
Concept explainers
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
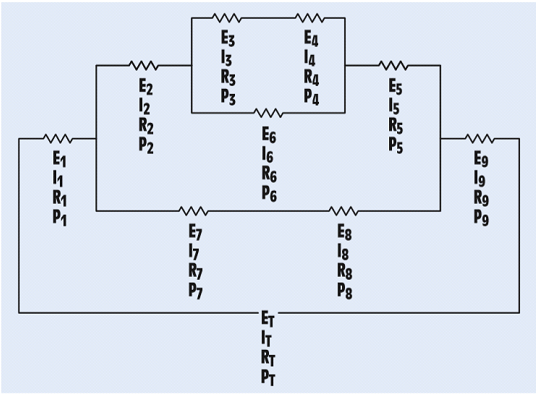
FIGURE 8-26 A combination circuit.
The unknown values in the circuit.
Answer to Problem 8PP
| ET = 24.04 V | E1 = 3.4V | E2 = 4.8 V | E3 = 0.478 V | E4 = 1.248 V |
| IT = 24.02mA | I1 = 24.02mA | I2 = 9.614 mA | I3 = 3.854 mA | I4 = 3.854 mA |
| RT = 942 Ω | R1 = 144 Ω | R2 = 499 Ω | R3 = 124Ω | R4 = 324 Ω |
| PT = 0.576 W | P1 = 0.0806W | P2 = 0.0461W | P3 = 0.00184W | P4 = 0.00481W |
| E5 = 2.11 V | E6 = 1.726V | E7 = 3.6 V | E8 = 5.04V | E9 = 12 V |
| I5 = 9.614 mA | I6 = 5.76 mA | I7 = 14.41 mA | I8 = 14.41 mA | I9 = 24.02 mA |
| R5 = 220 Ω | R6 = 300Ω | R7 = 86Ω | R8 = 360Ω | R9 = 500 Ω |
| P5 = 0.0203 W | P6 = 0.00995 W | P7 = 0.0518W | P8 = 0.0726W | P9 = 0.288 W |
Explanation of Solution
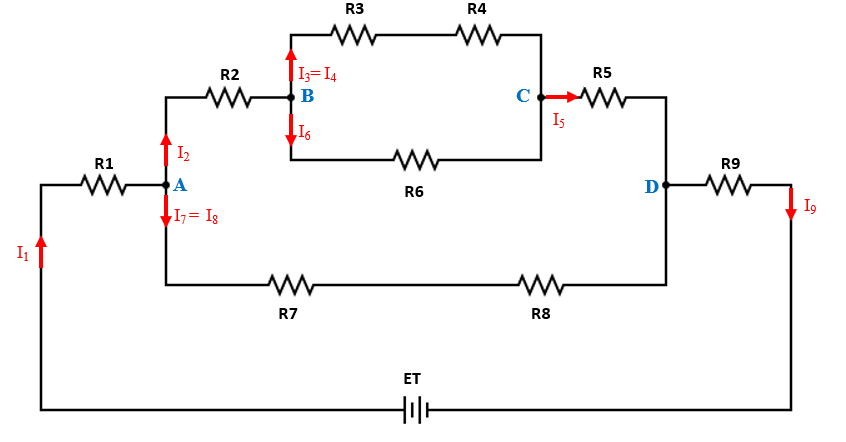
In the given question,
Current flowing through R1 is denoted by I1
Current flowing through R2is denoted by I2
Current flowing through R3 and R4 is denoted by I3(= I4)
Current flowing through R5 is denoted by I5
Current flowing through R6 is denoted by I6
Current flowing through R7 and R8 is denoted by I7 (= I8)
Current flowing through R9is denoted by I9
The total power consumed by the circuit is equal to sum of power consumed by individual resistors. Hence,
Using the voltage E4 and Power P4, we calculate resistance R4 and current I4
Since R3 and R4 are in series, the same current flows through both. Therefore, I3=I4=3.854 mA
Using the current I3 and resistance R3 find the voltage E3
Since R6 is in parallel with series combination of R3 and R4. Hence,
E6= 0.478 + 1.248 =1.726 V
Using the voltage E6 and Power P6, we calculate resistance R6 and current I6
At node B,
Using P2 and I2, we calculate R2
Using P2 and I2, we calculate E2
Since the incoming current in a network is equal to the outgoing current, current at node B= current at node C: I2=I5=9.614 mA
Using the voltage E5 and Power P5, we calculate resistance R5 and current I5
The total voltage drop across R7 and R8 i.e. E7 and E8 will be
The total power consumed in the branch containing resistors R7 and R8 will be 0.0518+0.0726 = 0.1244 W
Using the total power consumed and the total voltage, we can compute the total current in the network of R7 and R8.
Using the voltage and Power, we calculate R7, R8 and current I7, I8
At node A,
Since the incoming current in a network is equal to the outgoing current, current at node A=current at node D: I1 = I9 =IT=24.02 mA
Using the current I1 and Power P1, we calculate resistance R1 and voltage E1
Using the current I9 and Power P9, we calculate resistance R9 and voltage E9
Total voltage applied across the network will be,
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 8 Solutions
DELMAR'S STANDARD TEXT OF ELECTRICITY
- Solve only no 8, Don't use chatgpt or any , only expertarrow_forwardI need help in creating a matlab code to find the currents USING MARTIXS AND INVERSE to find the currentarrow_forwardQuestion 2 A transistor is used as a switch and the waveforms are shown in Figure 2. The parameters are Vcc = 225 V, VBE(sat) = 3 V, IB = 8 A, VCE(sat) = 2 V, Ics = 90 A, td = 0.5 µs, tr = 1 µs, ts = 3 µs, tƒ = 2 μs, and f 10 kHz. The duty cycle is k 50%. The collector- emitter leakage current is ICEO = 2 mA. Determine the power loss due to the collector current: = = = (a) during turn-on ton = td + tr VCE Vcc (b) during conduction period tn V CE(sat) 0 toff" ton Ics 0.9 Ics (c) during turn-off toff = ts + tf (d) during off-time tot (e) the total average power losses PT ICEO 0 IBS 0 Figure 2 V BE(sat) 0 主 * td tr In Is If to iB VBE T= 1/fsarrow_forward
- Question 1: The beta (B) of the bipolar transistor shown in Figure 1 varies from 12 to 60. The load resistance is Rc = 5. The dc supply voltage is VCC = 40 V and the input voltage to the base circuit is VB = 5 V. If VCE(sat) = 1.2 V, VBE(sat) = 1.6 V, and RB = 0.8 2, calculate: (a) the overdrive factor ODF. (b) the forced ẞ (c) the power loss in the transistor PT. IB VB RB + V BE RC Vcc' Ic + IE Figure 1 VCEarrow_forwardI need help in creating a matlab code to find the currentsarrow_forwardI need help fixing this MATLAB code: as I try to get it working there were some problems:arrow_forward
- I need help in construct a matlab code to find the voltage of VR1 to VR4, the currents, and the watts based on that circuit.arrow_forwardQ2: Using D flip-flops, design a synchronous counter. The counter counts in the sequence 1,3,5,7, 1,7,5,3,1,3,5,7,.... when its enable input x is equal to 1; otherwise, the counter count 0.arrow_forwardFrom the collector characteristic curves and the dc load line given below, determine the following: (a) Maximum collector current for linear operation (b) Base current at the maximum collector current (c) VCE at maximum collector current. lc (mA) 600 ΜΑ 60- 500 με 50- 400 με 40- 300 μ Α 30- Q-point 200 ΜΑ 20- 10- 100 μ Α 0 VCE (V) 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 [6 Paarrow_forward
- Procedure:- 1- Connect the cct. shown in fig.(2). a ADDS DS Fig.(2) 2-For resistive load, measure le output voltage by using oscilloscope ;then sketch this wave. 3- Measure the average values ::f VL and IL: 4- Repeat steps 2 & 3 but for RL load. Report:- 1- Calculate the D.C. output vcl age theoretically and compare it with the test value. 2- Calculate the harmonic cont :nts of the load voltage, and explain how filter components may be selected. 3- Compare between the three-phase half & full-wave uncontrolled bridge rectifier. 4- Draw the waveform for the c:t. shown in fig.(2) but after replaced Di and D3 by thyristors with a 30° and a2 = 90° 5- Draw the waveform for the cct. shown in fig.(2) but after replace the 6-diodes by 6- thyristor. 6- Discuss your results. Please solve No. 4 and 5arrow_forwardPlease I want solution by handwrittenarrow_forward8 00 ! Required information Consider the circuit given below. 0/2 points awarded 3 ΚΩ www t=0 6kM Scored R 1.5i Vc 1 μF 10 V If R = 5.00 kQ, determine vao+). The value of va(0) is 1.4545 V.arrow_forward
 Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning

