
Three 4-kg packages A, B, and C are placed on a conveyor belt that is at rest. Between the belt and both packages A and C, the coefficients of friction are μs = 0.30 and μk = 0.20; between package B and the belt, the coefficients are μs = 0.10 and μk = 0.08. The packages are placed on the belt so that they are in contact with each other and at rest. Determine which, if any, of the packages will move and the friction force acting on each package.
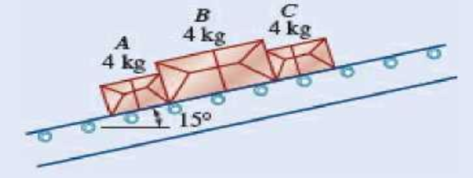
Fig. P8.13
Find whether any of the package moves and the friction force acting on each package.
Answer to Problem 8.13P
The package C will
The friction force in the package C is
The packages A and B will
The friction force in the package B is
The friction force in the package A is
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The mass of the package A, B, and C is
The static coefficient of friction between packages A and C and the belt is
The static coefficient of friction between package B and belt is
The kinetic coefficient of friction between packages A and C and belt is
The kinetic coefficient of friction between package B and belt is
Calculation:
Consider the acceleration due to gravity as
Consider Block C:
Show the free body diagram of the block C as in Figure 1.
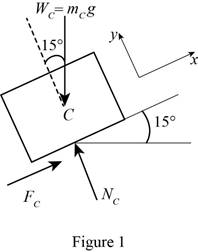
Resolve the vertical component of forces.
Resolve the horizontal component of forces.
Find the maximum friction force
Substitute 0.30 for
The maximum friction force is greater than the friction force.
Therefore, the package C will
Therefore, the friction force in the package C is
Consider Block B:
Show the free body diagram of the block B as in Figure 2.
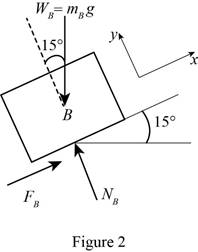
Resolve the vertical component of forces.
Resolve the horizontal component of forces.
Find the maximum friction force
Substitute 0.10 for
The maximum friction force is less than the friction force.
Therefore, the package B will
Find the friction force in the package B using the kinetic relation.
Substitute 0.08 for
Therefore, the friction force in the package B is
Consider Block A and B together:
Show the free body diagram of the block A and B as in Figure 3.
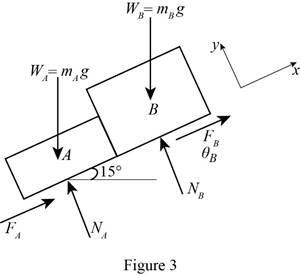
The normal force in package A is
The normal force in package B is
The friction force in package A is
The friction force in package B is
Find the total normal force in package A and B as follows;
Find the total friction force in package A and B as follows;
The maximum friction force in package A is
The maximum friction force in package B is
Find the maximum friction force
The maximum friction force is less than the friction force.
Therefore, the packages A and B will
Find the friction force in the package A using the kinetic relation.
Substitute 0.20 for
Therefore, the friction force in the package A is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 8 Solutions
VEC MECH 180-DAT EBOOK ACCESS(STAT+DYNA)
- reading is 0.4 mas SHOWN. Assume h₁ = 0.4 m, h₂ = 0.5 m. (a) Do you know the specific weight of mercury? (b) Do you know the specific weight of gasoline? (c) Do you know the specific weight of oil? (a) YHg = 133,000 (b) Ygas = 6867 (c) Yoil = 8829 eTextbook and Media Part 2 N/m³ N/m³ N/m³ A+ Gasoline t +B Oil -Mercury Attempts: unlimited Did you calculate the pressure difference between two locations using the correct specific weight? Did you assume that the pressures in fluid are the same in a horizontal plane even though they are in different tubes? Are the calculated pressures in a column of fluid always higher at lower elevations? Did you account for the fact that the two horizontal tubes of the U-tube are above the ground? Concepts: The pressure in a fluid is a function of the specific weight of the fluid and the height relative to a reference. Pressure is constant in a horizontal plane of a continuous mass of fluid. (a) What is the initial pressure difference? (PA-PB) (b) What is…arrow_forwardFind the solution of the following Differential Equations 1) "-4y+3y=0 3) "+16y=0 2) y"-16y=0 4) y"-y-6y=0 5) y"+2y=0 7) y"+y=0, (#0) 9) y"-y=0, y(0) = 6, y'(0) = -4 11) y"-4y+3y=0, y(0)=-1, 13) y'(0) = -5 "+2y+2y=0 15) y"-9y=0 17) y"-4y=0 6) y"-2y+2y=0 8) "+4y+5y=0 10) y"-9y=0, y(0) = 2, y'(0) = 0 12) y"-3y+2y= 0, y(0)=-1, y'(0) = 0 14) 4y+4y+y=0 16) "+6y+12y=0 18) 4y+4y+17y=0arrow_forwardAccess Pearson Mastering Engineering Back to my courses Course Home Course Home Scoresarrow_forward
- Access Pearson Mastering Engineering Back to my courses Course Home Course Home Scores Review Next >arrow_forwardAccess Pearson Course Home Scoresarrow_forwardAccess Pearson Mastering Engineering Back to my courses Course Home Course Home Scoresarrow_forwardarrow_back_iosSEE MORE QUESTIONSarrow_forward_ios
 International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305501607Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan KiusalaasPublisher:CENGAGE L
International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305501607Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan KiusalaasPublisher:CENGAGE L
