
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
10th Edition
ISBN: 9780134319650
Author: Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 8.2, Problem 8.54P
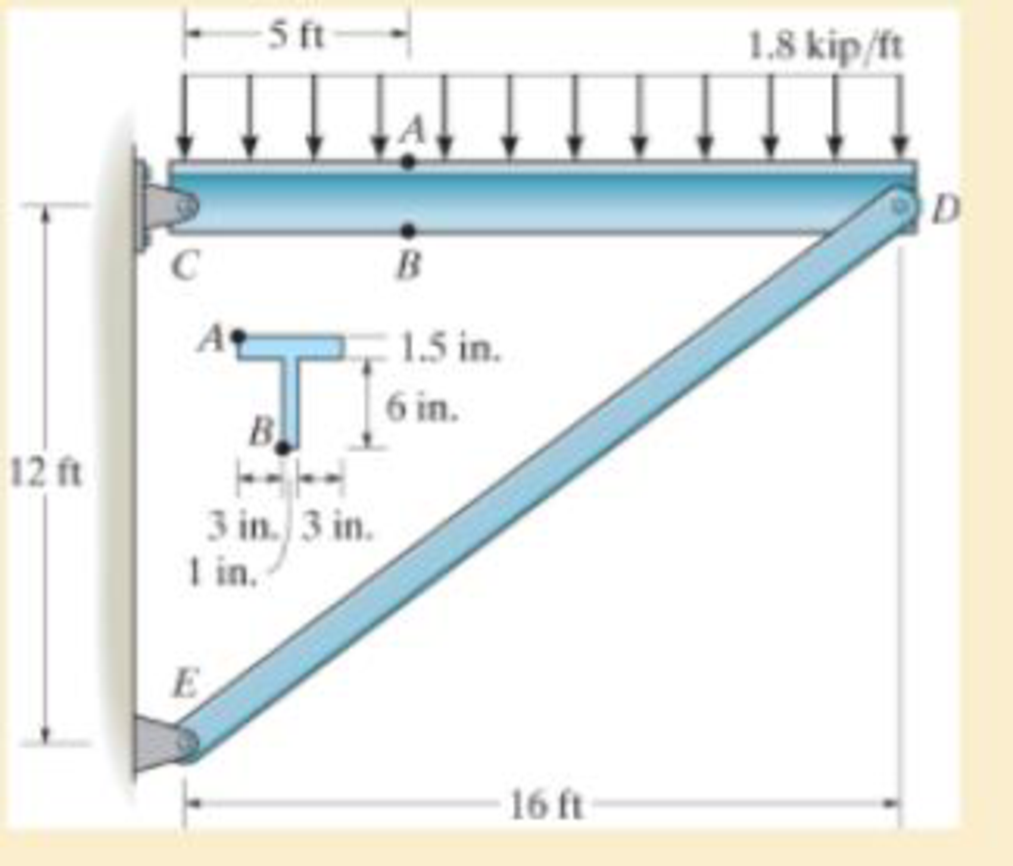
The pins at C and D are at the same location as the neutral axis for the cross section.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
my ID# 016948724. Please solve this problem step by step
My ID# 016948724 please find the forces for Fx=0: fy=0: fz=0: please help me to solve this problem step by step
My ID# 016948724 please solve the proble step by step find the forces fx=o: fy=0; fz=0; and find shear moment and the bending moment diagran please draw the diagram for the shear and bending moment
Chapter 8 Solutions
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Ch. 8.1 - If it is subjected to an internal pressure of p =...Ch. 8.1 - If it is subjected to an internal pressure of p =...Ch. 8.1 - The thin-walled cylinder can be supported in one...Ch. 8.1 - If the inner diameter of the tank is 22 in., and...Ch. 8.1 - Air pressure in the cylinder is increased by...Ch. 8.1 - Determine the maximum force P that can be exerted...Ch. 8.1 - A boiler is constructed of 8-mm-thick steel plates...Ch. 8.1 - 88. The steel water pipe has an inner diameter of...Ch. 8.1 - The steel water pipe has an inner diameter of 12...Ch. 8.1 - The A-36-steel band is 2 in. wide and is secured...
Ch. 8.1 - The gas pipe line is supported every 20 ft by...Ch. 8.1 - A pressure-vessel head is fabricated by welding...Ch. 8.1 - An A-36-steel hoop has an inner diameter of 23.99...Ch. 8.1 - The ring, having the dimensions shown, is placed...Ch. 8.1 - The inner ring A has an inner radius r1 and outer...Ch. 8.1 - Two hemispheres having an inner radius of 2 ft and...Ch. 8.1 - In order to increase the strength of the pressure...Ch. 8.2 - Show the results on the left segment.Ch. 8.2 - Show the stress that each of these loads produce...Ch. 8.2 - Fundamental Problems F81. Determine the normal...Ch. 8.2 - Show the results in a differential element at the...Ch. 8.2 - Determine the state of stress at point A on the...Ch. 8.2 - Determine the magnitude of the load P that will...Ch. 8.2 - Determine the state of stress at point B. Show the...Ch. 8.2 - Determine the state of stress at point A on the...Ch. 8.2 - Determine the state of stress at point A on the...Ch. 8.2 - Show the results in a differential element at the...Ch. 8.2 - Determine the shortest distance d to the edge of...Ch. 8.2 - The plate has a thickness of 20 mm and P acts...Ch. 8.2 - Plot the distribution of normal stress acting...Ch. 8.2 - Also, plot the normal-stress distribution over the...Ch. 8.2 - If the allowable normal stress for the steel is...Ch. 8.2 - If the applied force P = 1.50 kip, determine the...Ch. 8.2 - Determine the maximum normal stress on the cross...Ch. 8.2 - If the wood has an allowable normal stress of...Ch. 8.2 - Determine the maximum normal stress along section...Ch. 8.2 - Sketch the stress distribution along section aa of...Ch. 8.2 - Sketch the normal-stress distribution acting over...Ch. 8.2 - Determine the state of stress at points A and B,...Ch. 8.2 - If the force of 100 N is applied to the handles,...Ch. 8.2 - Determine the stress components at point A on the...Ch. 8.2 - Determine the stress components at point B on the...Ch. 8.2 - Determine the normal stress developed at points A...Ch. 8.2 - Sketch the normal-stress distribution acting over...Ch. 8.2 - Determine the state of stress at points A and B,...Ch. 8.2 - Determine the state of stress at point A on the...Ch. 8.2 - Determine the state of stress at point B on the...Ch. 8.2 - Determine the state of stress acting at point D....Ch. 8.2 - Determine the state of stress acting at point E....Ch. 8.2 - If it is subjected to the force system shown,...Ch. 8.2 - Solve Prob.840 for point B.Ch. 8.2 - Determine the stress components acting on the...Ch. 8.2 - Determine the stress components acting on the...Ch. 8.2 - Neglect the weight of the block.Ch. 8.2 - Neglect the weight of the block.Ch. 8.2 - He is supported uniformly by two bars, each having...Ch. 8.2 - Determine the state of stress at point A, and show...Ch. 8.2 - Determine the state of stress at point B, and show...Ch. 8.2 - Determine the state of stress at point C, and show...Ch. 8.2 - Determine the maximum radius e at which the load P...Ch. 8.2 - Specify the region to which this load can be...Ch. 8.2 - Determine the smallest force P that can be applied...Ch. 8.2 - The coiled spring is subjected to a force P. If we...Ch. 8.2 - The pins at C and D are at the same location as...Ch. 8.2 - Determine the state of stress at point A, and show...Ch. 8.2 - Determine the state of stress at point B, and show...Ch. 8.2 - Determine the stress components at points A and B...Ch. 8.2 - Determine the stress components at points C and D...Ch. 8.2 - Determine the stress components in the support...Ch. 8.2 - Determine the stress components in the support...Ch. 8.2 - If the force at the ram on the clamp at D is P= 8...Ch. 8.2 - Determine the maximum ram force P that can be...Ch. 8.2 - and an outer radius of 3.00 in. If the face of the...Ch. 8.2 - for points E and F.Ch. 8.2 - Determine the stress components at points A and B...Ch. 8.2 - Solve Prob.8-65 for points C and D.Ch. 8.2 - Due to internal gearing, this causes the block to...Ch. 8.2 - Determine the state of stress at point A and show...Ch. 8.2 - Solve Prob.868 for point B.Ch. 8.2 - Determine the stress components at point A. Sketch...Ch. 8.2 - for the stress components at point B.Ch. 8.2 - Determine the state of stress at point A at...Ch. 8.2 - Determine the state of stress at point B at...Ch. 8 - If it supports a cable loading of 800 lb,...Ch. 8 - Determine the state of stress at point E on the...Ch. 8 - Determine the state of stress at point F on the...Ch. 8 - The suspender arm AE has a square cross-sectional...Ch. 8 - If the cross section of the femur at section aa...Ch. 8 - If it has a mass of 5 kg/m, determine the largest...Ch. 8 - and is used to support the vertical reactions of...Ch. 8 - and is used to support the vertical reactions of...
Additional Engineering Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
Which of the following are illegal variable names in Python, and why? x 99bottles july2009 theSalesFigureForFis...
Starting Out with Python (4th Edition)
What types of coolant are used in vehicles?
Automotive Technology: Principles, Diagnosis, And Service (6th Edition) (halderman Automotive Series)
This optional Google account security feature sends you a message with a code that you must enter, in addition ...
SURVEY OF OPERATING SYSTEMS
What is an uninitialized variable?
Starting Out with Programming Logic and Design (5th Edition) (What's New in Computer Science)
1.2 Explain the difference between geodetic and plane
surveys,
Elementary Surveying: An Introduction To Geomatics (15th Edition)
Convert each of the following binary representations to its equivalent base ten form: a. 101010 b. 100001 c. 10...
Computer Science: An Overview (13th Edition) (What's New in Computer Science)
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- My ID#016948724 please solve this problems and show me every step clear to follow pleasearrow_forwardMy ID# 016948724arrow_forwardPlease do not use any AI tools to solve this question. I need a fully manual, step-by-step solution with clear explanations, as if it were done by a human tutor. No AI-generated responses, please.arrow_forward
- Please do not use any AI tools to solve this question. I need a fully manual, step-by-step solution with clear explanations, as if it were done by a human tutor. No AI-generated responses, please.arrow_forwardPlease do not use any AI tools to solve this question. I need a fully manual, step-by-step solution with clear explanations, as if it were done by a human tutor. No AI-generated responses, please.arrow_forward[Q2]: The cost information supplied by the cost accountant is as follows:Sales 20,00 units, $ 10 per unitCalculate the (a/ newsale guantity and (b) new selling price to earn the sameVariable cost $ 6 per unit, Fixed Cost $ 30,000, Profit $ 50,000profit ifi) Variable cost increases by $ 2 per unitil) Fixed cost increase by $ 10,000Ili) Variable cost increase by $ 1 per unit and fixed cost reduces by $ 10,000arrow_forward
- can you please help me perform Visual Inspection and Fractography of the attatched image: Preliminary examination to identify the fracture origin, suspected fatigue striation, and corrosion evidences.arrow_forwardcan you please help[ me conduct Causal Analysis (FTA) on the scenario attatched: FTA diagram which is a fault tree analysis diagram will be used to gain an overview of the entire path of failure from root cause to the top event (i.e., the swing’s detachment) and to identify interactions between misuse, material decay and inspection errors.arrow_forwardhi can you please help me in finding the stress intensity factor using a k-calcluator for the scenario attathced in the images.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Everything About COMBINED LOADING in 10 Minutes! Mechanics of Materials; Author: Less Boring Lectures;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=N-PlI900hSg;License: Standard youtube license