
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation: Check whether the given molecule is polar or not. If the molecule is polar then the direction of polarity has to be indicated.
Concept Introduction:
Polar molecules are the molecules having a positive and negative end and so there will be a charge separation.
A polar molecule is a molecule where the polar bonds are asymmetrically arranged (the dipoles do not cancel)
A nonpolar molecule is a molecule with no polar bonds or a molecule where the polar bonds are symmetrically arranged.
In polar molecule the charge separation occurred with respect to the difference in electronegativity of atoms in the molecule.
Direction of dipole moment in a molecule is can be represented as follows,

Different types of molecules and their geometry in accordance with the VSEPR theory are mentioned below,
(a)
Explanation of Solution
The structure of
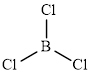
This molecule has a trigonal planar geometry. The direction dipole in the molecule is represented below,
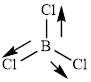
However
(b)
Interpretation: Check whether the given molecule is polar or not. If the molecule is polar then the direction of polarity has to be indicated.
Concept Introduction:
Polar molecules are the molecules having a positive and negative end and so there will be a charge separation.
A polar molecule is a molecule where the polar bonds are asymmetrically arranged (the dipoles do not cancel)
A nonpolar molecule is a molecule with no polar bonds or a molecule where the polar bonds are symmetrically arranged.
In polar molecule the charge separation occurred with respect to the difference in electronegativity of atoms in the molecule.
Direction of dipole moment in a molecule is can be represented as follows,

Different types of molecules and their geometry in accordance with the VSEPR theory are mentioned below,
(b)
Explanation of Solution
The structure of
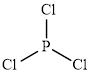
This molecule has a trigonal planar geometry. The direction dipole in the molecule is represented below,
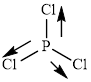
However
(c)
Interpretation: Check whether the given molecule is polar or not. If the molecule is polar then the direction of polarity has to be indicated.
Concept Introduction:
Polar molecules are the molecules having a positive and negative end (dipole) and so there will be a charge separation.
A polar molecule is a molecule where the polar bonds are asymmetrically arranged (the dipoles do not cancel)
A nonpolar molecule is a molecule with no polar bonds or a molecule where the polar bonds are symmetrically arranged.
In polar molecule the charge separation occurred with respect to the difference in electronegativity of atoms in the molecule.
Direction of dipole in a molecule is can be represented as follows,

Different types of molecules and their geometry in accordance with the VSEPR theory are mentioned below,
(c)
Explanation of Solution
The structure of
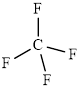
This molecule has a tetrahedral geometry. The direction dipole in the molecule is represented below,
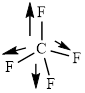
However
(d)
Interpretation: Check whether the given molecule is polar or not. If the molecule is polar then the direction of polarity has to be indicated.
Concept Introduction:
Polar molecules are the molecules having a positive and negative end and so there will be a charge separation.
A polar molecule is a molecule where the polar bonds are asymmetrically arranged (the dipoles do not cancel)
A nonpolar molecule is a molecule with no polar bonds or a molecule where the polar bonds are symmetrically arranged.
In polar molecule the charge separation occurred with respect to the difference in electronegativity of atoms in the molecule.
Direction of dipole moment in a molecule is can be represented as follows,

Different types of molecules and their geometry in accordance with the VSEPR theory are mentioned below,
(d)
Explanation of Solution
The structure of
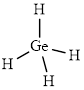
This molecule has a tetrahedral geometry. The direction dipole in the molecule is represented below,
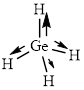
However
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 8 Solutions
Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
- a. H3C CH3 H, 1.0 equiv. Br2arrow_forwardH3C. H3C CH 3 CH 3 CH3 1. LDA 2. PhSeCl 3. H2O2arrow_forwardPlease predict the products for each of the following reactions: 1.03 2. H₂O NaNH, 1. n-BuLi 2. Mel A H₂ 10 9 0 H2SO4, H₂O HgSO4 Pd or Pt (catalyst) B 9 2 n-BuLi ♡ D2 (deuterium) Lindlar's Catalyst 1. NaNH2 2. EtBr Na, ND3 (deuterium) 2. H₂O2, NaOH 1. (Sia)2BH с Darrow_forward
- in the scope of ontario SCH4U grade 12 course, please show ALL workarrow_forwardIs the chemical reaction CuCl42-(green) + 4H2O <==> Cu(H2O)42+(blue) + 4Cl- exothermic or endothermic?arrow_forwardIf we react tetraethoxypropane with hydrazine, what is the product obtained (explain its formula). State the reason why the corresponding dialdehyde is not used.arrow_forward
- drawing, no aiarrow_forwardIf CH3COCH2CH(OCH3)2 (4,4-dimethoxy-2-butanone) and hydrazine react, two isomeric products are formed. State their structure and which will be the majority.arrow_forward+ Reset Provide the correct IUPAC name for the compound shown here. 4-methylhept-2-ene (Z)- (E)- 1-6-5-2-3-4- cyclo iso tert- sec- di tri hept hex oct meth eth pent ane yne ene ylarrow_forward
 Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning
World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning


