
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern Physics, Technology Update
9th Edition
ISBN: 9781305401969
Author: SERWAY, Raymond A.; Jewett, John W.
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 9, Problem 22P
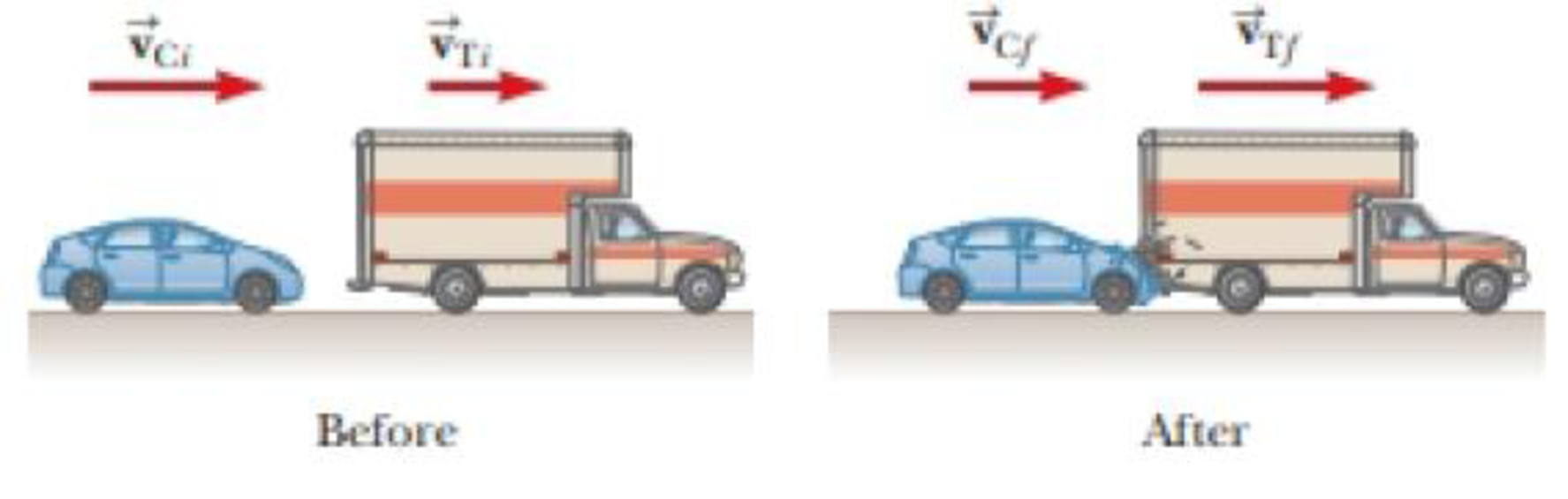
A 1 200-kg car traveling initially at vCi = 25.0 m/s in an easterly direction crashes into the back of a 9 000-kg truck moving in the same direction at vTi = 20.0 m/s (Fig. P9.12). The velocity of the car immediately after the collision is vCf = 18.0 m/s to the east. (a) What is the velocity of the truck immediately after the collision? (b) What is the change in mechanical energy of the car–truck system in the collision? (c) Account for this change in mechanical energy.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
ROTATIONAL DYNAMICS
Question 01
A solid circular cylinder and a solid spherical ball of the same mass and radius are rolling
together down the same inclined. Calculate the ratio of their kinetic energy. Assume pure
rolling motion Question 02
A sphere and cylinder of the same mass and radius start from ret at the same point and more
down the same plane inclined at 30° to the horizontal
Which body gets the bottom first and what is its acceleration
b) What angle of inclination of the plane is needed to give the slower body the same
acceleration
Question 03
i)
Define the angular velocity of a rotating body and give its SI unit
A car wheel has its angular velocity changing from 2rads to 30 rads
seconds. If the radius of the wheel is 400mm. calculate
ii)
The angular acceleration
iii)
The tangential linear acceleration of a point on the rim of the wheel
Question 04
in 20
Question B3
Consider the following FLRW spacetime:
t2
ds² = -dt² +
(dx²
+ dy²+ dz²),
t2
where t is a constant.
a)
State whether this universe is spatially open, closed or flat.
[2 marks]
b) Determine the Hubble factor H(t), and represent it in a (roughly drawn) plot as a function
of time t, starting at t = 0.
[3 marks]
c) Taking galaxy A to be located at (x, y, z) = (0,0,0), determine the proper distance to galaxy
B located at (x, y, z) = (L, 0, 0). Determine the recessional velocity of galaxy B with respect
to galaxy A.
d) The Friedmann equations are
2
k
8πG
а
4πG
+
a²
(p+3p).
3
a
3
[5 marks]
Use these equations to determine the energy density p(t) and the pressure p(t) for the
FLRW spacetime specified at the top of the page.
[5 marks]
e) Given the result of question B3.d, state whether the FLRW universe in question is (i)
radiation-dominated, (ii) matter-dominated, (iii) cosmological-constant-dominated, or (iv)
none of the previous. Justify your answer.
f)
[5 marks]
A conformally…
SECTION B
Answer ONLY TWO questions in Section B
[Expect to use one single-sided A4 page for each Section-B sub question.]
Question B1
Consider the line element
where w is a constant.
ds²=-dt²+e2wt dx²,
a) Determine the components of the metric and of the inverse metric.
[2 marks]
b) Determine the Christoffel symbols. [See the Appendix of this document.]
[10 marks]
c)
Write down the geodesic equations.
[5 marks]
d) Show that e2wt it is a constant of geodesic motion.
[4 marks]
e)
Solve the geodesic equations for null geodesics.
[4 marks]
Chapter 9 Solutions
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern Physics, Technology Update
Ch. 9.1 - Two objects have equal kinetic energies. How do...Ch. 9.1 - Your physical education teacher throws a baseball...Ch. 9.3 - Two objects are at rest on a frictionless surface....Ch. 9.3 - Rank an automobile dashboard, seat belt, and air...Ch. 9.4 - Prob. 9.5QQCh. 9.4 - A table-tennis ball is thrown at a stationary...Ch. 9.6 - A baseball bat of uniform density is cut at the...Ch. 9.7 - A cruise ship is moving at constant speed through...Ch. 9 - Prob. 1OQCh. 9 - Prob. 2OQ
Ch. 9 - Prob. 3OQCh. 9 - Prob. 4OQCh. 9 - Prob. 5OQCh. 9 - Prob. 6OQCh. 9 - The momentum of an object is increased by a factor...Ch. 9 - The kinetic energy of an object is increased by a...Ch. 9 - If two particles have equal momenta, are their...Ch. 9 - Prob. 10OQCh. 9 - Prob. 11OQCh. 9 - Two particles of different mass start from rest....Ch. 9 - Prob. 13OQCh. 9 - A basketball is tossed up into the air, falls...Ch. 9 - Prob. 15OQCh. 9 - Prob. 16OQCh. 9 - Prob. 17OQCh. 9 - Prob. 18OQCh. 9 - Prob. 1CQCh. 9 - Prob. 2CQCh. 9 - Prob. 3CQCh. 9 - While in motion, a pitched baseball carries...Ch. 9 - You are standing perfectly still and then take a...Ch. 9 - Prob. 6CQCh. 9 - Two students hold a large bed sheet vertically...Ch. 9 - A juggler juggles three balls in a continuous...Ch. 9 - Prob. 9CQCh. 9 - Does a larger net force exerted on an object...Ch. 9 - Does a larger net force always produce a larger...Ch. 9 - A bomb, initially at rest, explodes into several...Ch. 9 - A particle of mass m moves with momentum of...Ch. 9 - Prob. 2PCh. 9 - Prob. 3PCh. 9 - A 3.00-kg particle has a velocity of...Ch. 9 - A baseball approaches home plate at a speed of...Ch. 9 - Prob. 6PCh. 9 - Prob. 7PCh. 9 - A 65.0-kg boy and his 40.0-kg sister, both wearing...Ch. 9 - Prob. 9PCh. 9 - When you jump straight up as high as you can, what...Ch. 9 - Two blocks of masses m and 3m are placed on a...Ch. 9 - Prob. 12PCh. 9 - An estimated forcetime curve for a baseball struck...Ch. 9 - Prob. 14PCh. 9 - A glider of mass m is free to slide along a...Ch. 9 - Prob. 16PCh. 9 - The front 1.20 m of a 1 400-kg car Ls designed as...Ch. 9 - A tennis player receives a shot with the ball...Ch. 9 - The magnitude of the net force exerted in the x...Ch. 9 - Prob. 20PCh. 9 - Water falls without splashing at a rate of 0.250...Ch. 9 - A 1 200-kg car traveling initially at vCi = 25.0...Ch. 9 - Prob. 23PCh. 9 - A car of mass m moving at a speed v1 collides and...Ch. 9 - A railroad car of mass 2.50 104 kg is moving with...Ch. 9 - Prob. 26PCh. 9 - Prob. 27PCh. 9 - A 7.00-g bullet, when fired from a gun into a...Ch. 9 - A tennis ball of mass 57.0 g is held just above a...Ch. 9 - Prob. 30PCh. 9 - Prob. 31PCh. 9 - Prob. 32PCh. 9 - Prob. 33PCh. 9 - (a) Three carts of masses m1 = 4.00 kg, m2 = 10.0...Ch. 9 - Prob. 35PCh. 9 - Prob. 36PCh. 9 - Prob. 37PCh. 9 - Two shuffleboard disks of equal mass, one orange...Ch. 9 - Prob. 39PCh. 9 - A proton, moving with a velocity of vii, collides...Ch. 9 - Prob. 41PCh. 9 - A 90.0-kg fullback running east with a speed of...Ch. 9 - Prob. 43PCh. 9 - Prob. 44PCh. 9 - Prob. 45PCh. 9 - Prob. 46PCh. 9 - Explorers in the jungle find an ancient monument...Ch. 9 - A uniform piece of sheet metal is shaped as shown...Ch. 9 - A rod of length 30.0 cm has linear density (mass...Ch. 9 - Prob. 50PCh. 9 - Prob. 51PCh. 9 - Consider a system of two particles in the xy...Ch. 9 - Prob. 53PCh. 9 - The vector position of a 3.50-g particle moving in...Ch. 9 - Prob. 55PCh. 9 - Prob. 56PCh. 9 - Prob. 57PCh. 9 - Prob. 58PCh. 9 - Prob. 59PCh. 9 - Prob. 60PCh. 9 - A garden hose is held as shown in Figure P9.32....Ch. 9 - Prob. 62PCh. 9 - Prob. 63PCh. 9 - A rocket has total mass Mi = 360 kg, including...Ch. 9 - A ball of mass m is thrown straight up into the...Ch. 9 - Prob. 66APCh. 9 - A 3.00-kg steel ball strikes a wall with a speed...Ch. 9 - (a) Figure P9.36 shows three points in the...Ch. 9 - Review. A 60.0-kg person running at an initial...Ch. 9 - A cannon is rigidly attached to a carriage, which...Ch. 9 - A 1.25-kg wooden block rests on a table over a...Ch. 9 - A wooden block of mass M rests on a table over a...Ch. 9 - Prob. 73APCh. 9 - Prob. 74APCh. 9 - Two gliders are set in motion on a horizontal air...Ch. 9 - Why is the following situation impossible? An...Ch. 9 - Prob. 77APCh. 9 - Prob. 78APCh. 9 - Prob. 79APCh. 9 - A small block of mass m1 = 0.500 kg is released...Ch. 9 - Review. A bullet of mass m = 8.00 g is fired into...Ch. 9 - Review. A bullet of mass m is fired into a block...Ch. 9 - A 0.500-kg sphere moving with a velocity expressed...Ch. 9 - Prob. 84APCh. 9 - Prob. 85APCh. 9 - Prob. 86APCh. 9 - Review. A light spring of force constant 3.85 N/m...Ch. 9 - Prob. 88APCh. 9 - Prob. 89APCh. 9 - Prob. 90APCh. 9 - Prob. 91APCh. 9 - Prob. 92CPCh. 9 - Prob. 93CPCh. 9 - Sand from a stationary hopper falls onto a moving...Ch. 9 - On a horizontal air track, a glider of mass m...Ch. 9 - Prob. 96CP
