
Concept explainers
Which requires more work: stretching a strong spring a certain distance or stretching a weak spring the same distance? Defend your answer.
To Choose:The spring which required more work for stretching.
Answer to Problem 43A
Workdone required to stretch strong spring is large than the work done required to stretchweak spring at same distance.
Explanation of Solution
Introduction:
Spring motion is one of the best examples of harmonic motion. Many of the systems in nature follow nature of spring system.
From kinematics theory, it is known that, for a given spring of mass m and spring constant k, force required to stretch a spring at distance x from its mean position is,
∴F = -kx---------(1)
Negative sign indicate the direction of internal restoring force is opposite to the direction of displacement.
Then the work done to stretch a spring at distance x is,
∴W = 12kx2−−−−−−−−−−−(2)
The magnitude of the work done can be visualized by the area under the curve of force-displacement graph as below:
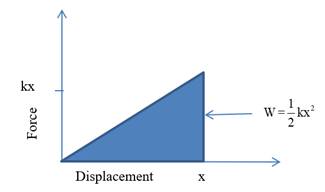
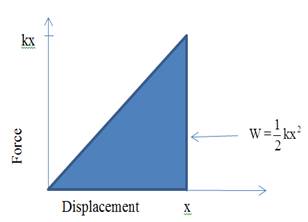
From equation (1) if the spring is strong it requires more force to stretch at a distance x . Therefore, from equation (2) work done corresponding to this force is also large. The graphical representation shown in below diagram:
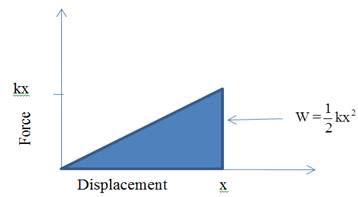
Similarly, for a weak spring, work done required to move spring at a distance x is:
Conclusion:
Therefore, from the above discussion, area under the curve for strong spring is greater than the area under the curve for weak spring. So, to move strong spring at a distance x requires more work done than the work done to move weak spring at same distance.
Chapter 9 Solutions
CONCEPTUAL PHYSICS-W/PRACTICING PHYSICS
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Biology: Life on Earth with Physiology (11th Edition)
Brock Biology of Microorganisms (15th Edition)
Microbiology: An Introduction
Biology: Life on Earth (11th Edition)
Cosmic Perspective Fundamentals
Campbell Biology (11th Edition)
- is 0.3026 a finite numberarrow_forwardPlastic beads can often carry a small charge and therefore can generate electric fields. Three beads are oriented such that system of all three beads is zero. 91 E field lines 93 92 What charge does each bead carry? 91 92 -1.45 = = What is the net charge of the system? What charges have to be equal? μC 2.9 × What is the net charge of the system? What charges have to be equal? μC 93 = 2.9 μС 92 is between and 91 93° The sum of the charge on q₁ and 92 is 91 + 92 = −2.9 μC, and the net charge of thearrow_forwardPlastic beads can often carry a small charge and therefore can generate electric fields. Three beads are oriented such that 92 is between q₁ and 93. The sum of the charge on 9₁ and 92 is 9₁ + 92 = −2.9 µС, and the net charge of the system of all three beads is zero. E field lines 93 92 What charge does each bead carry? 91 92 -1.45 What is the net charge of the system? What charges have to be equal? μC 2.9 ✓ What is the net charge of the system? What charges have to be equal? μC 93 2.9 μεarrow_forward
- No chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forwardPoint charges of 6.50 μC and -2.50 μC are placed 0.300 m apart. (Assume the negative charge is located to the right of the positive charge. Include the sign of the value in your answers.) (a) Where can a third charge be placed so that the net force on it is zero? 0.49 m to the right of the -2.50 μC charge (b) What if both charges are positive? 0.49 xm to the right of the 2.50 μC chargearrow_forwardFind the electric field at the location of q, in the figure below, given that q₁ =9c9d = +4.60 nC, q = -1.00 nC, and the square is 20.0 cm on a side. (The +x axis is directed to the right.) magnitude direction 2500 x What symmetries can you take advantage of? What charges are the same magnitude and the same distance away? N/C 226 × How does charge sign affect the direction of the electric field? counterclockwise from the +x-axis 9a 9b % 9 9darrow_forward
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON





