
Concept explainers
(a)
The speed of the ball as it begins rolling without slipping.
(a)
Answer to Problem 107P
Explanation of Solution
Given:
Radius of the ball is
Initial speed of the ball is
The coefficient of kinetic friction between the ball and billiard table is
Forward spin of the ball just after its release is
Formula Used:
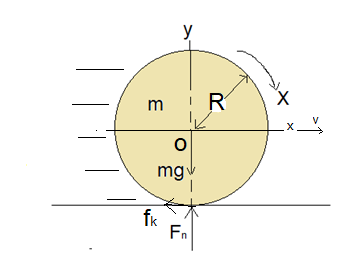
FIGURE: 1
Constant acceleration equation that relates the speed of the ball to the acceleration and time,
Where,
Referring to the force diagram shown in figure 1, applying Newton’s second law to the ball when it is rolling without slipping,
And
Where,
Calculation:
Where,
From equation
Substituting this in equation
Now,substituting the expression for
Substituting for
From equation
Moment of inertia with respect to an axis through the center of the ball is
Substituting for
Now let us write constant-acceleration equation that connects angular speed of the ball to the angular acceleration and time,
Imposing the condition for rolling the ball without slipping,
Substituting for
Now equate the equations
Substituting this
Conclusion:
The speed of the ball as it begins rolling without slipping is
(b)
The time the ball moves before it begins to rolling without slipping .
(b)
Answer to Problem 107P
Explanation of Solution
Given:
Radius of the ball is
Initial speed of the ball is
The coefficient of kinetic friction between the ball and billiard table is
Forward spin of the ball just after its release is
Formula Used:
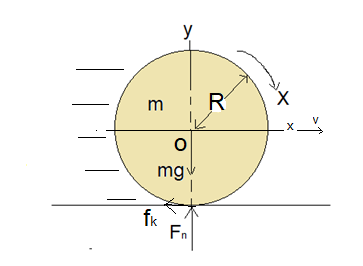
FIGURE: 2
Constant acceleration equation that relates the speed of the ball to the acceleration and time,
Where,
Referring to the force diagram shown in figure 2, applying Newton’s second law to the ball when it is rolling without slipping,
And
Where,
Calculation:
Where,
From equation
Substituting this in equation
Now,substituting the expression for
Substituting for
From equation
Moment of inertia with respect to an axis through the center of the ball is
Substituting for
Now let us write constant-acceleration equation that connects angular speed of the ball to the angular acceleration and time,
Imposing the condition for rolling the ball without slipping,
Substituting for
Now equate the equations
Conclusion:
The time the ball moves before it begins to rolling without slipping
(c)
The distance slide down the lane by the ball before it begins rolling without slipping.
(c)
Answer to Problem 107P
Explanation of Solution
Given:
Radius of the ball is
Initial speed of the ball is
The coefficient of kinetic friction between the ball and billiard table is
Forward spin of the ball just after its release is
Calculation:
Let
Now let us write expression that relates
Average speed of the ball is,
Substituting this average speed in equation
Substituting for
Conclusion:
The distance slide down the lane by the ball before it begins rolling without slipping is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 9 Solutions
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Vol. 1
- At point A, 3.20 m from a small source of sound that is emitting uniformly in all directions, the intensity level is 58.0 dB. What is the intensity of the sound at A? How far from the source must you go so that the intensity is one-fourth of what it was at A? How far must you go so that the sound level is one-fourth of what it was at A?arrow_forwardMake a plot of the acceleration of a ball that is thrown upward at 20 m/s subject to gravitation alone (no drag). Assume upward is the +y direction (and downward negative y).arrow_forwardLab Assignment #3 Vectors 2. Determine the magnitude and sense of the forces in cables A and B. 30° 30° 300KN 3. Determine the forces in members A and B of the following structure. 30° B 200kN Name: TA: 4. Determine the resultant of the three coplanar forces using vectors. F₁ =500N, F₂-800N, F, 900N, 0,-30°, 62-50° 30° 50° F₁ = 500N = 900N F₂ = 800Narrow_forward
- Lab Assignment #3 Vectors Name: TA: 1. With the equipment provided in the lab, determine the magnitude of vector A so the system is in static equilibrium. Perform the experiment as per the figure below and compare the calculated values with the numbers from the spring scale that corresponds to vector A. A Case 1: Vector B 40g Vector C 20g 0 = 30° Vector A = ? Case 2: Vector B 50g Vector C = 40g 0 = 53° Vector A ? Case 3: Vector B 50g Vector C 30g 0 = 37° Vector A = ?arrow_forwardThree point-like charges are placed at the corners of an equilateral triangle as shown in the figure. Each side of the triangle has a length of 20.0 cm, and the point (A) is located half way between q1 and q2 along the side. Find the magnitude of the electric field at point (A). Let q1=-1.30 µC, q2=-4.20µC, and q3= +4.30 µC. __________________ N/Carrow_forwardNo chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forward
- Find the total capacitance in micro farads of the combination of capacitors shown in the figure below. HF 5.0 µF 3.5 µF №8.0 μLE 1.5 µF Ι 0.75 μF 15 μFarrow_forwardthe answer is not 0.39 or 0.386arrow_forwardFind the total capacitance in micro farads of the combination of capacitors shown in the figure below. 2.01 0.30 µF 2.5 µF 10 μF × HFarrow_forward
 Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University
University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University Classical Dynamics of Particles and SystemsPhysicsISBN:9780534408961Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. MarionPublisher:Cengage Learning
Classical Dynamics of Particles and SystemsPhysicsISBN:9780534408961Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. MarionPublisher:Cengage Learning Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning





