
Identify solid figures, including prisms, cubes, cones, cylinders, pyramids, spheres, and frustums.
- (a)
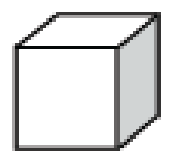 _____________________
_____________________ - (b)
 _____________________
_____________________ - (c)
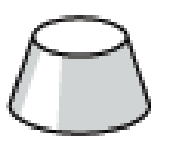 _____________________
_____________________
(a)
To identify: The given solid figure.
Answer to Problem 1P
The given solid figure is a
Explanation of Solution
From the given figure, observe that the given solid object has 6 equal sized square faces with three meeting at each vertex.
It is known that. a cube is a three dimensional object with 6 identical square faces with three edges meeting at each vertex.
Therefore, the given solid figure is a
(b)
To identify: The given solid figure.
Answer to Problem 1P
The given solid figure is a
Explanation of Solution
From the given figure, observe that the given solid object has 2 identical ends and 6 faces that are rectangles.
It is known that. a prism is a solid object with 2 identical ends and flat sides and a rectangular prism is a solid object with 6 faces are rectangles.
Therefore, the given solid figure is a
(c)
To identify: The given solid figure.
Answer to Problem 1P
The given solid figure is a
Explanation of Solution
It is known that the frustum of a cone is formed from a right circular cone by cutting of the tip of the cone in such a way that the cut is perpendicular to the height and forms the lower base and the upper base are circular and parallel.
From the given figure, observe that the given solid object is a cone and has an upper and a lower circular base with the upper base is parallel.
Therefore, the given solid figure is a
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 9 Solutions
Mathematics for the Trades: A Guided Approach, Books a la Carte edition (11th Edition)
- not use ai pleasearrow_forward9:43 AS く Akbar © Printed in the United States 15) Scale: 1 cmal unit on both axes .ill 64% The graph above shows a straight line QT intersecting the y-axis at T. i State the co-ordinates of T. ii Calculate the gradient of QT 16) iii Determine the equation of QT. A (-1, 9) ||| i L Г (5 marks)arrow_forwardConsider the graphs of y = f(x) and y = g(x) in the given diagram y= f(x). y = g(x) Evaluate (f+g)(2) -5 Determine all for which g(x) < f(x) Determine all for which f(x) +3 = g(x)arrow_forward
- I) For what value(s) of x does g(x) = -4? Separate multiple answers with commas as needed. J) Give the interval(s) of such that g(x) > 0. Use the union symbol between multiple intervals. K) Give the interval(s) of such that g(x) <0. Use the union symbol between multiple intervals.arrow_forwardMost people know that the probability of getting a head when you flip a fair coin is . You want to use the relative frequency of the event to show that the probability is . How many times should you simulate flipping the coin in the experiment? Would it be better to use 300 trials or 3000 trials? Explain.arrow_forwardneed help on Barrow_forward
- Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic GeometryAlgebraISBN:9781133382119Author:SwokowskiPublisher:Cengage
