
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: A Strategic Approach with Modern Physics, Books a la Carte Edition; Student Workbook for Physics for Scientists ... eText -- ValuePack Access Card (4th Edition)
4th Edition
ISBN: 9780134564234
Author: Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus)
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 8, Problem 70EAP
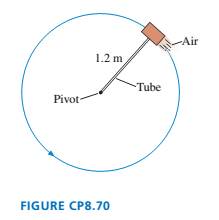
A 500 g steel block rotates on a steel table while attached to a 1.2-m-long hollow tube as shown in FIGURE CP8.70. Compressed air fed through the tube and ejected from a nozzle on the back of the block exerts a thrust force of 4.0 N perpendicular to the tube.
The maximum tension the tube can withstand without breaking is 50 N. If the block starts from rest, how many revolutions does it make before the tube breaks?
Expert Solution & Answer
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Students have asked these similar questions
Please solve and answer this problem correctly please. Thank you!!
a) Use the node-voltage method to find v1, v2, and
v3 in the circuit in Fig. P4.14.
b) How much power does the 40 V voltage source
deliver to the circuit?
Figure P4.14
302
202
w
w
+
+
+
40 V
V1
80 Ω 02
ΣΑΩ
28 A
V3 +
w
w
102
202
Please solve and answer this problem correctly please. Thank you!!
Chapter 8 Solutions
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: A Strategic Approach with Modern Physics, Books a la Carte Edition; Student Workbook for Physics for Scientists ... eText -- ValuePack Access Card (4th Edition)
Ch. 8 - In uniform circular motion, which of the following...Ch. 8 - A car runs out of gas while driving down a hill....Ch. 8 - FIGURE Q8.3 is a bird's-eye view of particles on...Ch. 8 - Tarzan swings through the jungle on a massless...Ch. 8 - FIGURE Q8.5 shows two balls of equal mass moving...Ch. 8 - Ramon and Sally are observing a toy car speed up...Ch. 8 - A jet plane is flying on a level course at...Ch. 8 - A small projectile is launched parallel to the...Ch. 8 - 9. You can swing a ball on a string in a vertical...Ch. 8 - A golfer starts with the club over her head and...
Ch. 8 - As a science fair project, you want to launch an...Ch. 8 - A 500 g model rocket is on a cart that is rolling...Ch. 8 - A 4.0 × 1010 kg asteroid is heading directly...Ch. 8 - A 55 kg astronaut who weighs 180 N on a distant...Ch. 8 - A 1500 kg car drives around a flat 200-m-diameter...Ch. 8 - A 1500 kg car takes a 50-m-radius unbanked curve...Ch. 8 - A 200 g block on a 50-cm-long string swings in a...Ch. 8 - In the Bohr model of the hydrogen atom, an...Ch. 8 - Suppose the moon were held in its orbit not by...Ch. 8 - 10. A highway curve of radius 500 m is designed...Ch. 8 - It is proposed that future space stations create...Ch. 8 - A 5.0 g coin is placed 15 cm from the center of a...Ch. 8 - Mass m1on the frictionless table of FIGURE EX8.13...Ch. 8 - A satellite orbiting the moon very near the...Ch. 8 - What is free-fall acceleration toward the sun at...Ch. 8 - 16. A 9.4 × 1021 kg moon orbits a distant planet...Ch. 8 - Communications satellites are placed in circular...Ch. 8 - A car drives over the top of a hill that has a...Ch. 8 - The weight of passengers on a roller coaster...Ch. 8 - A roller coaster car crosses the top of a circular...Ch. 8 - The normal force equals the magnitude of the...Ch. 8 - A student has 65-cm-long arms. What is the minimum...Ch. 8 - While at the county fair, you decide to ride the...Ch. 8 - A 500 g ball swings in a vertical circle at the...Ch. 8 - A 500 g ball moves in a vertical circle on a...Ch. 8 - A heavy ball with a weight of 100 N (m = 10.2 kg)...Ch. 8 - A toy train rolls around a horizontal...Ch. 8 - 28. A new car is tested on a 200-m-diameter track....Ch. 8 - An 85,000 kg stunt plane performs a loop-the-loop,...Ch. 8 - Three cars are driving at 25 m/s along the road...Ch. 8 - Derive Equations 8.3 for the acceleration of a...Ch. 8 - 32. A 100 g bead slides along a frictionless wire...Ch. 8 - 33. Space scientists have a large test chamber...Ch. 8 - 34. A 5000 kg interceptor rocket is launched at an...Ch. 8 - Prob. 35EAPCh. 8 - 36. A rocket- powered hockey puck has a thrust of...Ch. 8 - Prob. 37EAPCh. 8 - A 2.0 kg projectile with initial velocity m/s...Ch. 8 - A 75 kg man weighs himself at the north pole and...Ch. 8 - A concrete highway curve of radius 70 m banked at...Ch. 8 - a. an object of mass m swings in horizontal circle...Ch. 8 -
42. You’ve taken your neighbor’s young child to...Ch. 8 - A 4.4-cm-diameter, 24 g plastic ball is attached...Ch. 8 - A charged particle of mass m moving with speed v...Ch. 8 - Two wires are tied to the 2.0 kg sphere shown in...Ch. 8 - Two wires are tied to the 300 g sphere shown in...Ch. 8 - A conical pendulum is formed by attaching a ball...Ch. 8 - The 10 mg bead in FIGURE P8.48 is free to slide on...Ch. 8 - In an old-fashioned amusement park ride,...Ch. 8 - The ultracentrifuge is an important tool for...Ch. 8 - In an amusement park ride called The Roundup,...Ch. 8 - 52. Suppose you swing a ball of mass m in a...Ch. 8 - A 30 g ball rolls around a 40-cm-diameter L-shaped...Ch. 8 - FIGURE P8.54 shows a small block of mass m sliding...Ch. 8 - The physics of circular motion sets an upper limit...Ch. 8 - A 100 g ball on a 60-cm-long string is swung in a...Ch. 8 - A 60 g ball is tied to the end of a 50-cm-long...Ch. 8 - Elm Street has a pronounced dip at the bottom of a...Ch. 8 - 59. A 100 g ball on a 60-cm-long string is swung...Ch. 8 - Scientists design a new particle accelerator in...Ch. 8 - 61. A 1500 kg car starts from rest and drives...Ch. 8 - Prob. 62EAPCh. 8 - 63. A 2.0 kg ball swings in a vertical circle on...Ch. 8 - In Problems 64 and 65 you are given the equation...Ch. 8 - In Problems 64 and 65 you are given the equation...Ch. 8 - Sam (75 kg) takes off up a 50-m-high, 10°...Ch. 8 - In the absence of air resistance, a projectile...Ch. 8 - The father of Example 8.2 stands at the summit of...Ch. 8 - A small bead slides around a horizontal circle at...Ch. 8 - A 500 g steel block rotates on a steel table while...Ch. 8 - If a vertical cylinder of water (or any other...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- You're on an interplanetary mission, in an orbit around the Sun. Suppose you make a maneuver that brings your perihelion in closer to the Sun but leaves your aphelion unchanged. Then you must have Question 2 options: sped up at perihelion sped up at aphelion slowed down at perihelion slowed down at aphelionarrow_forwardThe force of the quadriceps (Fq) and force of the patellar tendon (Fp) is identical (i.e., 1000 N each). In the figure below angle in blue is Θ and the in green is half Θ (i.e., Θ/2). A) Calculate the patellar reaction force (i.e., R resultant vector is the sum of the horizontal component of the quadriceps and patellar tendon force) at the following joint angles: you need to provide a diagram showing the vector and its components for each part. a1) Θ = 160 degrees, a2) Θ = 90 degrees. NOTE: USE ONLY TRIGNOMETRIC FUNCTIONS (SIN/TAN/COS, NO LAW OF COSINES, NO COMPLICATED ALGEBRAIC EQUATIONS OR ANYTHING ELSE, ETC. Question A has 2 parts!arrow_forwardThe force of the quadriceps (Fq) and force of the patellar tendon (Fp) is identical (i.e., 1000 N each). In the figure below angle in blue is Θ and the in green is half Θ (i.e., Θ/2). A) Calculate the patellar reaction force (i.e., R resultant vector is the sum of the horizontal component of the quadriceps and patellar tendon force) at the following joint angles: you need to provide a diagram showing the vector and its components for each part. a1) Θ = 160 degrees, a2) Θ = 90 degrees. NOTE: USE DO NOT USE LAW OF COSINES, NO COMPLICATED ALGEBRAIC EQUATIONS OR ANYTHING ELSE, ETC. Question A has 2 parts!arrow_forward
- No chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forwardThe force of the quadriceps (Fq) and force of the patellar tendon (Fp) is identical (i.e., 1000 N each). In the figure below angle in blue is Θ and the in green is half Θ (i.e., Θ/2). A) Calculate the patellar reaction force (i.e., R resultant vector is the sum of the horizontal component of the quadriceps and patellar tendon force) at the following joint angles: you need to provide a diagram showing the vector and its components for each part. a1) Θ = 160 degrees, a2) Θ = 90 degrees. NOTE: USE ONLY TRIGNOMETRIC FUNCTIONS (SIN/TAN/COS, NO LAW OF COSINES, NO COMPLICATED ALGEBRAIC EQUATIONS OR ANYTHING ELSE, ETC. Question A has 2 parts!arrow_forwardNo chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forward
- No chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forwardSolve and answer the question correctly please. Thank you!!arrow_forward་ The position of a particle is described by r = (300e 0.5t) mm and 0 = (0.3t²) rad, where t is in seconds. Part A Determine the magnitude of the particle's velocity at the instant t = 1.5 s. Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. v = Value Submit Request Answer Part B ? Units Determine the magnitude of the particle's acceleration at the instant t = 1.5 s. Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. a = Value A ? Unitsarrow_forward
- Solve and answer the question correctly please. Thank you!!arrow_forwardSolve and answer the question correctly please. Thank you!!arrow_forwardA spiral transition curve is used on railroads to connect a straight portion of the track with a curved portion. (Figure 1) Part A v = v₁ft/s 600 ft y = (106) x³ If the spiral is defined by the equation y = (106)³, where x and y are in feet, determine the magnitude of the acceleration of a train engine moving with a constant speed of v₁ = 30 ft/s when it is at point x = 600 ft. Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. ? a = Value Unitsarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University
University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:9781133104261
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics Volume 1
Physics
ISBN:9781938168277
Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:OpenStax - Rice University

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...
Physics
ISBN:9781133939146
Author:Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781285737027
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781938168000
Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger Hinrichs
Publisher:OpenStax College

Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...
Physics
ISBN:9780078807213
Author:Paul W. Zitzewitz
Publisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
Moment of Inertia; Author: Physics with Professor Matt Anderson;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ZrGhUTeIlWs;License: Standard Youtube License