. 9.2 - The truss consists of three members, each made...Ch. 9.2 - Prob. 27PCh. 9.2 - The observation cage C has a weight of 250 kip and...Ch. 9.2 - Determine the elongation of the aluminum strap...Ch. 9.2 - The ball is truncated at its ends and is used to...Ch. 9.5 - The column is constructed from high-strength...Ch. 9.5 - The column is constructed from high-strength...Ch. 9.5 - The A-36 steel pipe has a 6061-T6 aluminum core....Ch. 9.5 - If column AB is made from high strength precast...Ch. 9.5 - If column AB is made from high strength precast...Ch. 9.5 - Determine the support reactions at the rigid...Ch. 9.5 - If the supports at A and C are flexible and have a...Ch. 9.5 - The load of 2000 lb is to be supported by the two...Ch. 9.5 - The load of 2000 lb is to be supported by the two...Ch. 9.5 - The A-36 steel pipe has an outer radius of 20 mm...Ch. 9.5 - The 10-mm-diameter steel bolt is surrounded by a...Ch. 9.5 - The 10-mm-diametcr steel bolt is surrounded by a...Ch. 9.5 - The assembly consists of two red brass C83400...Ch. 9.5 - The rigid beam is supported by the three suspender...Ch. 9.5 - Prob. 45PCh. 9.5 - If the gap between C and the rigid wall at D is...Ch. 9.5 - The support consists of a solid red brass C83400...Ch. 9.5 - The specimen represents a filament-reinforced...Ch. 9.5 - The rigid bar is pinned at A and supported by two...Ch. 9.5 - The rigid bar is pinned at A and supported by two...Ch. 9.5 - The rigid bar is pinned at A and supported by two...Ch. 9.5 - The rigid bar is pinned at A and supported by two...Ch. 9.5 - The 2014-T6 aluminum rod AC is reinforced with the...Ch. 9.5 - The 2014-T6 aluminum rod AC is reinforced with the...Ch. 9.5 - The three suspender bars are made of A992 steel...Ch. 9.6 - The C83400-red-brass rod AB and 2014-T6-aluminum...Ch. 9.6 - The assembly has the diameters and material...Ch. 9.6 - The rod is made of A992 steel and has a diameter...Ch. 9.6 - The two cylindrical rod segments are fixed to the...Ch. 9.6 - The two cylindrical rod segments are fixed to the...Ch. 9.6 - Prob. 61PCh. 9.6 - The bronze C86100 pipe has an inner radius of 0.5...Ch. 9.6 - The 40-ft-long A-36 steel rails on a train track...Ch. 9.6 - The device is used to measure a change in...Ch. 9.6 - Prob. 65PCh. 9.6 - Prob. 66PCh. 9.6 - Prob. 67PCh. 9.6 - When the temperature is at 30C, the A-36 steel...Ch. 9.6 - The 50-mm-diameter cylinder is made from Am...Ch. 9.6 - The 50-mm-diametcr cylinder is made from Am...Ch. 9.6 - Prob. 71PCh. 9.6 - The cylinder CD of the assembly is heated from T1...Ch. 9.6 - The cylinder CD of the assembly is heated from T1...Ch. 9.6 - Prob. 74PCh. 9 - The assembly consists of two A992 steel bolts AB...Ch. 9 - The assembly shown consists of two A992 steel...Ch. 9 - The rods each have the same 25-mm diameter and...Ch. 9 - Two A992 steel pipes, each having a...Ch. 9 - The 2014-T6 aluminum rod has a diameter of 0.5 in....Ch. 9 - The 2014-T6 aluminum rod has a diameter of 0.5 in....Ch. 9 - The rigid link is supported by a pin at A and two...Ch. 9 - The joint is made from three A992 steel plates...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- The d = 13-mm-diameter solid rod passes through a D = 20-mm-diameter hole in the support plate. When a load Pis applied to the rod, the rod head rests on the support plate. The support plate has a thickness of b = 15 mm. The rod head has a diameter of a = 31 mm, and the head has a thickness of t= 10 mm. If the normal stress produced in the rod by load Pis 150 MPa, determine (a) the bearing stress acting between the support plate and the rod head. (b) the average shear stress produced in the rod head. (c) the punching shear stress produced in the support plate by the rod head. Support Plate - Hole diameter D P Rod Нead a Calculate the cross-sectional area of the rod. Answer: Arod = i mm2arrow_forwardThe uniform sign has a weight of 1500 lb and is supported by the pipe AB, which has an inner radius of 2.75 in. and an outer radius of 3.00 in. If the face of the sign is subjected to a uniform wind pressure of p = 150 lb/ft2, determine the state of stress at points Cand D. Show the results on a differential volume element located at each of these points. Neglect the thickness of the sign, and assume that it is supported along the outside edge of the pipe. 6 ft 3 ft 上 A B x 12 ft 150 lb/ft²arrow_forwardThe A-36 steel drill shaft of an oil well extends 12,000 ft into the ground. Assuming that the pipe used to drill the well is suspended freely from the derrick at A, determine the maximum average normal stress in each pipe string and the elongation of its end Dwith respect to the fixed end at A. The shaft consists of three different sizes of pipe, AB, BC, and CD, each having the length, weight per unit length, and cross-sectional area indicated. Hint: You will need to develop a series of FBDs to establish the necessary functions to integrate to determine the displacement. AAB = 2.50 in.² WAB=3.2 lb/ft 5000 ft B ABC= 1.75 in? WBC= 2.8 lb/ft 5000 ft C ACD= 1.25 in.² 2000 ft WCD=2.0 lb/ft Darrow_forward
