
Concept explainers
A cylindrical pressure vessel having a radius r = 14 in. and wall thickness t = 0,5 in, is subjected to internal pressure p = 375 psi, In addition, a torque T = 90 kip-ft acts at each end of the cylinder (see figure),
(a) Determine the maximum tensile stress ctniXand the maximum in-plane shear stress Tmjv in the wall of the cylinder.
(b) If the allowable in-plane shear stress is 4.5 ksi, what is the maximum allowable torque T\
(c) If 7 = 150 kip-ft and allowable in-plane shear and allowable normal stresses are 4.5 ksi and 11.5 ksi, respectively, what is the minimum required wall thickness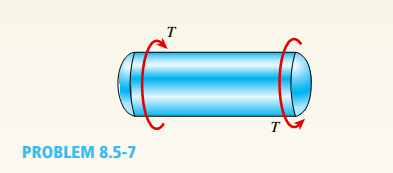
(a)
The maximum tensile stress
Answer to Problem 8.5.7P
The maximum tensile stress is
Explanation of Solution
Given Information:
Type of vessel = cylindrical
Radius =
Internal pressure =
Wall thickness =
Torque =
Concept used:
Where
Calculation:
Use the following relation to find the longitudinal stress.
Here, wall thickness is
Substitute
Use the following relation to find the hoop stress.
Substitute
Use the following relation to find the shear stress.
Here, torque is
Express the value of
Substitute
From equation
Find the maximum stress
Use the following relation to find the principal stresses.
Substitute
Calculate the principal stress,
As
Use the following relation to find the maximum in plane shear stress
Substitute
Hence, the maximum shear stress is
Conclusion
The values are found by the concept of longitudinal stress and hoop stress.
(b)
Maximum torque.
Answer to Problem 8.5.7P
The maximum torque is
Explanation of Solution
Given Information:
Concept used:
Calculation:
Find the maximum torque
Substitute
Conclusion:
The maximum torque is calculated by equating 1p , Tmax, r, etc.
(C)
What is the minimum required wall thickness.
Answer to Problem 8.5.7P
The minimum required wall thickness is
Explanation of Solution
Given Information:
Concept used:
Calculation:
Here, allowable in plane shear stress is
Substitute
Express the value of
Here, assumed
Variable are
Evaluate the value of
Evaluate the value of
Substitute
Substitute the value of
Use the trial and error method to find the thickness
Trial
Substitute
Trial
Substitute
Trial
Substitute
Substitute
Express the allowable in plane shear stress.
Substitute
Substitute
As
Hence, from the trial and error method the minimum wall thickness
Conclusion:
The minimum thickness is calculated by trial and error method.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 8 Solutions
Mechanics of Materials, SI Edition
- Solve this problem and show alll of the workarrow_forwardI need drawing solution,draw each one by one no Aiarrow_forwardQu. 17 Compute linear density values for [100] for silver (Ag). Express your answer in nm''. . Round off the answer to three significant figures. Qu. 18 Compute linear density value for [111] direction for silver (Ag). Express your answer in nm'. Round off the answer to three significant figures. Qu. 19 Compute planar density value for (100) plane for chromium (Cr). Express your answer in nm?. Round off the answer to two significant figures. Qu. 20 Compute planar density value for (110) plane for chromium (Cr). Express your answer in nm ≥ to four significant figures. show all work please in material engineeringarrow_forward
- Large wind turbines with a power capacity of 8 MW and blade span diameters of over 160 m areavailable for electric power generation. Consider a wind turbine with a blade span diameter of 120m installed at a site subjected to steady winds at 8.25 m/s. Taking the overall efficiency of thewind turbine to be 33 percent and the air density to be 1.25 kg/m3, determine the electric powergenerated by this wind turbine. Also, assuming steady winds of 8.25 m/s during a 24-h period,determine the amount of electric energy and the revenue generated per day for a unit price of$0.08/kWh for electricity.arrow_forwardThe basic barometer can be used to measure the height of a building. If the barometric readingsat the top and at the bottom of a building are 672 and 696 mmHg, respectively, determine theheight of the building. Take the densities of air and mercury to be 1.18 kg/m3 and 13,600 kg/m3,respectivelyarrow_forwardA 7.25-hp (shaft) pump is used to raise water to an elevation of 17 m. If the mechanical efficiencyof the pump is 84 percent, determine the maximum volume flow rate of water.arrow_forward
- Consider a double-fluid manometer attached to an air pipe shown below. If the specific gravity ofone fluid is 13.8, determine the specific gravity of the other fluid for the indicated absolutepressure of air. Take the atmospheric pressure to be 95 kPaarrow_forwardA race car enters the circular portion of a track that has a radius of 65 m. Disregard the 70 m in the picture. When the car enters the curve at point P, it is traveling with a speed of 120 km/h that is increasing at 5 m/s^2 . Three seconds later, determine the x and y components of velocity and acceleration of the car. I'm having trouble getting the correct y component of acceleration. all the other answers are correct. thank you!arrow_forwardFigure: 06_P041 Copyright 2013 Pearson Education, publishing a Prentice Hall 2. Determine the force that the jaws J of the metal cutters exert on the smooth cable C if 100-N forces are applied to the handles. The jaws are pinned at E and A, and D and B. There is also a pin at F. 400 mm 15° 20 mm A 15° 15 D B 30 mm² 80 mm 20 mm 400 mm Figure: 06_P090 Copyright 2013 Pearson Education, publishing as Prentice Hall 15° 100 N 100 N 15°arrow_forward
 Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