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Page 2 SECTION A Answer ALL questions in Section A [Expect to use one single-sided A4 page for each Section-A sub question.] Question A1 SPA6308 (2024) Consider Minkowski spacetime in Cartesian coordinates th = (t, x, y, z), such that ds² = dt² + dx² + dy² + dz². (a) Consider the vector with components V" = (1,-1,0,0). Determine V and V. V. (b) Consider now the coordinate system x' (u, v, y, z) such that u =t-x, v=t+x. [2 marks] Write down the line element, the metric, the Christoffel symbols and the Riemann curvature tensor in the new coordinates. [See the Appendix of this document.] [5 marks] (c) Determine V", that is, write the object in question A1.a in the coordinate system x'. Verify explicitly that V. V is invariant under the coordinate transformation. Question A2 [5 marks] Suppose that A, is a covector field, and consider the object Fv=AAμ. (a) Show explicitly that F is a tensor, that is, show that it transforms appropriately under a coordinate transformation. [5 marks] (b)…arrow_forwardHow does boiling point of water decreases as the altitude increases?arrow_forwardNo chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forward
- 14 Z In figure, a closed surface with q=b= 0.4m/ C = 0.6m if the left edge of the closed surface at position X=a, if E is non-uniform and is given by € = (3 + 2x²) ŷ N/C, calculate the (3+2x²) net electric flux leaving the closed surface.arrow_forwardNo chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forwardsuggest a reason ultrasound cleaning is better than cleaning by hand?arrow_forward
- Checkpoint 4 The figure shows four orientations of an electric di- pole in an external electric field. Rank the orienta- tions according to (a) the magnitude of the torque on the dipole and (b) the potential energy of the di- pole, greatest first. (1) (2) E (4)arrow_forwardWhat is integrated science. What is fractional distillation What is simple distillationarrow_forward19:39 · C Chegg 1 69% ✓ The compound beam is fixed at Ę and supported by rollers at A and B. There are pins at C and D. Take F=1700 lb. (Figure 1) Figure 800 lb ||-5- F 600 lb بتا D E C BO 10 ft 5 ft 4 ft-—— 6 ft — 5 ft- Solved Part A The compound beam is fixed at E and... Hình ảnh có thể có bản quyền. Tìm hiểu thêm Problem A-12 % Chia sẻ kip 800 lb Truy cập ) D Lưu of C 600 lb |-sa+ 10ft 5ft 4ft6ft D E 5 ft- Trying Cheaa Những kết quả này có hữu ích không? There are pins at C and D To F-1200 Egue!) Chegg Solved The compound b... Có Không ☑ ||| Chegg 10 וחarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University
University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...
Physics
ISBN:9781133939146
Author:Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:9781133104261
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics Volume 1
Physics
ISBN:9781938168277
Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:OpenStax - Rice University

Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...
Physics
ISBN:9781337553292
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...
Physics
ISBN:9780078807213
Author:Paul W. Zitzewitz
Publisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781285737027
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Impulse Derivation and Demonstration; Author: Flipping Physics;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=9rwkTnTOB0s;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY