
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
10th Edition
ISBN: 9780134319650
Author: Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 8.1, Problem 8.15P
The inner ring A has an inner radius r1 and outer radius r2. The outer ring B has an inner radius r3 and an outer radius r4, and r2 > r3. If the outer ring is heated and then fitted over the inner ring, determine the pressure between the two rings when ring B reaches the temperature of the inner ring. The material has a modulus of elasticity of E and a coefficient of thermal expansion of α
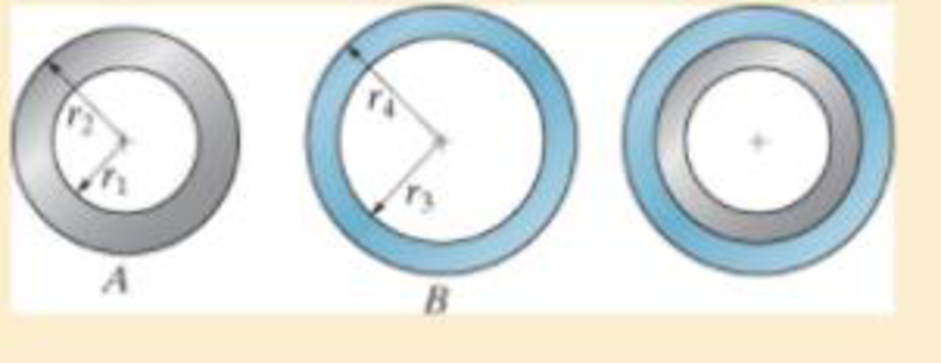 .
.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Consider a double-fluid manometer attached to an air pipe shown below. If the specific gravity ofone fluid is 13.8, determine the specific gravity of the other fluid for the indicated absolutepressure of air. Take the atmospheric pressure to be 95 kPa
A race car enters the circular portion of a track that has a radius of 65 m. Disregard the 70 m in the picture. When the car enters the curve at point P, it is traveling with a speed of 120 km/h that is increasing at 5 m/s^2 . Three seconds later, determine the x and y components of velocity and acceleration of the car. I'm having trouble getting the correct y component of acceleration. all the other answers are correct. thank you!
Figure: 06_P041
Copyright 2013 Pearson Education, publishing a Prentice Hall
2. Determine the force that the jaws J of the metal cutters exert on the smooth cable C if 100-N
forces are applied to the handles. The jaws are pinned at E and A, and D and B. There is also
a pin at F.
400 mm
15°
20 mm
A
15°
15
D
B
30 mm² 80 mm
20 mm
400 mm
Figure: 06_P090
Copyright 2013 Pearson Education, publishing as Prentice Hall
15°
100 N
100 N
15°
Chapter 8 Solutions
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Ch. 8.1 - If it is subjected to an internal pressure of p =...Ch. 8.1 - If it is subjected to an internal pressure of p =...Ch. 8.1 - The thin-walled cylinder can be supported in one...Ch. 8.1 - If the inner diameter of the tank is 22 in., and...Ch. 8.1 - Air pressure in the cylinder is increased by...Ch. 8.1 - Determine the maximum force P that can be exerted...Ch. 8.1 - A boiler is constructed of 8-mm-thick steel plates...Ch. 8.1 - 88. The steel water pipe has an inner diameter of...Ch. 8.1 - The steel water pipe has an inner diameter of 12...Ch. 8.1 - The A-36-steel band is 2 in. wide and is secured...
Ch. 8.1 - The gas pipe line is supported every 20 ft by...Ch. 8.1 - A pressure-vessel head is fabricated by welding...Ch. 8.1 - An A-36-steel hoop has an inner diameter of 23.99...Ch. 8.1 - The ring, having the dimensions shown, is placed...Ch. 8.1 - The inner ring A has an inner radius r1 and outer...Ch. 8.1 - Two hemispheres having an inner radius of 2 ft and...Ch. 8.1 - In order to increase the strength of the pressure...Ch. 8.2 - Show the results on the left segment.Ch. 8.2 - Show the stress that each of these loads produce...Ch. 8.2 - Fundamental Problems F81. Determine the normal...Ch. 8.2 - Show the results in a differential element at the...Ch. 8.2 - Determine the state of stress at point A on the...Ch. 8.2 - Determine the magnitude of the load P that will...Ch. 8.2 - Determine the state of stress at point B. Show the...Ch. 8.2 - Determine the state of stress at point A on the...Ch. 8.2 - Determine the state of stress at point A on the...Ch. 8.2 - Show the results in a differential element at the...Ch. 8.2 - Determine the shortest distance d to the edge of...Ch. 8.2 - The plate has a thickness of 20 mm and P acts...Ch. 8.2 - Plot the distribution of normal stress acting...Ch. 8.2 - Also, plot the normal-stress distribution over the...Ch. 8.2 - If the allowable normal stress for the steel is...Ch. 8.2 - If the applied force P = 1.50 kip, determine the...Ch. 8.2 - Determine the maximum normal stress on the cross...Ch. 8.2 - If the wood has an allowable normal stress of...Ch. 8.2 - Determine the maximum normal stress along section...Ch. 8.2 - Sketch the stress distribution along section aa of...Ch. 8.2 - Sketch the normal-stress distribution acting over...Ch. 8.2 - Determine the state of stress at points A and B,...Ch. 8.2 - If the force of 100 N is applied to the handles,...Ch. 8.2 - Determine the stress components at point A on the...Ch. 8.2 - Determine the stress components at point B on the...Ch. 8.2 - Determine the normal stress developed at points A...Ch. 8.2 - Sketch the normal-stress distribution acting over...Ch. 8.2 - Determine the state of stress at points A and B,...Ch. 8.2 - Determine the state of stress at point A on the...Ch. 8.2 - Determine the state of stress at point B on the...Ch. 8.2 - Determine the state of stress acting at point D....Ch. 8.2 - Determine the state of stress acting at point E....Ch. 8.2 - If it is subjected to the force system shown,...Ch. 8.2 - Solve Prob.840 for point B.Ch. 8.2 - Determine the stress components acting on the...Ch. 8.2 - Determine the stress components acting on the...Ch. 8.2 - Neglect the weight of the block.Ch. 8.2 - Neglect the weight of the block.Ch. 8.2 - He is supported uniformly by two bars, each having...Ch. 8.2 - Determine the state of stress at point A, and show...Ch. 8.2 - Determine the state of stress at point B, and show...Ch. 8.2 - Determine the state of stress at point C, and show...Ch. 8.2 - Determine the maximum radius e at which the load P...Ch. 8.2 - Specify the region to which this load can be...Ch. 8.2 - Determine the smallest force P that can be applied...Ch. 8.2 - The coiled spring is subjected to a force P. If we...Ch. 8.2 - The pins at C and D are at the same location as...Ch. 8.2 - Determine the state of stress at point A, and show...Ch. 8.2 - Determine the state of stress at point B, and show...Ch. 8.2 - Determine the stress components at points A and B...Ch. 8.2 - Determine the stress components at points C and D...Ch. 8.2 - Determine the stress components in the support...Ch. 8.2 - Determine the stress components in the support...Ch. 8.2 - If the force at the ram on the clamp at D is P= 8...Ch. 8.2 - Determine the maximum ram force P that can be...Ch. 8.2 - and an outer radius of 3.00 in. If the face of the...Ch. 8.2 - for points E and F.Ch. 8.2 - Determine the stress components at points A and B...Ch. 8.2 - Solve Prob.8-65 for points C and D.Ch. 8.2 - Due to internal gearing, this causes the block to...Ch. 8.2 - Determine the state of stress at point A and show...Ch. 8.2 - Solve Prob.868 for point B.Ch. 8.2 - Determine the stress components at point A. Sketch...Ch. 8.2 - for the stress components at point B.Ch. 8.2 - Determine the state of stress at point A at...Ch. 8.2 - Determine the state of stress at point B at...Ch. 8 - If it supports a cable loading of 800 lb,...Ch. 8 - Determine the state of stress at point E on the...Ch. 8 - Determine the state of stress at point F on the...Ch. 8 - The suspender arm AE has a square cross-sectional...Ch. 8 - If the cross section of the femur at section aa...Ch. 8 - If it has a mass of 5 kg/m, determine the largest...Ch. 8 - and is used to support the vertical reactions of...Ch. 8 - and is used to support the vertical reactions of...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A telemetry system is used to quantify kinematic values of a ski jumper immediately before the jumper leaves the ramp. According to the system r=560 ft , r˙=−105 ft/s , r¨=−10 ft/s2 , θ=25° , θ˙=0.07 rad/s , θ¨=0.06 rad/s2 Determine the velocity of the skier immediately before leaving the jump. The velocity of the skier immediately before leaving the jump along with its direction is ? I have 112.08 ft/s but can't seem to get the direction correct. Determine the acceleration of the skier at this instant. At this instant, the acceleration of the skier along with its direction is ? acceleration is 22.8 ft/s^2 but need help with direction. Need help with velocity direction and acceleration direction please.arrow_forwardFor Problems 18-22 (Table 7-27), design a V-belt drive. Specify the belt size, the sheave sizes, the number of belts, the actual output speed, and the center distance.arrow_forwardonly 21arrow_forward
- only 41arrow_forwardNormal and tangential components-relate to x-y coordinates A race car enters the circular portion of a track that has a radius of 65 m. When the car enters the curve at point P, it is traveling with a speed of 120 km/h that is increasing at 5 m/s^2 . Three seconds later, determine the x and y components of velocity and acceleration of the car. I need help with finding the y component of the total acceleration. I had put -32 but its incorrect. but i keep getting figures around that numberarrow_forwardThe bracket BCD is hinged at C and attached to a control cable at B. Let F₁ = 275 N and F2 = 275 N. F1 B a=0.18 m C A 0.4 m -0.4 m- 0.24 m Determine the reaction at C. The reaction at C N Z F2 Darrow_forward
- Consider the angle bar shown in the given figure A W 240 mm B 80 mm Draw the free-body diagram needed to determine the reactions at A and B when a = 150 mm. This problem could also be approached as a 3-force body using method of Section 4.2B.arrow_forwardA telemetry system is used to quantify kinematic values of a ski jumper immediately before the jumper leaves the ramp. According to the system r=560 ft , r˙=−105 ft/s , r¨=−10 ft/s2 , θ=25° , θ˙=0.07 rad/s , θ¨=0.06 rad/s2 Determine the velocity of the skier immediately before leaving the jump. The velocity of the skier immediately before leaving the jump along with its direction is ? I have 112.08 ft/s but can't seem to get the direction correct. Determine the acceleration of the skier at this instant. At this instant, the acceleration of the skier along with its direction is ? acceleration is 22.8 ft/s^2 but need help with direction. Need help with velocity direction and acceleration direction please.arrow_forwardFor the stop bracket shown, locate the x coordinate of the center of gravity. Consider a = = 16.50 mm. 34 mm 62 mm 51 mm 10 mm 100 mm 88 mm 55 mm 45 mm The x coordinate of the center of gravity is mm.arrow_forward
- In the given figure, the bent rod ABEF is supported by bearings at C and D and by wire AH. The portion AB of the rod is 250 mm long, and the load W is 580 N. Assume that the bearing at D does not exert any axial thrust. H B A с 30° 250 mm D Z 50 mm 300 mm F 250 mm 50 mm W Draw the free-body diagram needed to determine the tension in wire AH and the reactions at C and D.arrow_forwardA 10-ft boom is acted upon by the 810-lb force as shown in the figure. D 6 ft 6 ft E B 7 ft C 6 ft x 4 ft W Draw the free-body diagram needed to determine the tension in each cable and the reaction at the ball-and-socket joint at A.arrow_forwardLocate the center of gravity of the sheet-metal form shown. Given: r = 26.40 mm . 50 mm 40 mm X 150 mm The center of gravity (✗) of the sheet-metal form is The center of gravity (Y) of the sheet-metal form is The center of gravity ( Z ) of the sheet-metal form is mm. mm. (Round the final answer to three decimal places.) mm.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY
Material Properties 101; Author: Real Engineering;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=BHZALtqAjeM;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY
Mechanical Properties of Materials; Author: Academic Gain Tutorials;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=6L-r3hx0NLM;License: Standard Youtube License