
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The drug which has greater partition coefficient is to be stated.
Concept introduction:
The partition coefficient is defined as the ratio of the concentration of the compound in two different solvents. The octanol-water partition coefficient is one of the most used partition coefficients which is the ratio concentration in octanol to the water.
Answer to Problem 8.54AP
The
Explanation of Solution
The structure of the two drugs is shown below.
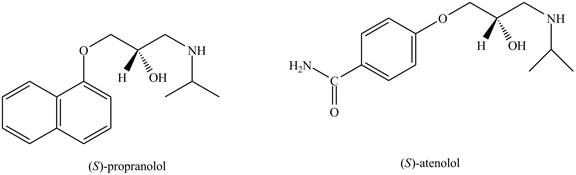
Figure 1
From the structure of two drugs, it is clear that
Therefore, the partition coefficient of
The
(b)
Interpretation:
The concentration of atenolol in each phase is to be stated.
Concept introduction:
The partition coefficient is defined as the ratio of the concentration of the compound in two different solvents. The octanol-water partition coefficient is one of the most used partition coefficients which is the ratio concentration in octanol to the water.
Answer to Problem 8.54AP
The amount of atenolol is
Explanation of Solution
The given value of the logarithm of the partition coefficient is shown below.
Take antilog on both sides to find out value of
The formula of the partition coefficient is shown below.
Substitute the value of
The concentration of drug in octanol is
Since the volume of each phase is given same.
Therefore, the ratio of amount of atenolol in octanol to water is
Assume x to be the ratio constant to find out the amount in each solvent. Therefore, the amount of atenolol in water is x and in octanol is
The sum of both amounts is equal to the total amount.
Therefore the amount of atenolol is
The amount of atenolol is
(c)
Interpretation:
The relative water solubility’s of the crystalline atenolol and propranolol are to be stated.
Concept introduction:
The partition coefficient is defined as the ratio of the concentration of the compound in two different solvents. The octanol-water partition coefficient is one of the most used partition coefficients which is the ratio concentration in octanol to the water.
Answer to Problem 8.54AP
The
Explanation of Solution
From the structure of two drugs, it is clear that
Therefore, the partition coefficient of
That means
The
(d)
Interpretation:
The structure of the conjugated acids of the both drugs is to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
The drugs
Answer to Problem 8.54AP
The structure of the conjugated acids of the both drugs is shown below.
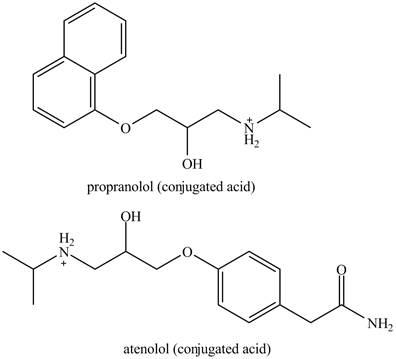
Explanation of Solution
The structure of conjugate acids of both drugs can be made by protonating the amino groups of each drug.
The structures of conjugate acids of each drug are shown below.
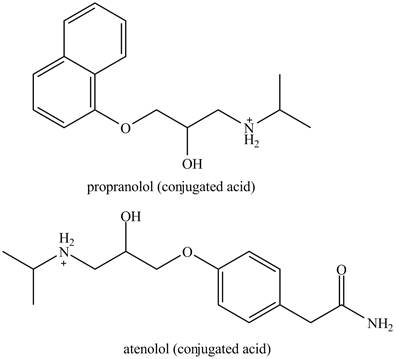
Figure 2
The structure of the conjugated acids of the both drugs is shown in Figure 2.
(e)
Interpretation:
An explanation about the change in the partition coefficient of each drug if it was determined again using water of
Concept introduction:
Answer to Problem 8.54AP
The value of partition coefficient for both the drugs will decrease on using water of
Explanation of Solution
The
This means the polarity of both the drugs will increase due to which their solubility in the water phase will increase. Therefore, the value of partition coefficient for both the drugs will decrease.
The value of partition coefficient for both the drugs will decrease because both the drugs will be present in the conjugated acids form and therefore their solubility in the water will increase.
(f)
Interpretation:
The reason as to why the drugs are formulated in the form of hydrogen chloride instead of using their basic form is to be stated.
Concept introduction:
Answer to Problem 8.54AP
The drugs are generally weak acids and bases and for dissolution or absorption in the body these forms are generally not ideal.
To boost their absorption and dissolution in the body, the drugs are formulated in the form of salts.
Explanation of Solution
The drugs are usually weak acids and bases but these forms are usually not optimal for the dissolution or absorption in the body. Medicines need to be water soluble as well.
The drugs are formulated in the form of the salts in order to increase their absorption and dissolution in the body. The salt forms are more optimal for the dissolution and boost its absorption in the stream of blood.
The drugs used in the form of salts in order to enhance its activity and dissolution in the body.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 8 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
- Please help me with number 5 using my data and graph. I think I might have number 3 and 4 but if possible please check me. Thanks in advance!arrow_forwarddict the major products of this organic reaction. C Explanation Check 90 + 1.0₂ 3 2. (CH3)2S Click and drag f drawing a stru © 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. • 22 4 5 7 8 Y W E R S F H Bilarrow_forwardcan someone draw out the reaction mechanism for this reaction showing all the curly arrows and 2. Draw the GPNA molecule and identify the phenylalanine portion. 3. Draw L-phenylalanine with the correct stereochemistryarrow_forward
- What is the reaction mechanism for this?arrow_forwardPredict the major products of both organic reactions. Be sure to use wedge and dash bonds to show the stereochemistry of the products when it's important, for example to distinguish between two different major products. esc esc Explanation Check 2 : + + X H₁₂O + Х ง WW E R Y qab Ccaps lock shift $ P X Click and drag to start drawing a structure. © 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Center | Accessibility Bil T FR F18 9 G t K L Z X V B N M control opption command command T C darrow_forwardDraw the Markovnikov product of the hydrohalogenation of this alkene. this problem. Note for advanced students: draw only one product, and don't worry about showing any stereochemistry. Drawing dash and wedge bonds has been disabled for caps lock Explanation Check 2 W E R + X 5 HCI Click and drag to start drawing a structure. © 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Center | Accessibility Bil Y F G H K L ZZ X C V B N M control opption command F10 F10 command 4 BA Ar Carrow_forward
- I don't understand why the amide on the top left, with the R attached to one side, doesn't get substituted with OH to form a carboxylic acid. And if only one can be substituted, why did it choose the amide it chose rather than the other amide?arrow_forwardesc Draw the Markovnikov product of the hydration of this alkene. Note for advanced students: draw only one product, and don't worry about showing any stereochemistry. Drawing dash and wedge bonds has been disabled for this problem. Explanation Check BBB + X 0 1. Hg (OAc)2, H₂O 2. Na BH 5 Click and drag to start drawing a structure. © 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Center | Accessibility Bl P 豆 28 2 28 N 9 W E R T Y A S aps lock G H K L Z X C V B N M T central H command #e commandarrow_forwardC A student proposes the transformation below in one step of an organic synthesis. There may be one or more products missing from the right-hand side, but there are no reagents missing from the left-hand side. There may also be catalysts, small inorganic reagents, and other important reaction conditions missing from the arrow. • Is the student's transformation possible? If not, check the box under the drawing area. . If the student's transformation is possible, then complete the reaction by adding any missing products to the right-hand side, and adding required catalysts, inorganic reagents, or other important reaction conditions above and below the arrow. • You do not need to balance the reaction, but be sure every important organic reactant or product is shown. (X) This transformation can't be done in one step. + Tarrow_forward
- く Predict the major products of this organic reaction. If there aren't any products, because nothing will happen, check the box under the drawing area instead. No reaction. Explanation Check OH + + ✓ 2 H₂SO 4 O xs H₂O 2 Click and drag to start drawing a structure. © 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Centerarrow_forwardDraw the skeletal ("line") structure of 1,3-dihydroxy-2-pentanone. Click and drag to start drawing a structure. X Parrow_forwardPredicting edict the major products of this organic reaction. If there aren't any products, because nothing will happen, check the box under the drawing area instead. + No reaction. Explanation Check HO Na O H xs H₂O 2 Click and drag to start drawing a structure. © 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Center Iarrow_forward
 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
