
Concept explainers
(a) Using the superposition theorem, determine the current through the 12
b. Convert both voltage sources to current sources and recalculate the current to the 12
c. How do the results of parts (a) and (b) compare?
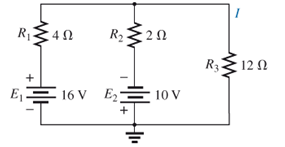
Fig. 9.125
(a)
The current through
Answer to Problem 1P
The current through
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The resistors values are
The voltage sources are
Concept Used:
Elements in the series have the same current.
Elements in the parallels have the same voltage.
Superposition theorem states that in any linear bilateral network having more than one source response in any one of the branches is equal to algebraic sum of the responses caused by individual source while rest of the sources are replaced by their internal impedances.
Short circuit the voltage source and open circuit the current source.
If the resistors are in series, then the value of the equivalent resistance for N series resistors is
If the resistors are in parallel, then the value of the equivalent resistance for N series resistors is
The special case for only two parallel resistors is
Current:
Current division is used to express the current across one of several parallel resistors in terms of current across the combination:
If there are two resistors in parallel then the current across second resistor is
Calculation:
Firstly, short circuit the voltage source
Conclusion:
Hence, the current through
(b)
The current through
Answer to Problem 1P
The current through
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The resistors values are
The voltage sources are
Concept Used:
Elements in the series have the same current.
Elements in the parallels have the same voltage.
Superposition theorem states that in any linear bilateral network having more than one source response in any one of the branches is equal to algebraic sum of the responses caused by individual source while rest of the sources are replaced by their internal impedances.
Short circuit the voltage source and open circuit the current source.
If the resistors are in series, then the value of the equivalent resistance for N series resistors is
If the resistors are in parallel, then the value of the equivalent resistance for N series resistors is
The special case for only two parallel resistors is
Current:
Current division is used to express the current across one of several parallel resistors in terms of current across the combination:
If there are two resistors in parallel then the current across second resistor is
Calculation:
Conclusion:
Hence, the current through
(c)
Compare the results of both the part (a) and (b).
Answer to Problem 1P
The results are similar in both the part (a) and (b).
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The resistors values are
The voltage sources are
Concept Used:
Elements in the series have the same current.
Elements in the parallels have the same voltage.
Superposition theorem states that in any linear bilateral network having more than one source response in any one of the branches is equal to algebraic sum of the responses caused by individual source while rest of the sources are replaced by their internal impedances.
Short circuit the voltage source and open circuit the current source.
Calculation:
The results are similar in both the part (a) and (b).
Conclusion:
Hence, the results are similar in both the part (a) and (b).
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 9 Solutions
Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)
Additional Engineering Textbook Solutions
Starting Out with C++ from Control Structures to Objects (9th Edition)
Degarmo's Materials And Processes In Manufacturing
Java: An Introduction to Problem Solving and Programming (8th Edition)
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)
Introduction To Programming Using Visual Basic (11th Edition)
- Determine the values of the necessary resistances, design and run the circuit in TINKERCAD for an integrated 555 Astable with T1 (on time) of 8 seconds and a T2 (off time) of 4 seconds. The value for capacitor C1 must be 100 uF (0.0001 F).arrow_forward- What are Flip Flop circuits used for? Explain the operation of an R-S Flip Flop.- What function do Multiplexers or MUXs perform?arrow_forward- What function do Demultiplexers or DEMUX perform?- According to the implementation of automation circuits with ARDUINO boards, what would they be, Conceptually, the main components of any system of automation? Draw a representative schematic or block diagram.arrow_forward
- Solve problems 5.2 in detail and thank youarrow_forward5.1 Determine the three zone settings for the relay Rab in the system shown in Figure 5.26. The system nominal voltage is 138 kV, and the positive sequence impedances for the various elements are given in the figure. The transformer impedance is given in ohms as viewed from the 138 kV side. Assume that the maximum load at the relay site is 120 MVA, and select a CT ratio accordingly. The available distance relay has zone 1 and zone 2 settings from 0.2 to 10 2, and zone 3 settings from 0.5 to 40 2, in increments of 0.1 2. The angle of maximum torque can be adjusted to 75° or 80°. Remember that the zone 3 of the relay must back up the line BC, as well as the transformer. A Rab (3+j40) B (2+ j50) (0+j9) с Fu D Figure 5.26 System for problem 5.1arrow_forwardPlease solve question 4.7 in detail and thank youarrow_forward
- Solve in detail to understandarrow_forwardE2.6 Consider the following neural network. Input Sat. Linear Layer Linear Layer purelin(Wa+b) Sketch the following responses (plot the indicated variable versus p for (-3arrow_forwardE2.3 Given a two-input neuron with the following weight matrix and input vector: w=[32] and p = [-5 7], we would like to have an output of 0.5. Do you suppose that there is a combination of bias and transfer function that might allow this? i. Is there a transfer function from Table 2.1 that will do the job if the bias is zero? ii. Is there a bias that will do the job if the linear transfer function is used? If yes, what is it? iii. Is there a bias that will do the job if a log-sigmoid transfer function is used? Again, if yes, what is it? iv. Is there a bias that will do the job if a symmetrical hard limit transfer function is used? Again, if yes, what is it?arrow_forwardE2.2 Consider a single-input neuron with a bias. We would like the output to be -1 for inputs less than 3 and +1 for inputs greater than or equal to 3. i. What kind of a transfer function is required? ii. What bias would you suggest? Is your bias in any way related to the input weight? If yes, how? iii. Summarize your network by naming the transfer function and stating the bias and the weight. Draw a diagram of the network.arrow_forwardE2.1 A single input neuron has a weight of 1.3 and a bias of 3.0. What possible kinds of transfer functions, from Table 2.1, could this neuron have, if its output is given below. In each case, give the value of the input that would produce these outputs. i. 1.6 ii. 1.0 iii. 0.9963 iv. -1.0arrow_forwardQ2. The slew rate of an amplifier can cause signal distortion at its output if wrongly chosen. State the criterion for selecting the slew rate of an amplifier to avoid signal distortion. A step signal of 5 mV is applied to an inverting amplifier shown in Figure 2, which has a slew rate of 0.05 V/us. Estimate the time required for the output voltage of the amplifier to reach within 10% of its final value. If the input to Figure 2 is a sinusoidal signal of 0.02 sin(2πft) V, determine the maximum frequency that can be applied to the circuit without causing signal distortion due to the limitation of its slew rate (0.05 V/µs). In order to minimise the output offset voltage of Figure 2, a compensating resistor should be added to Figure 2. Draw a modified circuit diagram that includes the compensating resistor. Determine the appropriate value for the compensating resistor. V₁ 2 ΚΩ 100 ΚΩ +arrow_forwardarrow_back_iosSEE MORE QUESTIONSarrow_forward_ios
 Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON
Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON
Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,





