
Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)
13th Edition
ISBN: 9780133923605
Author: Robert L. Boylestad
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 9, Problem 14P
Find the Thévenin equivalent circuit for the network external to the resistor R in Fig.9.138.
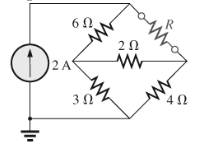
Fig.9.138
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
13. Find the Thévenin equivalent circuit for the network exter-
nal to the resistor R for the network in Fig. 9.137.
0+ 16 V
2.2 k2
8 mA
R
5.6 k2
FIG. 9.137
Problem 13.
Basic Electrical Engineering
Chapter 9. Laws, Theorems and Methods used in Network Analysis
LESSON TITLE:
Laws, Theorems and Methods used in Network Analysis
Determine the equivalent resistance between terminals a and b.
9.6540 Q
8.2756Q
9.2715Q
O 8.3025 Q
R5
5 Ohms
.R1
www
1 Ohm
R2
2 Ohms
R6
6 Ohms
R3
3 Ohms
www
R4
4 Ohms
Chapter 9 Solutions
Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)
Ch. 9 - (a) Using the superposition theorem, determine the...Ch. 9 - a. Using the superposition theorem, determine the...Ch. 9 - Using the superposition theorem, determine the...Ch. 9 - Using superposition, find the current l through...Ch. 9 - Using superposition, find the voltage VR3 for the...Ch. 9 - Using superposition, find the voltage V2 for the...Ch. 9 - Using superposition, find the current through R1...Ch. 9 - Using superposition, find the voltage across the...Ch. 9 - a. Find the Thévenin equivalent circuit for the...Ch. 9 - a. Find the Thévenin equivalent circuit for the...
Ch. 9 - a. Find the Thévenin equivalent circuit for the...Ch. 9 - Find the Thévenin equivalent circuit for the...Ch. 9 - Find the Thévenin equivalent circuit for the...Ch. 9 - Find the Thévenin equivalent circuit for the...Ch. 9 - a. Find the Thévenin equivalent circuit for the...Ch. 9 - Determine the Thevénin equivalent circuit for the...Ch. 9 - a. Determine the Thévenin equivalent circuit for...Ch. 9 - For the network in Fig. 9.142, find the Thévenin...Ch. 9 - For the transistor network in Fig. 9.143. a. Find...Ch. 9 - For each vertical set of measurements appearing in...Ch. 9 - For the network of Fig.9.145, find the Thévenin...Ch. 9 - a. Find the Norton equivalent circuit for the...Ch. 9 - a. Find the Norton equivalent circuit for the...Ch. 9 - Find the Norton equivalent circuit for the network...Ch. 9 - Find the Norton equivalent circuit for the network...Ch. 9 - Find the Norton equivalent circuit for the network...Ch. 9 - Find the Norton equivalent circuit for the network...Ch. 9 - Find the Norton equivalent circuit for the network...Ch. 9 - Find the Norton equivalent circuit for the network...Ch. 9 - a. Find the Norton equivalent circuit external to...Ch. 9 - a. Find the value of R for maximum power transfer...Ch. 9 - a. Find the value of R for maximum power transfer...Ch. 9 - a. Find the value of R for maximum power transfer...Ch. 9 - a. Find the value of RL in Fig.9.142 for maximum...Ch. 9 - a. For the network of Fig. 9.147, determine the...Ch. 9 - Find the resistance R1 in Fig.9.148 such that the...Ch. 9 - a. For the network in Fig.9.149, determine the...Ch. 9 - For the network in Fig. 9.150, determine the level...Ch. 9 - Using Millmans theorem, find the current through...Ch. 9 - Repeat Problem 38 for the network in Fig.9.152....Ch. 9 - Using Millmans theorem, find the current through...Ch. 9 - Using the dual of Millmans theorem, find the...Ch. 9 - Using the dual of Millmans theorem, find the...Ch. 9 - Using the substitution theorem, draw three...Ch. 9 - Using the substituion theorem, draw three...Ch. 9 - Using the substitution theorem, draw three...Ch. 9 - a. For the network in Fig. 9.159(a), determine the...Ch. 9 - a. For the network of Fig.9.16(a), determine the...Ch. 9 - a. Determine the voltageV for the network in...Ch. 9 - Using PSpice or Multisim and the superposition...Ch. 9 - Using PSpice or Multisim, determine the Thévenin...Ch. 9 - a. Using PSpice, plot the power delivered to the...Ch. 9 - Change the 300 resistor in Fig. 9.145 to a...
Additional Engineering Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
When travelers from the USA and Canada visit Europe, they encounter a different power distribution system. Wall...
Electric machinery fundamentals
Find I0 and I1 in the circuit in Fig.P2.12.
Basic Engineering Circuit Analysis
Three point charges of equal magnitude q, that will yield a zero net electric field at the origin.
Engineering Electromagnetics
A constant voltage of 10V is applied to a 50H inductance, as shown in Figure P3.51 Figure P3 51 The current in ...
Electrical Engineering: Principles & Applications (7th Edition)
With respect to the circuit in Fig. 5.90, (a) employ Thévenin’s theorem to determine the equivalent network see...
Loose Leaf for Engineering Circuit Analysis Format: Loose-leaf
The voltage source of the circuit shown in Fig. P1.29 is given by s(t)=25cos(4104t45)(V). Obtain an expression ...
Fundamentals of Applied Electromagnetics (7th Edition)
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, electrical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Basic Electrical Engineering Chapter 9. Laws, Theorems and Methods used in Network Analysis LESSON TITLE: Laws, Theorems and Methods used in Network Analysisarrow_forwarda. For the network of Fig. 9.136, determine the value of R for maximum power to R. b. Determine the maximum power to R. c. Plot a curve of power to R versus R for R equal to . 1, 14, 1, 14, and 2 times the value obtained in part (a). R1 1 SA R2 E 24 V FIG. 9.136arrow_forward• 1- a. For the network of Fig. 9.136, determine the value of R for maximum power to R. b. Determine the maximum power to R. c. Plot a curve of power to R versus R for R equal to . 1, 14. 14, 14, and 2 times the value obtained in 1(SA R4n E 24 V part (a). FIG. 9.136arrow_forward
- Basic Electrical Engineering Chapter 9. Laws, Theorems and Methods used in Network Analysis LESSON TITLE: Laws, Theorems and Methods used in Network Analysisarrow_forwardNETWORK LAWS Using Nodal Analysis Calculate for Vb with node c being the reference node. (Vref = 0) NOTE: The units of the resistors are in ohms. (ANS: 90.973 V)arrow_forwardFor the network of Fig. 9.145, find the Thévenin equivalent circuit for the network external to the 300 N resistor. 300 N 6 VE 4 " 2 V FIG. 9.145 Problem 21.arrow_forward
- Basic Electrical Engineering Chapter 9. Laws, Theorems and Methods used in Network Analysis LESSON TITLE: Laws, Theorems and Methods used in Network Analysisarrow_forwardB) You are required to analyze the operation of DC circuit shown in Fig.2 and apply Ohm's law and Kirchhoff's voltage and current laws to find all the Voltages (with the associated polarities) and currents (with the associated direction)for all resistors. Test your procedures by simulate the circuit using Multisim to verify your hand calculations (Show all steps, equations, and calculations). IR1 R1 IR6 5.1KO IR3 R6 1ko IR2 ww 2.2KO R3 ww R2 1KO V2 V1 10V 5V IR5 IR7 IR4 1KO 2.2KΩ R7 1kQ R4 R5 Figure 2: DC-Circuit ww wwarrow_forwardBasic Electrical Engineering Chapter 9. Laws, Theorems and Methods used in Network Analysis LESSON TITLE: Laws, Theorems and Methods used in Network Analysisarrow_forward
- HW • 1- a. For the network of Fig. 9.136, determine the value of R for maximum power to R b. Determine the maximum power to R. c. Plot a curve of power to R versus R for R equal to . 1,14 14, 14, and 2 times the value obtained in part (a). SA Rn 24 V FIG. 9,136arrow_forwardPROBLEM #7 FOR THE NETWORK THE NETWORK HAS AN EQUIVALENT RESISTANCE USE A S-Y CONVERSION. 100% m 4252 MR 2002 W 682 SELECT A VALUE OF R SUCH THAT OF 70.65.arrow_forwardNETWORK LAWS Using Thevenin’s Theorem Determine VTH as seen by Resistor R1. (the units of the resistors are in Ohms) (ANS: 257 V)arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON
Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON
Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,

Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780133923605
Author:Robert L. Boylestad
Publisher:PEARSON

Delmar's Standard Textbook Of Electricity
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9781337900348
Author:Stephen L. Herman
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Programmable Logic Controllers
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780073373843
Author:Frank D. Petruzella
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Fundamentals of Electric Circuits
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780078028229
Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew Sadiku
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780134746968
Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan Riedel
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Electromagnetics
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780078028151
Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.
Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Thevenin's Theorem; Author: Neso Academy;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=veAFVTIpKyM;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY