
Concept explainers
A ball is released at the left end of the metal track shown below. Assume it has only enough friction to roll, but not to lessen its speed.
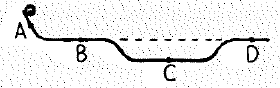
a. Rank from greatest to least the ball’s momentum at each point.
b. Rank from greatest to least the ball’s kinetic energy at each point.
c. Rank from greatest to least the ball’s potential energy at each point.
(a)
To Rank:Ball's momentum from greatest to least.
Answer to Problem 28A
Explanation of Solution
Introduction:
Momentum is mass times velocity. It is a vector quantity.
Momentum is proportional to ball's speed or velocity. If ball's speed is high it will be high and vise versa.
At point A, the ball is at height so its speed is zero. When ball comes to Point B, its potential energy gets converted to kinetic energy. So, it comes to position B with high speed. So, at point B its speed is high. Again, ball goes to point C so its speed increases and then ball speed decreases at point D. The momentum of ball at B and D is same since both are at the same height.
Conclusion:
The rank of ball's momentum from greatest to least is C,B = D,A.
(b)
To Rank: Ball's kinetic energy from greatest to least.
Answer to Problem 28A
Explanation of Solution
Introduction:
When an object is in motion, it possess kinetic energy. This energy is measured in joules.
As velocity of a ball increases, the kinetic energy of the ball increases. At highest point, ball has high potential energy and low kinetic energy. Velocity of ball is high when ball comes to lower position.Here, ball's velocity is highest at point C and it decreases for point B, D and A.
The kinetic energy of ball at B and D is same since both are at same height.
Conclusion:
Ranking of ball's kinetic energy from greatest to least is C, B = D, A.
(c)
To Rank: Ball's potential energy from greatest to least.
Answer to Problem 28A
Explanation of Solution
Introduction:
Potential energy is the energy possessed by the object due to its position. Potential energy is high if object’s position is high and low if object position is low.
Potential energy of ball is proportional to ball's height. Potential energy will be high for high ball's position and low for low position.
Here ball's position is measured from ground and so, will be from highest to lowest will be A, B, = D, C.
The potential energy of ball at B and D is same since both are at same height.
Conclusion:
Ranking of ball's potential energy from greatest to least is A, B = D, C.
Chapter 9 Solutions
CONCEPTUAL PHYSICS-W/PRACTICING PHYSICS
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Biological Science (6th Edition)
Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Microbiology: An Introduction
Biology: Life on Earth (11th Edition)
Campbell Biology in Focus (2nd Edition)
Microbiology: An Introduction
- two satellites are in circular orbits around the Earth. Satellite A is at an altitude equal to the Earth's radius, while satellite B is at an altitude equal to twice the Earth's radius. What is the ratio of their periods, Tb/Taarrow_forwardFresnel lens: You would like to design a 25 mm diameter blazed Fresnel zone plate with a first-order power of +1.5 diopters. What is the lithography requirement (resolution required) for making this lens that is designed for 550 nm? Express your answer in units of μm to one decimal point. Fresnel lens: What would the power of the first diffracted order of this lens be at wavelength of 400 nm? Express your answer in diopters to one decimal point. Eye: A person with myopic eyes has a far point of 15 cm. What power contact lenses does she need to correct her version to a standard far point at infinity? Give your answer in diopter to one decimal point.arrow_forwardParaxial design of a field flattener. Imagine your optical system has Petzal curvature of the field with radius p. In Module 1 of Course 1, a homework problem asked you to derive the paraxial focus shift along the axis when a slab of glass was inserted in a converging cone of rays. Find or re-derive that result, then use it to calculate the paraxial radius of curvature of a field flattener of refractive index n that will correct the observed Petzval. Assume that the side of the flattener facing the image plane is plano. What is the required radius of the plano-convex field flattener? (p written as rho )arrow_forward
- 3.37(a) Five free electrons exist in a three-dimensional infinite potential well with all three widths equal to \( a = 12 \, \text{Å} \). Determine the Fermi energy level at \( T = 0 \, \text{K} \). (b) Repeat part (a) for 13 electrons. Book: Semiconductor Physics and Devices 4th ed, NeamanChapter-3Please expert answer only. don't give gpt-generated answers, & please clear the concept of quantum states for determining nx, ny, nz to determine E, as I don't have much idea about that topic.arrow_forward3.37(a) Five free electrons exist in a three-dimensional infinite potential well with all three widths equal to \( a = 12 \, \text{Å} \). Determine the Fermi energy level at \( T = 0 \, \text{K} \). (b) Repeat part (a) for 13 electrons. Book: Semiconductor Physics and Devices 4th ed, NeamanChapter-3Please expert answer only. don't give gpt-generated answers, & please clear the concept of quantum states for determining nx, ny, nz to determine E, as I don't have much idea about that topic.arrow_forwardNo chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forward
- Use the following information to answer the next question. Two mirrors meet an angle, a, of 105°. A ray of light is incident upon mirror A at an angle, i, of 42°. The ray of light reflects off mirror B and then enters water, as shown below: Incident ray at A Note: This diagram is not to scale. a Air (n = 1.00) Water (n = 1.34) 1) Determine the angle of refraction of the ray of light in the water. Barrow_forwardHi can u please solvearrow_forward6. Bending a lens in OpticStudio or OSLO. In either package, create a BK7 singlet lens of 10 mm semi-diameter and with 10 mm thickness. Set the wavelength to the (default) 0.55 microns and a single on-axis field point at infinite object distance. Set the image distance to 200 mm. Make the first surface the stop insure that the lens is fully filled (that is, that the entrance beam has a radius of 10 mm). Use the lens-maker's equation to calculate initial glass curvatures assuming you want a symmetric, bi-convex lens with an effective focal length of 200 mm. Get this working and examine the RMS spot size using the "Text" tab of the Spot Diagram analysis tab (OpticStudio) or the Spd command of the text widnow (OSLO). You should find the lens is far from diffraction limited, with a spot size of more than 100 microns. Now let's optimize this lens. In OpticStudio, create a default merit function optimizing on spot size.Then insert one extra line at the top of the merit function. Assign the…arrow_forward
- No chatgpt pls will upvote Already got wrong chatgpt answer .arrow_forwardUse the following information to answer the next question. Two mirrors meet an angle, a, of 105°. A ray of light is incident upon mirror A at an angle, i, of 42°. The ray of light reflects off mirror B and then enters water, as shown below: A Incident ray at A Note: This diagram is not to scale. Air (n = 1.00) Water (n = 1.34) Barrow_forwardUse the following information to answer the next question. Two mirrors meet an angle, a, of 105°. A ray of light is incident upon mirror A at an angle, i, of 42°. The ray of light reflects off mirror B and then enters water, as shown below: A Incident ray at A Note: This diagram is not to scale. Air (n = 1.00) Water (n = 1.34) Barrow_forward
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON





