
Concept explainers
(a)
To Calculate: The initial
(a)
Answer to Problem 118P
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
Height of each vertical beam
Width of each vertical beam
Length horizontal cross-member
The mass of the vertical beam
The mass of the horizontal beam
Formula Used:
From Newton’s second law of motion
Where, F is the net force, m is the mass and a is the acceleration.
Calculation:
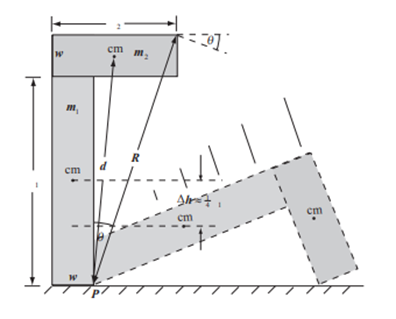
Here, one of the structures initially in its upright position. But later, it is about to strike the floor. The moments about the axis of rotation (a line through point P) can be considered.
Use the parallel-axis theorem to find the moments of inertia of the two parts of this composite structure. Let the numeral 1 denote the vertical member and the numeral 2 the horizontal member.
Apply Newton’s second law of motion in rotational form to the structure to express its angular acceleration in terms of the net torque causing it to fall and its moment of inertia with respect to point P.
Taking clockwise rotation to be positive, use
Here,
The mass of the vertical beam =
mass of the horizontal beam =
Length of vertical beam =
Width of the beam =
Acceleration of the beam =
Gravitational acceleration =
Because
Conclusion:
The initial angular acceleration of the structure is
(b)
ToCalculate: The magnitude of the initial linear acceleration of the right end of the horizontal beam.
(b)
Answer to Problem 118P
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
Height of each vertical beam
Width of each vertical beam
Length horizontal cross-member
The mass of the vertical beam
The mass of the horizontal beam
The initial angular acceleration of the structure is
Formula used:
From Newton’s second law of motion
Where, F is the net force, m is the mass and a is the acceleration.
Linear acceleration (a) in terms of angular acceleration (
Calculation:
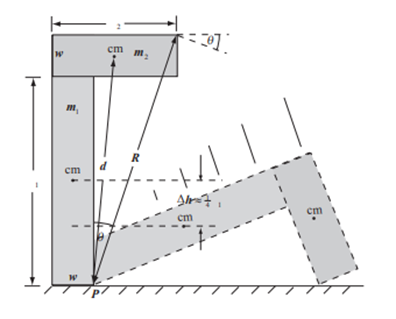
Conclusion:
The magnitude of the initial linear acceleration of the right end of the horizontal beam is
(c)
To explain: The horizontal component of the initial linear acceleration be at this same location.
(c)
Answer to Problem 118P
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
Height of each vertical beam
Width of each vertical beam
Length horizontal cross-member
The mass of the vertical beam
The mass of the horizontal beam
The magnitude of the initial linear acceleration of the right end of the horizontal beam is
Formula used:
Horizontal component of acceleration is
Calculation:
Conclusion:
The horizontal component of the initial linear acceleration be at this same location is
(d)
To Calculate: The beam’s rotational speed when they caught it.
(d)
Answer to Problem 118P
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
Height of each vertical beam
Width of each vertical beam
Length horizontal cross-member
The mass of the vertical beam
The mass of the horizontal beam
Formula used:
Rotational kinetic energy:
Where, I is the moment of inertia and
Potential energy,
Where, m is the mass, g is the acceleration due to gravity and h is the height.
Calculation:
By applying the conservation of mechanical energy to the beam:
Conclusion:
The beam’s rotational speed when they caught it is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 9 Solutions
Physics for Scientists and Engineers
- A capacitor with a capacitance of C = 5.95×10−5 F is charged by connecting it to a 12.5 −V battery. The capacitor is then disconnected from the battery and connected across an inductor with an inductance of L = 1.55 H . At the time 2.35×10−2 s after the connection to the inductor is made, what is the current in the inductor? At that time, how much electrical energy is stored in the inductor?arrow_forwardCan someone help me with this question. Thanks.arrow_forwardCan someone help me with this question. Thanks.arrow_forward
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University
University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning





