
(Financial tsunami) Banks lend money to each other. In tough economic times, if a bank goes bankrupt, it may not be able to pay back the loan. A bank’s total assets are its current balance plus its loans to other banks. The diagram in Figure 8.8 shows five banks. The banks’ current balances are 25, 125, 175, 75, and 181 million dollars, respectively. The directed edge from node 1 to node 2 indicates that bank I lends 40 million dollars to bank 2.
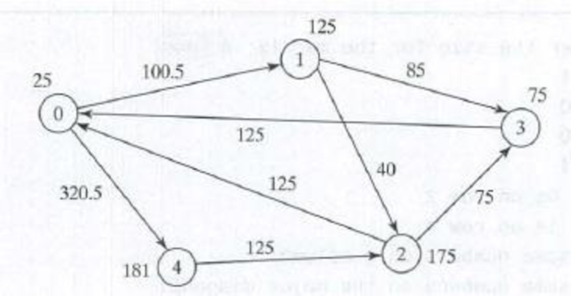
figure 8.8 Banks lend money to each other.
If a bank’s total assets are under a certain Limit, the bank is unsafe. The money it borrowed cannot be returned to the lender, and the lender cannot count the loan in its total assets. Consequently, the lender may also be unsafe, if its total assets are under the Limit. Write a
5 201
25 2 1 100.5 4 320.5
125 2 2 40 3 85
175 2 0 125 3 75
75 1 0 125
181 1 2 125
The total assets of bank 3 are (75 + 125), which is under 201, so bank 3 is unsafe. After bank 3 becomes unsafe, the total assets of bank 1 fall below (125 + 40). Thus, bank 1 is also unsafe. The output of the program should be
Un safe banks are 3 1
(Hint: Use a two-dimensional array borrowers to represent loans. borrowers [i] [j] indicates the loan that bank i provides to bank j . Once bank j becomes unsafe, borrowers[i] [j] should be set to 0.)
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 8 Solutions
Introduction to Java Programming and Data Structures, Comprehensive Version (11th Edition)
Additional Engineering Textbook Solutions
Modern Database Management (12th Edition)
Java: An Introduction to Problem Solving and Programming (7th Edition)
Database Concepts (8th Edition)
Starting Out with Python (4th Edition)
Digital Fundamentals (11th Edition)
Introduction To Programming Using Visual Basic (11th Edition)
- A deck of cards contains 52 cards with four suits: club, diamond, heart and spade ranging in values from 2, ... to 10, Jack, Queen, King and Ace. Ace has the highest value in the same suit. Cards can be compared using their face values. A card with higher face value is bigger than a card with lower face value. If two cards have the same face value, then the suit determines the order. Club is smaller than diamond which is smaller than heart which is smaller than spade. For example: club 2 < diamond 2 < heart 2 < spade 2 if compared.Write an interactive Java program that allows you play cards with a computer. For this project, we are going to focus on one suit of the deck of cards. There are only 13 cards (value: 2, ... to 10, Jack, Queen, King and Ace) in a suit. To play:(a). You first pick a suit at random from the four suits (club, diamond, heart and spade), and display the suit. (b) Then you randomly draw a card from the suit, and let computer draw a card from the same…arrow_forwardA deck of cards contains 52 cards with four suits: club, diamond, heart and spade ranging in values from 2, ... to 10, Jack, Queen, King and Ace. Ace has the highest value in the same suit. Cards can be compared using the face value. A card with higher face value is bigger than a card with lower face value. If two cards have the same face value, then the suit determines the order. Club is smaller than diamond which is smaller than heart which is smaller than spade. For example: club 2 < diamond 2 < heart 2 < spade 2 if compared. Write an interactive Java program that allows a user to randomly pick a card from the deck of 52 cards (using a random number between 1 and 4 to represent the four suits: club, diamond, heart and spade and then another random number to represent the face value) to play. Show the suit and face value of the user card. Then the program acts as a card dealer which randomly draws another card and displays the card (again showing the suit and face value of…arrow_forwardCelebrity problem A celebrity among a group of n people is a person who knows nobody but is known by everybody else. The task is to identify a celebrity by only asking questions to people of the form: ”Do you know him/her?” Solution Select two people from the group given, say, A and B, and ask A whether A knows B. If A knows B, remove A from the remaining people who can be a celebrity; if A doesn’t know B, remove B from this group. Solve the problem recursively for the remaining group of people who can be a celebrity Which design strategy does the following solution use? A-)Decrease-by-a-constant factor algorithm B-)Variable-size-decrease algorithm C-)Decrease-by-a-constant algorithm D-)Divide-and-Conquerarrow_forward
- Python Programing: Sahil is an outstanding entertainer. He is expert in what he does. At a day, he accepted Samir's challenge to plant 20 million trees by 2020. Currently, there are N trees (numbers 1 to N) planted in different places in the row; for each valid I, the location of the i-Ayi tree. A bunch of trees is good if for each tree in this set (let's say its place in x), there is a tree in x - 1 and / or a tree in x + 1. Sahil task is to plant more trees (perhaps zero) in such a way that the effect of all the trees planted (the first N trees and the ones planted by Sahil) is good. It is only allowed to plant trees in complete (perhaps unfavorable) areas. Help Sahil to find the minimum number of trees they need to plant to achieve that using Python Programming. Input: 1 3 538 Output: 3.arrow_forwardExercise # 2 - Detecting Cycle between List of N Airports The following graph is an example from Rosen (2011). It shows the flights and distances between some of the major airports in the United States. Dallas 200 1300 200 Austin Washington Denver 1400 Atlanta 160 800 800 Chicago Houston Write a function that takes a list of N airports and checks if they form a cycle of size N. {A cycle is a directed path that starts and ends at the same vertex. Before writing code, make sure you can identify cycles yourself} >> check_cycles (G, ['Austin','Houston', 'Atlanta','Washington','Dallas'l) Yes >>> check_cycles (G, ['Austin', 'Houston','Atlanta','Washington']) No 600 600 780 0000 000L 006arrow_forward[Fish Tank] You play with a clown fish that has an initial size so. The fish can eat other fish in a tank organized in m columns and n rows. The fish at column i and row j has a positive size si,j. When your fish eats another fish, it grows by that amount. For example, if your clown fish has a size of 10 and eats a fish of size 5, it becomes of size 15. You cannot eat a fish that is bigger than your size. The game starts by eating any fish in the first (left-most) column that is not bigger than yours. After that, you advance one column at a time by moving right. You have only three allowed moves. You either stay at the same row, move one row higher or one row lower. You will always move to the right. Thus, you will make exactly m moves to advance from left to right. Your goal is to exit the fish tank from the right with the biggest possible size. The figure below shows an example with the best answer highlighted. In this case, the final fish size is 71 (10+8+7+24+22). You are required…arrow_forward
- 1. Astronomy Board Game In an astronomy board game, N planets in an imaginary universe do not follow the normal law of gravitation. All the planets are positioned in a row. The planetary system can be in a stable state only if the sum of the mass of all planets at even positions is equal to the sum of the mass of planets at the odd positions. Initially, the system is not stable, but a player can destroy one planet to make it stable. Find the planet that should be destroyed to make the system stable. If no such planet exists, then return -1. If there are multiple such planets, then destroy the planet with the smallest index and return the index of the destroyed planet. Example Let N=5 and planets = [2,4,6,3,4]. Destroying the fourth planet of mass 3 will result in planets= [2,4,6,4], and here, the sum of odd positioned planets is (2+6)=8, and the sum of even positioned planets is (4+4)=8, and both are equal now. Hence, we destroy the fourth planet. Function Description Complete the…arrow_forward22.........a) Write a program that asks the user to enter the number of vertices in a directed graph and then the adjacency matrix representing the directed graph. The program, then, must display the node with the highest outdegree. Assume that nodes are named as 0, 1, 2, and so on.asaparrow_forwardComputer Science In C++ no vectors include int main follow all directionsarrow_forward
- Programming Language :- Carrow_forwardBus Loading Problem. You are in charge of filling busses with passengers at a bus terminal. Each bus has space for ten (10) passengers. Four (4) of those spaces can hold only wheelchair passengers, and the other six (6) can hold only non-wheelchair passengers. Busses and both types of passengers arrive at random. As busses arrive, you are to fill them up with passengers. Once a bus is full (containing 6 non-wheelchair, and 4 wheelchair passengers), it is allowed to leave the terminal, along with its passengers. You are responsible only for loading the passengers on the bus and having the bus depart. You do not need to worry about what happens to the busses or passengers after they leave. Each bus process has available to it the functions ArriveAtTerminal(), OpenDoors(), CloseDoors(), and DepartTerminal(). Each passenger process has available to it the functions ArriveAtTerminal() and GetOnBus(). Executing GetOnBus() loads the passenger on the bus, and the function returns when the…arrow_forwardCorrect answer will be upvoted else downvoted. Computer science. In each progression you pick some integer k>0, take the top k cards from the first deck and submit them, in the request they are presently, on top of the new deck. You play out this activity until the first deck is vacant. (Allude to the notes area for the better arrangement.) We should characterize a request for a deck as ∑i=1nnn−i⋅pi. Given the first deck, output the deck with greatest conceivable request you can make utilizing the activity above. Input The main line contains a solitary integer t (1≤t≤1000) — the number of experiments. The principal line of each experiment contains the single integer n (1≤n≤105) — the size of deck you have. The subsequent line contains n integers p1,p2,… ,pn (1≤pi≤n; pi≠pj if i≠j) — upsides of card in the deck from base to top. It's dependable that the amount of n over all experiments doesn't surpass 105. Output For each experiment print the deck with…arrow_forward
 C++ for Engineers and ScientistsComputer ScienceISBN:9781133187844Author:Bronson, Gary J.Publisher:Course Technology Ptr
C++ for Engineers and ScientistsComputer ScienceISBN:9781133187844Author:Bronson, Gary J.Publisher:Course Technology Ptr
