
Organic Chemistry: A Guided Inquiry
2nd Edition
ISBN: 9780618974122
Author: Andrei Straumanis
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Chapter 9, Problem 11CTQ
Interpretation Introduction
Interpretation: The correct product needs to be identified for the given reaction.
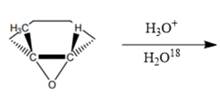
Concept Introduction: The given reaction is an acid-catalyzed
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
>
You are trying to decide if there is a single reagent you can add that will make the following synthesis possible without any other
major side products:
1. ☑
CI
2. H3O+
O
Draw the missing reagent X you think will make this synthesis work in the drawing area below.
If there is no reagent that will make your desired product in good yield or without complications, just check the box under the
drawing area and leave it blank.
Click and drag to start drawing a
structure.
Explanation
Check
?
DO
18
Ar
B
© 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Center | Accessibility
Don't use ai to answer I will report you answer
Consider a solution of 0.00304 moles of 4-nitrobenzoic acid (pKa = 3.442) dissolved in 25 mL water and titrated with 0.0991 M NaOH. Calculate the pH at the equivalence point
Chapter 9 Solutions
Organic Chemistry: A Guided Inquiry
Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- What is the name of the following compound? SiMe3arrow_forwardK Draw the starting structure that would lead to the major product shown under the provided conditions. Drawing 1. NaNH2 2. PhCH2Br 4 57°F Sunny Q Searcharrow_forward7 Draw the starting alkyl bromide that would produce this alkyne under these conditions. F Drawing 1. NaNH2, A 2. H3O+ £ 4 Temps to rise Tomorrow Q Search H2arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning EBK A SMALL SCALE APPROACH TO ORGANIC LChemistryISBN:9781305446021Author:LampmanPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT
EBK A SMALL SCALE APPROACH TO ORGANIC LChemistryISBN:9781305446021Author:LampmanPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT

Organic Chemistry: A Guided Inquiry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780618974122
Author:Andrei Straumanis
Publisher:Cengage Learning

EBK A SMALL SCALE APPROACH TO ORGANIC L
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305446021
Author:Lampman
Publisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT