
Concept explainers
Interpretation:
The structures of the major organic products formed in the reaction of
Concept introduction:
When an unsymmetrically substituted alkene reacts with a hydrogen halide, the hydrogen adds to the carbon that has the greater number of hydrogens, and the halogen adds to the carbon that has fewer hydrogens. This rule is called Markovnikov’s rule.
During hydroboration oxidation, hydrogen forms a bond with the carbon atom that has fewer hydrogens attached to it and the hydroxyl atom forms a bond with the carbon atom that has a greater number of hydrogens attached to it. This is a rule opposite to the Markovnikov’s addition.
Answer to Problem 28P
Solution:
Explanation of Solution
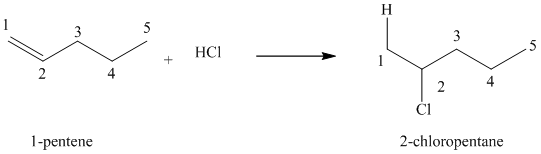
(a) Reaction of

The given alkene,
Hydrogen chloride gets added to the double bond of
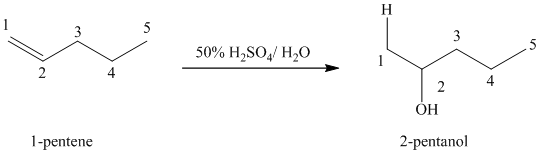
(b) Reaction of
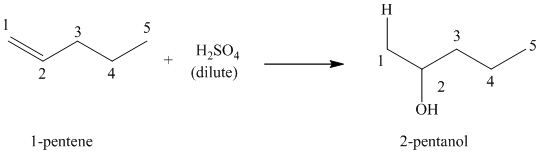
This reaction is an acid catalyzed electrophilic addition reaction of alkenes in which water molecule adds to the double bond in
A molecule of water adds to the double bond of
The addition mechanism for this reaction follows the Markovnikov’s rule. Therefore, the major organic product for the above acid-catalyzed electrophilic addition reaction is
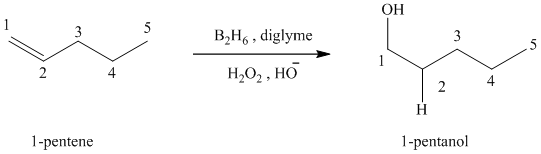
(c) Reaction of
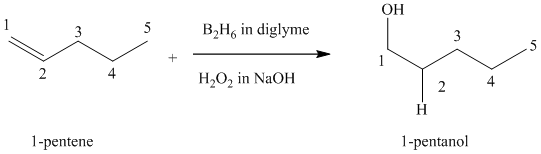
Hydroboration-oxidation leads to the overall hydration of an alkene. In hydroboration-oxidation,
The hydrogen atom in the water molecule adds to the carbon
In case of
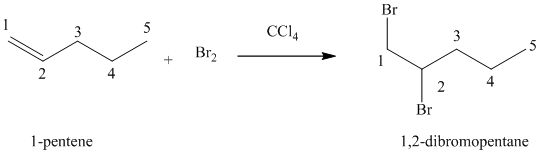
(d) Reaction of

Bromine reacts rapidly with alkenes by electrophilic addition. The products are called vicinal dibromides, meaning that the bromine atoms get attached to adjacent double bonded carbon atoms. It is carried out in suitable solvents like
A molecule of bromine adds across the double bond in
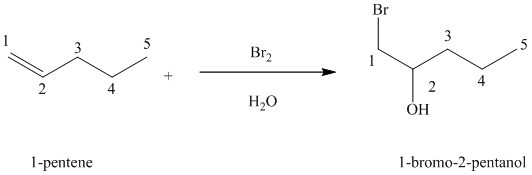
(e) Reaction of
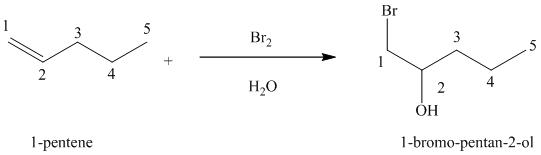
Chlorine and bromine react with alkenes in aqueous solution to give the corresponding vicinal halohydrins – compounds that add a halogen and hydroxyl group on adjacent carbon atoms in the alkene. The halogen atom forms a bond with that carbon atom in alkene, which has a greater number of hydrogen atoms, while the hydroxyl group bonds to that carbon atom in alkene, which has a fewer number of hydrogen atoms.
In the reaction of
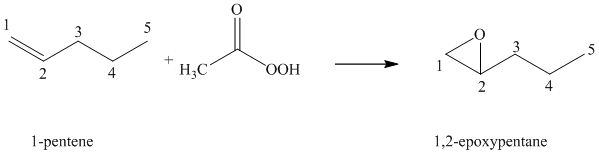
(f) Reaction of
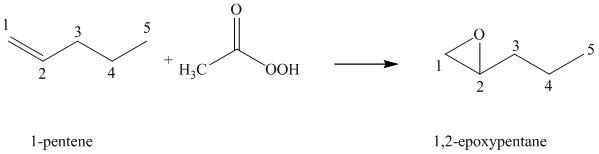
Peroxyacid transfers oxygen to the double bond of alkene to yield epoxides, which is a three-membered oxygen-containing ring.
When
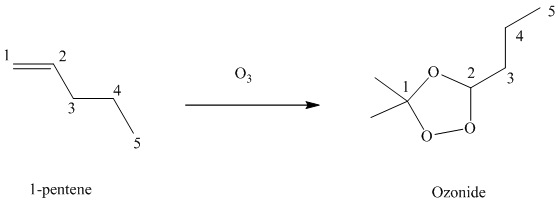
(g) Reaction of
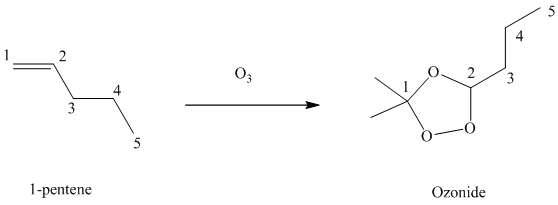
Ozone is a powerful electrophile and reacts with alkenes to cleave the double bond between two oxygen atoms in the molecule, forming an ozonide.
When
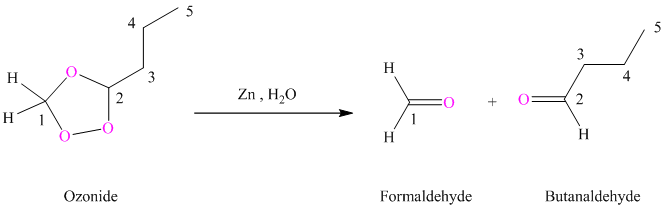
(h) Product of part (g) treated with zinc in water
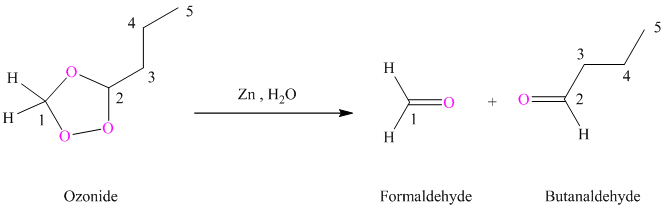
Ozonides are formed as a result of the reaction of ozone with an alkene. Ozonides undergo hydrolysis in water giving carbonyl compounds. Depending upon the structure of the starting alkene, various carbonyl compounds such as formaldehyde, aldehydes, or ketones are formed.
When corresponding ozonide of
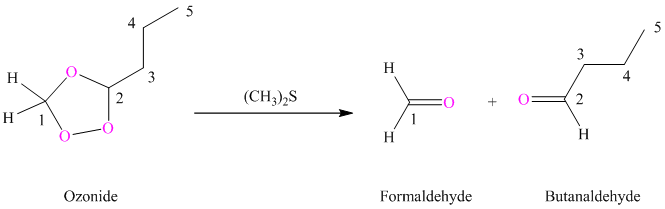
(i) Product of part (g) is treated with dimethyl sulfide.
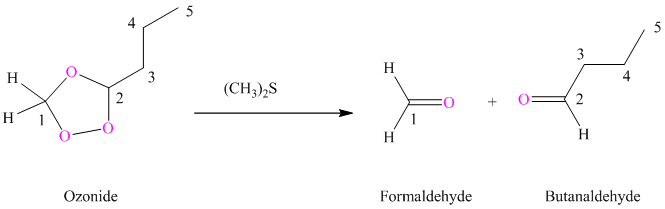
Ozonides are formed as a result of the reaction of ozone with an alkene. Ozonides undergo hydrolysis in water, giving carbonyl compounds. Depending upon the structure of the starting alkene, various carbonyl compounds such as formaldehyde, aldehydes, or ketones are formed.
When corresponding ozonide of
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 8 Solutions
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY (LL)-W/SOLN.>CUSTOM<
- Concentration (mg/l) Peak Area 0 158 10 10241 20 18425 30 26457 40 37125 50 44256 60 56124 You have been asked to determine the concentration of citral in a highly valued magnolia essential oil. QUESTION: Calculate the concentration of citral in your highly valued magnolia essential oil which returns a peak area of 41658arrow_forwardNeed help with these problems...if you can please help me understand problems E & F.arrow_forwardPlease help me solve these problems. Thank you in advance.arrow_forward
- Predict the products of this organic reaction: O N IN A N + H2O + HCI ? Specifically, in the drawing area below draw the skeletal ("line") structure of the product, or products, of this reaction. If there's more than one product, draw them in any arrangement you like, so long as they aren't touching. If there aren't any products because this reaction won't happen, check the No reaction box under the drawing area. 田 C + Explanation Check Click and drag to start drawing a structure. C © 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Centerarrow_forward6. For each of the following, fill in the synthesis arrows with reagents and show the intermediates. You DO NOT need to use the same number of arrows that are shown (you may use more or less), but the product must be formed from the reactant. Then write the mechanism of one step in the synthesis (you can choose which step to write the mechanism for), including all reagents required, clearly labeling the nucleophile and electrophile for each step, and using curved arrows to show the steps in the mechanism. a. b. OHarrow_forwardDraw the productsarrow_forward
- Draw the correct productsarrow_forwardE Organic Chemistry Maxwell Draw the correct products, in either order, for the ozonolysis reaction: 1) O3, CH2Cl2, -78 °C Product 1 + Product 2 2) Zn, HOAc Draw product 1. Select Draw Templates More C H O presented by M Draw product 2. Erase Select Draw Templates M / # # carrow_forward✓ edict the products of this organic reaction: ---- ။ A CH3–C−NH–CH2–C−CH3 + KOH ? Specifically, in the drawing area below draw the condensed structure of the product, or products, of this reaction. If there's more than one product, draw them in any arrangement you like, so long as they aren't touching. If there aren't any products because this reaction won't happen, check the No reaction box under the drawing area. Explanation Check Click anywhere to draw the first atom of your structure. C 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Center | Accessibiliarrow_forward
- Predict the product of this organic reaction: A HO-C-CH3 + CH3NH2 P+ H2O Specifically, in the drawing area below draw the condensed structure of P. If there is no reasonable possibility for P, check the No answer box under the drawing area. Explanation Check Click anywhere to draw the first atom of your structure. marrow_forwardH 1) OsO4, pyridine 2) Na2SO3 or NaHSO3 in H₂O 2 productsarrow_forward● Biological Macromolecules Naming and drawing cyclic monosaccharides Your answer is incorrect. • Row 1: Your answer is incorrect. Row 3: Your answer is incorrect. • Row 4: Your answer is incorrect. Try again... 0/5 Give the complete common name, including anomer and stereochemistry labels, of the following molecules. You will find helpful information in the ALEKS resource. CH2OH OH OH H H I H OH OH H] H CH2OH H OH ẞ-L-sorbose HOCH2 OH OH H HOCH2 H OH OH H OH H H CH2OH OH H H OH H I- H OH H OH Explanation Recheck W E R % 25 α B Y X & 5 D F G H McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Pr Parrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