- 945. The press consists of two rigid heads that are held together by the twa A-36 steel 12-mm-diameter rods. A 6061-T6-solid-aluminum cylinder is placed in the press and the screw is adjusted so that it just preses up against the cylinder. If it is then tightened one-half turn, determine the average normal stress in the rods and in the cylinder. The single-threaded screw on the bolt has a lead of 0.25 mm. Note: The lead represents the distance the screw advances akong its axis for one complete turn of the screw. -300 mm so mm -250arrow_forwardThe assembly is used to support the distributed load of w=500 lb/ft. determine effortnormal in bar BC and the shear stress in pins B and C. The bar has adiameter of 0.40 in. and each of the bolts has a diameter of 0.30 in. Express theanswers in ksi.arrow_forwardAnswer the ff. The bell-crank mechanism is in equilibrium for an applied load of F1 = 19 kN applied at A. Assume a = 330mm, b = 160mm, c = 75mm, and θ = 35°. Pin B is in a double-shear connection and has a diameter of 24 mm. The bell crank has a thickness of 28 mm. Determine(a) the shear stress in pin B.(b) the bearing stress in the bell crank at B.arrow_forward
- The tension member is fastened together using two bolts, one on each side of the member as shown. Each bolt has a diameter of 0.3 in. Determine the maximum load P that can be applied to the member if the allowable shear stress for the bolts is tlow = 12 ksi allow and the allowable average normal stress is o, = 20 ksi. allow 60°arrow_forwardThe d = 13-mm-diameter solid rod passes through a D=21-mm-diameter hole in the support plate. When a load P is applied to the rod, the rod head rests on the support plate. The support plate has a thickness of b = 12 mm. The rod head has a diameter of a = 28 mm, and the head has a thickness of t = 8 mm. If the normal stress produced in the rod by load P is 150 MPa, determine (a) the bearing stress acting between the support plate and the rod head. (b) the average shear stress produced in the rod head. (c) the punching shear stress produced in the support plate by the rod head. Support Plate Hole diameter D Rod Head b Calculate the cross-sectional area of the rod. Answer: Arod mm²arrow_forwardThe railcar docklight is supported by the 1/8-in.-diameter pin at A. If the lamp weighs 4.1 lb, and the extension arm AB has a weight of 0.6 lb/ft. 3 ft -1.25 in Part A Determine the average shear stress in the pin needed to support the lamp. Hint:The shear force in the pin is caused by the couple moment required for equilibrium at A. Express your answer to three significant figures and include appropriate units. Value Unitsarrow_forward
- The d = 15-mm-diameter solid rod passes through a D = 20-mm-diameter hole in the support plate. When a load P is applied to the rod, the rod head rests on the support plate. The support plate has a thickness of b = 15 mm. The rod head has a diameter of a = 30 mm, and the head has a thickness of t = 9 mm. If the normal stress produced in the rod by load P is 200 MPa, determine (a) the bearing stress acting between the support plate and the rod head. (b) the average shear stress produced in the rod head. (c) the punching shear stress produced in the support plate by the rod head. Support Plate Hole diameter D Rod Head Calculate the cross-sectional area of the rod. Answer: Arodi mm²arrow_forwardThe bell-crank mechanism is in equilibrium for an applied load of F1 = 17 kN applied at A. Assume a = 300mm, b = 190mm, c = 85mm, and θ = 50°. Pin B is in a double-shear connection and has a diameter of 30 mm. The bell crank has a thickness of 32 mm. Determine(a) the shear stress in pin B.(b) the bearing stress in the bell crank at B.arrow_forwardThe bell-crank mechanism is in equilibrium for an applied load of F1 = 13 kN applied at A. Assume a = 300mm, b = 190mm, c = 90mm, and θ = 35°. Pin B is in a double-shear connection and has a diameter of 31 mm. The bell crank has a thickness of 26 mm. Determine(a) the shear stress in pin B.(b) the bearing stress in the bell crank at B.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY
Everything About COMBINED LOADING in 10 Minutes! Mechanics of Materials; Author: Less Boring Lectures;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=N-PlI900hSg;License: Standard youtube license