
University Physics Volume 1
18th Edition
ISBN: 9781938168277
Author: William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff Sanny
Publisher: OpenStax - Rice University
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 8, Problem 72AP
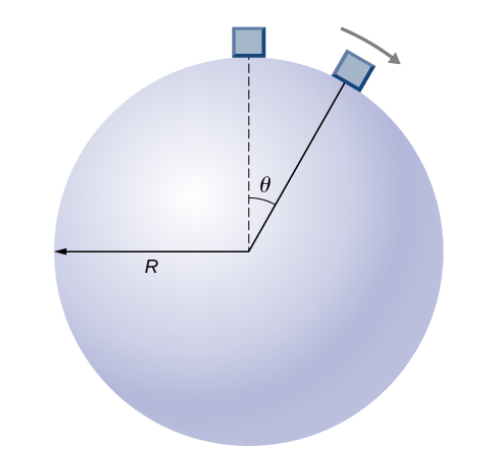
A body of mass m and negligible size starts from rest and slides down the surface of a frictionless solid sphere of radius
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
The force of the quadriceps (Fq) and force of the patellar tendon (Fp) is identical (i.e., 1000 N each). In the figure below angle in blue is Θ and the in green is half Θ (i.e., Θ/2). A) Calculate the patellar reaction force (i.e., R resultant vector is the sum of the horizontal component of the quadriceps and patellar tendon force) at the following joint angles: you need to provide a diagram showing the vector and its components for each part. a1) Θ = 160 degrees, a2) Θ = 90 degrees. NOTE: USE ONLY TRIGNOMETRIC FUNCTIONS (SIN/TAN/COS, NO LAW OF COSINES, NO COMPLICATED ALGEBRAIC EQUATIONS OR ANYTHING ELSE, ETC. Question A has 2 parts!
The force of the quadriceps (Fq) and force of the patellar tendon (Fp) is identical (i.e., 1000 N each). In the figure below angle in blue is Θ and the in green is half Θ (i.e., Θ/2). A) Calculate the patellar reaction force (i.e., R resultant vector is the sum of the horizontal component of the quadriceps and patellar tendon force) at the following joint angles: you need to provide a diagram showing the vector and its components for each part. a1) Θ = 160 degrees, a2) Θ = 90 degrees. NOTE: USE DO NOT USE LAW OF COSINES, NO COMPLICATED ALGEBRAIC EQUATIONS OR ANYTHING ELSE, ETC. Question A has 2 parts!
No chatgpt pls will upvote
Chapter 8 Solutions
University Physics Volume 1
Ch. 8 - Check Your understanding In Example 8.1 what are...Ch. 8 - Check Your Understanding What are the values of...Ch. 8 - Check Your Understanding When the length of the...Ch. 8 - Check Your Understanding Suppose the mass in...Ch. 8 - Check Your Understanding A two-dimensional,...Ch. 8 - Check Your Understanding Fend the forces on the...Ch. 8 - Check Your Understanding How high above the bottom...Ch. 8 - Check Your Understanding You probably recall that,...Ch. 8 - Check Your Understanding What potential energy...Ch. 8 - Check Your Understanding Repeat Example 8.10 when...
Ch. 8 - Check Your Understanding Find x(t) for the...Ch. 8 - The kinetic energy of a system must always be...Ch. 8 - The force exerted by a diving board is...Ch. 8 - Describe the gravitational potential energy...Ch. 8 - A couple of soccer balls of equal mass are kiched...Ch. 8 - What is the dominant factor that affects the speed...Ch. 8 - Two people observe a leaf falling from a tree. One...Ch. 8 - What is the physical meaning of a non-conservative...Ch. 8 - A bottle rocket is shot straight up in the air...Ch. 8 - An external force acts on a particle during a trip...Ch. 8 - When a body slides down an inclined plane, does...Ch. 8 - Consider the following scenario. A car for which...Ch. 8 - A dropped ball bounces to one-half its original...Ch. 8 - “ E=K+Uconstant is a special case of the work...Ch. 8 - In a common physics demonstration, a bowling ball...Ch. 8 - A child jumps tip and down on a bed, reaching a...Ch. 8 - Can a non-conservative force increase the...Ch. 8 - Neglecting air resistance, how much would I have...Ch. 8 - A box is dropped onto a spring at its equilibrium...Ch. 8 - Using values from Table 8.1, how many DNA...Ch. 8 - If the energy in fusion bombs were used to supply...Ch. 8 - A camera weighing 10 N falls from a small drone...Ch. 8 - Someone drops a 50 — g pebble off of a docked...Ch. 8 - A cat’s crinkle ball toy of mass 15 g is thrown...Ch. 8 - A force F(x)=(3.0/x)N acts on a particle as it...Ch. 8 - A force F(x)=(5.0x2+7.0x)N acts on a particle as...Ch. 8 - Find the force corresponding to the potential...Ch. 8 - The potential energy function for either one of...Ch. 8 - A particle of mass 2.0 kg moves under the...Ch. 8 - A particle of mass 2.0 kg moves under the...Ch. 8 - A crate on rollers is being pushed without...Ch. 8 - A boy throws a ball of mass 0.25 kg straight...Ch. 8 - A mouse of mass 200 g falls 100 m down a vertical...Ch. 8 - Using energy considerations and assuming...Ch. 8 - A 1.0-kg ball at the end of a 2.0-m string swings...Ch. 8 - Ignoring details associated with friction, extra...Ch. 8 - Tarzan grabs a vine hanging vertically from a tall...Ch. 8 - Assume that the force of a bow on an arrow behaves...Ch. 8 - A 100 — kg man is skiing across level ground at a...Ch. 8 - A sled of mass 70 kg starts from rest and slides...Ch. 8 - A girl on a skateboard (total mass of 40 kg) is...Ch. 8 - A baseball of mass 0.25 kg is hit at home plate...Ch. 8 - A small block of mass in slides without friction...Ch. 8 - The massless spring of a spring gun has a force...Ch. 8 - A small ball is tied to a string and set rotating...Ch. 8 - A mysterious constant force of 10 N acts...Ch. 8 - A single force F(x)=4.0x (in newtons) acts on a...Ch. 8 - A particle of mass 4.0 kg is constrained to move...Ch. 8 - The force on a particle of mass 2.0 kg varies with...Ch. 8 - A 4.0-kg particle moving along the x -axis is...Ch. 8 - A particle of mass 0.50 kg moves along the x -axis...Ch. 8 - (a) Sketch a graph of the potential energy...Ch. 8 - In the cartoon movie Pocahontas...Ch. 8 - In the reality television show “Amazing Race”...Ch. 8 - In the Back to the Future movies...Ch. 8 - In the Hunger Games movie...Ch. 8 - In a “Top Fail” video...Ch. 8 - In a Coyote/Road Runner cartoon clip...Ch. 8 - In an iconic movie scene, Forrest Gump...Ch. 8 - In the movie Monty Python and the Holy Grail...Ch. 8 - A 60.0-kg skier with an initial speed of 12.0 m/s...Ch. 8 - (a) How high a hill can a car coast up (engines...Ch. 8 - A 5.00105kg subway train is brought to a stop from...Ch. 8 - A pogo stick has a spring with a spring constant...Ch. 8 - A block of mass 500 g is attached to a spring of...Ch. 8 - A block of mass 200 g is attached at the end of a...Ch. 8 - A T-shirt cannon launches a shirt at 5.00 m/s from...Ch. 8 - A child (32 kg) jumps up and down on a trampoline....Ch. 8 - Shown below is a box of mass m1 that sits on a...Ch. 8 - A massless spring with force constant k=200N/m...Ch. 8 - A particle of mass 2.0 kg moves under the...Ch. 8 - Block 2 shown below slides along a frictionless...Ch. 8 - A body of mass m and negligible size starts from...Ch. 8 - A mysterious force acts on all particles along a...Ch. 8 - An object of mass 10 kg is released at point A,...Ch. 8 - Shown below is a small ball of mass m attached to...Ch. 8 - A block leaves a frictionless inclined surface...Ch. 8 - A block of mass m, after sliding down a...Ch. 8 - A block of mass 300 g is attached to a spring of...Ch. 8 - Consider a block of mass 0.200 kg attached to a...Ch. 8 - A skier starts from rest and slides downhill. What...Ch. 8 - Repeat the preceding problem, but this time,...Ch. 8 - Two bodies are interacting by a conservative force...Ch. 8 - In an amusement park, a car rolls in a track as...Ch. 8 - A 200-g steel ball is tied to a 2.00m “massless”...Ch. 8 - A 300 g hockey puck is shot across an ice-covered...Ch. 8 - A projectile of mass 2 kg is fired with a speed of...Ch. 8 - An artillery shell is fired at a target 200 m...Ch. 8 - How much energy is lost to a dissipative drag...Ch. 8 - A box slides on a frictionless surface with a...
