
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
cis isomer should be drawn for the given trans isomer.
Concept Introduction:
The arrangement of groups attached to the carbo atoms involved in a
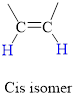
Cis Isomer: The two groups attached on same side of
In cis isomer the hydrogen atoms are on the same side of the two carbon atom.
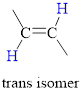
Trans isomer: The two groups are attached on opposite sides of the carbon-carbon double bond;.
The hydrogen atoms are on the opposite side of the two carbon atom.
(b)
Interpretation:
trans isomer should be drawn for the given cis isomer.
Concept Introduction:
The arrangement of groups attached to the carbo atoms involved in a
Cis Isomer: The two groups attached on same side of
In cis isomer the hydrogen atoms are on the same side of the two carbon atom.

Trans isomer: The two groups are attached on opposite sides of the carbon-carbon double bond;.
The hydrogen atoms are on the opposite side of the two carbon atom.

Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 9 Solutions
Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
- A covalent bond is the result of the a) b) c) d) e) overlap of two half-filled s orbitals overlap of a half-filled s orbital and a half-filled p orbital overlap of two half-filled p orbitals along their axes parallel overlap of two half-filled parallel p orbitals all of the abovearrow_forwardCan the target compound at right be efficiently synthesized in good yield from the unsubstituted benzene at left? starting material target If so, draw a synthesis below. If no synthesis using reagents ALEKS recognizes is possible, check the box under the drawing area. Be sure you follow the standard ALEKS rules for submitting syntheses. + More... Note for advanced students: you may assume that you are using a large excess of benzene as your starting material. C T Add/Remove step X ноarrow_forwardWhich one of the following atoms should have the largest electron affinity? a) b) c) d) 으으 e) 1s² 2s² 2p6 3s¹ 1s² 2s² 2p5 1s² 2s² 2p 3s² 3p² 1s² 2s 2p 3s² 3p6 4s2 3ds 1s² 2s² 2p6arrow_forward
- All of the following are allowed energy levels except _. a) 3f b) 1s c) 3d d) 5p e) 6sarrow_forwardA student wants to make the following product in good yield from a single transformation step, starting from benzene. Add any organic reagents the student is missing on the left-hand side of the arrow, and any addition reagents that are necessary above or below the arrow. If this product can't be made in good yield with a single transformation step, check the box below the drawing area. Note for advanced students: you may assume that an excess of benzene is used as part of the reaction conditions. : ☐ + I X This product can't be made in a single transformation step.arrow_forwardPredict the major products of this organic reaction:arrow_forward
- Name the family to which each organic compound belongs. The first answer has been filled in for you. compound CH₂ || CH3-C-NH2 0 ။ CH3-C-CH₂ CH=O–CH=CH, CH₂ HO CH2-CH2-CH-CH3 family amine Darrow_forward1b. Br LOHarrow_forwardI would like my graphs checked please. Do they look right? Do I have iodine and persulfate on the right axis ?arrow_forward
 Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning





