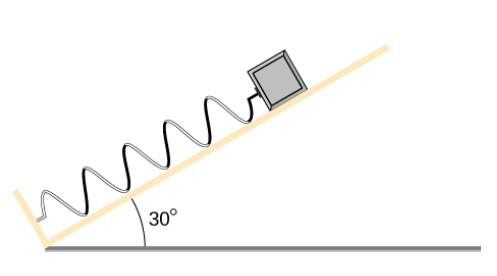
Problem 8.1CYU: Check Your understanding In Example 8.1 what are the potential energies of the particle at x=1 m and... Problem 8.2CYU: Check Your Understanding What are the values of the gravitational potential energy of the hiker at... Problem 8.3CYU: Check Your Understanding When the length of the spring in Example 8.3 changes from an initial value... Problem 8.4CYU: Check Your Understanding Suppose the mass in Equation 8.6 is doubled while keeping the all other... Problem 8.5CYU: Check Your Understanding A two-dimensional, conservative force is zero on the x- and y-axes, and... Problem 8.6CYU: Check Your Understanding Fend the forces on the particle in Example 8.6 when kinetic energy is 1.0 J... Problem 8.7CYU: Check Your Understanding How high above the bottom of its arc is the particle in the simple pendulum... Problem 8.8CYU: Check Your Understanding You probably recall that, neglecting air resistance, if you throw a... Problem 8.9CYU: Check Your Understanding What potential energy U(x) can you substitute in Equation 8.13 that will... Problem 8.10CYU: Check Your Understanding Repeat Example 8.10 when the particle’s mechanical energy is +0.25 J. Problem 8.11CYU: Check Your Understanding Find x(t) for the mass-spring system in Example 8.11 ii the particle starts... Problem 1CQ: The kinetic energy of a system must always be positive or zero. Explain whether this is true for the... Problem 2CQ: The force exerted by a diving board is conservative, provided the internal friction is negligible.... Problem 3CQ: Describe the gravitational potential energy transfers and transformations for a javelin, starting... Problem 4CQ: A couple of soccer balls of equal mass are kiched off the ground at the same speed but at different... Problem 5CQ: What is the dominant factor that affects the speed of an object that started from rest down a... Problem 6CQ: Two people observe a leaf falling from a tree. One person is standing on a ladder and the other is... Problem 7CQ: What is the physical meaning of a non-conservative force? Problem 8CQ: A bottle rocket is shot straight up in the air with a speed 30 m/s. if the air resistance is... Problem 9CQ: An external force acts on a particle during a trip from one point to another and back to that same... Problem 10CQ: When a body slides down an inclined plane, does the work of friction depend on the body’s initial... Problem 11CQ: Consider the following scenario. A car for which friction is not negligible accelerates from rest... Problem 12CQ: A dropped ball bounces to one-half its original height. Discuss the energy transformations that take... Problem 13CQ: “ E=K+Uconstant is a special case of the work energy theorem.” Discuss this statement. Problem 14CQ: In a common physics demonstration, a bowling ball is suspended from the ceiling by a rope. The... Problem 15CQ: A child jumps tip and down on a bed, reaching a higher height after each bounce. Explain how the... Problem 16CQ: Can a non-conservative force increase the mechanical energy of the system? Problem 17CQ: Neglecting air resistance, how much would I have to raise the vertical height if I wanted to double... Problem 18CQ: A box is dropped onto a spring at its equilibrium position. The spring compresses with the box... Problem 19P: Using values from Table 8.1, how many DNA molecules could be broken by the energy carried by a... Problem 20P: If the energy in fusion bombs were used to supply the energy needs of the world, how many of the... Problem 21P: A camera weighing 10 N falls from a small drone hovering 20 m overhead and enters free fall. What is... Problem 22P: Someone drops a 50 — g pebble off of a docked cruise ship, 70.0 m from the water line. A person on a... Problem 23P: A cat’s crinkle ball toy of mass 15 g is thrown straight up with an initial speed of 3 m/s. Assume... Problem 24P: A force F(x)=(3.0/x)N acts on a particle as it moves along the positive x-axis. (a) How much work... Problem 25P: A force F(x)=(5.0x2+7.0x)N acts on a particle as it moves along the positive x-axis. (a)How much... Problem 26P: Find the force corresponding to the potential energy U(x)=a/x=b/x2. Problem 27P: The potential energy function for either one of the two atoms in a diatomic molecule is often... Problem 28P: A particle of mass 2.0 kg moves under the influence of the force F(x)=(3/x)N. If its speed at x=2.0... Problem 29P: A particle of mass 2.0 kg moves under the influence of the force F(x)=(5x2=7x)N. If its speed at... Problem 30P: A crate on rollers is being pushed without frictional loss of energy across the floor of a freight... Problem 31P: A boy throws a ball of mass 0.25 kg straight upward with an initial speed of 20 m/s When the ball... Problem 32P: A mouse of mass 200 g falls 100 m down a vertical mine shaft and lands at the bottom with a speed of... Problem 33P: Using energy considerations and assuming negligible air resistance, show that a rock thrown from a... Problem 34P: A 1.0-kg ball at the end of a 2.0-m string swings in a vertical plane. At its lowest point the ball... Problem 35P: Ignoring details associated with friction, extra forces exerted by arm and leg muscles, and other... Problem 36P: Tarzan grabs a vine hanging vertically from a tall tree when he is running at 9.0 m/s. (a) How high... Problem 37P: Assume that the force of a bow on an arrow behaves like the spring force. In aiming the arrow, an... Problem 38P: A 100 — kg man is skiing across level ground at a speed of 8.0 m/s when he comes to the small slope... Problem 39P: A sled of mass 70 kg starts from rest and slides down a 10 incline 80 m long. It then travels for 20... Problem 40P: A girl on a skateboard (total mass of 40 kg) is moving at a speed of 10 m/s at the bottom of a long... Problem 41P: A baseball of mass 0.25 kg is hit at home plate with a speed of 40 m/s. When it lands in a seat in... Problem 42P: A small block of mass in slides without friction around the loop-the-loop apparatus shown below .... Problem 43P: The massless spring of a spring gun has a force constant k=12N/cm . When the gun is aimed... Problem 44P: A small ball is tied to a string and set rotating with negligible friction in a vertical circle.... Problem 45P: A mysterious constant force of 10 N acts horizontally on everything. The direction of the force is... Problem 46P: A single force F(x)=4.0x (in newtons) acts on a 1.0-kg body. When x=3.5 m, the speed of the body is... Problem 47P: A particle of mass 4.0 kg is constrained to move along the x -axis under a single force F(x)=cx3 ,... Problem 48P: The force on a particle of mass 2.0 kg varies with position according to F(x)=3.0x2 (x in meters,... Problem 49P: A 4.0-kg particle moving along the x -axis is acted upon by the force whose functional form appears... Problem 50P: A particle of mass 0.50 kg moves along the x -axis with a potential energy whose dependence on x is... Problem 51P: (a) Sketch a graph of the potential energy function U(x)=kx2/2+Aex2 where k , A, and are constants.... Problem 52P: In the cartoon movie Pocahontas (https://openstaxcollege.org/I/2lpocahontclip) Pocahontas runs to... Problem 53P: In the reality television show “Amazing Race” (https://openstaxcollege.org/l/2lamazraceclip), a... Problem 54P: In the Back to the Future movies (https://openstaxcollege.org/l/2lbactofutclip), a DeLorean car of... Problem 55P: In the Hunger Games movie (https://openstaxcollege.org/l/21HungGamesclip), Katniss Everdeen fires a... Problem 56P: In a “Top Fail” video (https://openstaxcollege.org/l/21topfailvideo), two women run at each other... Problem 57P: In a Coyote/Road Runner cartoon clip (https://openstaxcollege.org/l/21coyroadcarcl), a spring... Problem 58P: In an iconic movie scene, Forrest Gump (https://openstaxcollege.org/l/21ForrGumpvid) runs around the... Problem 59P: In the movie Monty Python and the Holy Grail (https://openstaxcollege. org/l/21monpytmovcl) a cow is... Problem 60P: A 60.0-kg skier with an initial speed of 12.0 m/s coasts up a 2.50-m high rise as shown. Find her... Problem 61P: (a) How high a hill can a car coast up (engines disengaged) if work done by friction is negligible... Problem 62P: A 5.00105kg subway train is brought to a stop from a speed of 0.500 m/s in 0.400 m by a large spring... Problem 63P: A pogo stick has a spring with a spring constant of 2.5104N/m , which can be compressed 12.0 cm. To... Problem 64P: A block of mass 500 g is attached to a spring of spring constant 80 N/m (see the following figure).... Problem 65P: A block of mass 200 g is attached at the end of a massless spring of spring constant 50 N/m. The... Problem 66P: A T-shirt cannon launches a shirt at 5.00 m/s from a platform height of 3.00 m from ground level.... Problem 67P: A child (32 kg) jumps up and down on a trampoline. The trampoline exerts a spring restoring force on... Problem 68P: Shown below is a box of mass m1 that sits on a frictionless incline at an angle above the horizontal... Problem 69AP: A massless spring with force constant k=200N/m hangs from the ceiling. A 2.0-kg block is attached to... Problem 70AP: A particle of mass 2.0 kg moves under the influence of the force F(x)=(5x2=7x)N . Suppose a... Problem 71AP: Block 2 shown below slides along a frictionless table as block 1 falls. Both blocks are attached by... Problem 72AP: A body of mass m and negligible size starts from rest and slides down the surface of a frictionless... Problem 73AP: A mysterious force acts on all particles along a particular line and always points towards a... Problem 74AP: An object of mass 10 kg is released at point A, slides to the bottom of the 30 incline, then... Problem 75AP: Shown below is a small ball of mass m attached to a string of length a. A small peg is located a... Problem 76AP: A block leaves a frictionless inclined surface horizontally after dropping off by a height h. Find... Problem 77AP: A block of mass m, after sliding down a frictionless incline, strikes another block of mass M that... Problem 78AP: A block of mass 300 g is attached to a spring of spring constant 100 N/m. The other end of the... Problem 79AP: Consider a block of mass 0.200 kg attached to a spring of spring constant 100 N/m. The block is... Problem 80AP: A skier starts from rest and slides downhill. What will be the speed of the skier if he drops by 20... Problem 81AP: Repeat the preceding problem, but this time, suppose that the work done by air resistance cannot be... Problem 82AP: Two bodies are interacting by a conservative force Show that the mechanical energy of an isolated... Problem 83AP: In an amusement park, a car rolls in a track as shown below. Find the speed of the car at A, B, and... Problem 84AP: A 200-g steel ball is tied to a 2.00m “massless” string and hung from the ceiling to make a... Problem 85AP: A 300 g hockey puck is shot across an ice-covered pond. Before the hockey puck was hit, the puck was... Problem 86AP: A projectile of mass 2 kg is fired with a speed of 20 m/s at an angle of 30 with respect to the... Problem 87AP: An artillery shell is fired at a target 200 m above the ground. When the shell is 100 m in the air,... Problem 88AP: How much energy is lost to a dissipative drag force if a 60-kg person falls at a constant speed for... Problem 89AP: A box slides on a frictionless surface with a total energy of 50 J. It hits a spring and compresses... format_list_bulleted


 Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University
University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning