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
Determine [OH], [H+], and the pH of each of the following solutions. a. 1.0 M KCl b. 1.0 M KC2H3O2
Chemistry
Based on your answers to Questions 2 and 3, which part of the Atlantic basin appears to have opened first?
Applications and Investigations in Earth Science (9th Edition)
Use the key to classify each of the following described tissue types into one of the four major tissue categori...
Anatomy & Physiology (6th Edition)
Use the following graph to answer questions 3 and 4. 3. Which of the lines best depicts the log phase of a ther...
Microbiology: An Introduction
All of the following terms can appropriately describe humans except: a. primary consumer b. autotroph c. hetero...
Human Biology: Concepts and Current Issues (8th Edition)
The indication about energy by first and second law of thermodynamics needs to be described. Concept introducti...
Living By Chemistry: First Edition Textbook
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- The force of the quadriceps (Fq) and force of the patellar tendon (Fp) is identical (i.e., 1000 N each). In the figure below angle in blue is Θ and the in green is half Θ (i.e., Θ/2). A) Calculate the patellar reaction force (i.e., R resultant vector is the sum of the horizontal component of the quadriceps and patellar tendon force) at the following joint angles: you need to provide a diagram showing the vector and its components for each part. a1) Θ = 160 degrees, a2) Θ = 90 degrees. NOTE: USE ONLY TRIGNOMETRIC FUNCTIONS (SIN/TAN/COS, NO LAW OF COSINES, NO COMPLICATED ALGEBRAIC EQUATIONS OR ANYTHING ELSE, ETC. Question A has 2 parts!arrow_forwardNo chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forwardNo chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forward
- Solve and answer the question correctly please. Thank you!!arrow_forward་ The position of a particle is described by r = (300e 0.5t) mm and 0 = (0.3t²) rad, where t is in seconds. Part A Determine the magnitude of the particle's velocity at the instant t = 1.5 s. Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. v = Value Submit Request Answer Part B ? Units Determine the magnitude of the particle's acceleration at the instant t = 1.5 s. Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. a = Value A ? Unitsarrow_forwardSolve and answer the question correctly please. Thank you!!arrow_forward
- Solve and answer the question correctly please. Thank you!!arrow_forwardA spiral transition curve is used on railroads to connect a straight portion of the track with a curved portion. (Figure 1) Part A v = v₁ft/s 600 ft y = (106) x³ If the spiral is defined by the equation y = (106)³, where x and y are in feet, determine the magnitude of the acceleration of a train engine moving with a constant speed of v₁ = 30 ft/s when it is at point x = 600 ft. Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. ? a = Value Unitsarrow_forwardsolve and answer the problem correctly please. Thank you!!arrow_forward
- Solve and answer the question correctly please. Thank you!!arrow_forwardSolve and answer the question correctly please. Thank you!!arrow_forwardWhen the motorcyclist is at A, he increases his speed along the vertical circular path at the rate of = (0.3t) ft/s², where t is in seconds. Take p = 360 ft. (Figure 1) Part A 60° Ρ B If he starts from rest at A, determine the magnitude of his velocity when he reaches B. Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. v = Value Submit Request Answer ་ Part B ? Units If he starts from rest at A, determine the magnitude of his acceleration when he reaches B. Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. 11 ? a = Value Unitsarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University
University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University Classical Dynamics of Particles and SystemsPhysicsISBN:9780534408961Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. MarionPublisher:Cengage Learning
Classical Dynamics of Particles and SystemsPhysicsISBN:9780534408961Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. MarionPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9781938168284Author:Andrew Fraknoi; David Morrison; Sidney C. WolffPublisher:OpenStax
AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9781938168284Author:Andrew Fraknoi; David Morrison; Sidney C. WolffPublisher:OpenStax Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics Volume 1
Physics
ISBN:9781938168277
Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:OpenStax - Rice University

Classical Dynamics of Particles and Systems
Physics
ISBN:9780534408961
Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. Marion
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:9781133104261
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9781938168284
Author:Andrew Fraknoi; David Morrison; Sidney C. Wolff
Publisher:OpenStax

Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...
Physics
ISBN:9781337553292
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning
8.01x - Lect 11 - Work, Kinetic & Potential Energy, Gravitation, Conservative Forces; Author: Lectures by Walter Lewin. They will make you ♥ Physics.;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=9gUdDM6LZGo;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY