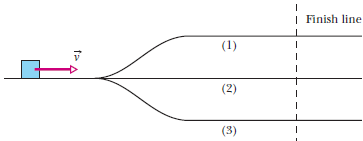
Problem 1Q: In Fig. 8-18, a horizontally moving block can take three frictionless routes, differing only in... Problem 2Q: Figure 8-19 gives the potential energy function of a particle. a Rank regions AB, BC, CD, and DE... Problem 3Q: Figure 8-20 shows one direct path and four indirect paths from point i to point f. Along the direct... Problem 4Q: In Fig. 8-21, a small, initially stationary block is released on a frictionless ramp at a height of... Problem 5Q: In Fig. 8-22, a block slides from A to C along a frictionless ramp, and then it passes through... Problem 6Q: In Fig. 8-23a, you pull upward on a rope that is attached to a cylinder on a vertical rod. Because... Problem 7Q: The arrangement shown in Fig. 8-24 is similar to that in Question 6. Here you pull downward on the... Problem 8Q: In Fig. 8-25, a block slides along a track that descends through distance h. The track is... Problem 9Q: Figure 8-26 shows three situations involving a plane that is not frictionless and a block sliding... Problem 10Q: Figure 8-27 shows three plums that are launched from the same level with the same speed. One moves... Problem 11Q: When a particle moves from f to i and from j to i along the paths shown in Fig. 8-28, and in the... Problem 1P: SSM What is the spring constant of a spring that stores 25 J of elastic potential energy when... Problem 2P: In Fig. 8-29, a single frictionless roller-coaster car of mass m = 825 kg tops the first hill with... Problem 3P: You drop a 2.00 kg book to a friend who stands on the ground at distance D = 10.0 m below. If your... Problem 4P: Figure 8-31 shows a ball with mass m = 0.341 kg attached to the end of a thin rod with length L =... Problem 5P: SSM In Fig. 8-32, a 2.00 g ice flake is released from the edge of a hemispherical bowl whose radius... Problem 6P: In Fig. 8-33, a small block of mass m = 0.032 kg can slide along the frictionless loop-the-loop,... Problem 7P: Figure 8-34 shows a thin rod, of length L = 2.00 m and negligible mass, that can pivot about one end... Problem 8P: A 1.50 kg snowball is fired from a cliff 12.5 m high. The snowballs initial velocity is 14.0 m/s,... Problem 9P: GO In Problem 2, what is the speed of the car at a point A, b point B, and c point C? d How high... Problem 10P: a In Problem 3, what is the speed of the book when it reaches the hands? b If we substituted a... Problem 11P: SSM WWW a In Problem 5, what is the speed of the flake when it reaches the bottom of the bowl? b If... Problem 12P: a In Problem 8, using energy techniques rather than the techniques of Chapter 4, find the speed of... Problem 13P: SSM A 5.0 g marble is fired vertically upward using a spring gun. The spring must be compressed 8.0... Problem 14P: a In Problem 4, what initial speed must be given the ball so that it reaches the vertically upward... Problem 15P: SSM In Fig. 8-35, a runaway truck with failed brakes is moving downgrade at 130 km/h just before the... Problem 16P: A 700 g block is released from rest at height h0 above a vertical spring with spring constant k =... Problem 17P: In Problem 6, what are the magnitudes of a the horizontal component and b the vertical component of... Problem 18P: a In Problem 7, what is the speed of the ball at the lowest point? b Does the speed increase,... Problem 19P: GO Figure 8-36 shows an 8.00 kg stone at rest on a spring. The spring is compressed 10.0 cm by the... Problem 20P: GO A pendulum consists of a 2.0 kg stone swinging on a 4.0 m string of negligible mass. The stone... Problem 21P: Figure 8-34 shows a pendulum of length L = 1.25 m. Its bob which effectively has all the mass has... Problem 22P: A 60 kg skier starts from rest at height H = 20 m above the end of a ski-jump ramp Fig. 8-37 and... Problem 23P: ILW The string in Fig. 8-38 is L = 120 cm long, has a ball attached to one end, and is fixed at its... Problem 24P: A block of mass m = 2.0 kg is dropped from height h = 40 cm onto a spring of spring constant k =... Problem 25P: At t = 0 a 1.0 kg ball is thrown from a tall tower with v=(18m/s) i +(24m/s) j . What is U of the... Problem 26P: A conservative force F=(6.0x12)i N, where x is in meters, acts on a particle moving along an x axis.... Problem 27P: Tarzan, who weighs 688 N, swings from a cliff at the end of a vine 18 m long Fig. 8-40. From the top... Problem 28P: Figure 8-41a applies to the spring in a cork gun Fig. 8-41b; it shows the spring force as a function... Problem 29P: SSM WWW In Fig. 8-42, a block of mass m = 12 kg is released from rest on a frictionless incline of... Problem 30P: GO A 2.0 kg breadbox on a frictionless incline of angle = 40 is connected, by a cord that runs over... Problem 31P: ILW A block with mass m = 2.00 kg is placed against a spring on a frictionless incline with angle =... Problem 32P: In Fig. 8-45, a chain is held on a frictionless table with one- fourth of its length hanging over... Problem 33P: GO In Fig. 8-46, a spring with k = 170 N/m is at the top of a frictionless incline of angle = 37.0.... Problem 34P: GO A boy is initially seated on the top of a hemispherical ice mound of radius R = 13.8 m. He begins... Problem 35P: GO In Fig. 8-42, a block of mass m = 3.20 kg slides from rest a distance d down a frictionless... Problem 36P: GO Two children are playing a game in which they try to hit a small box on the floor with a marble... Problem 37P: A uniform cord of length 25 cm and mass 15 g is initially stuck to a ceiling. Later, it hangs... Problem 38P: Figure 8-49 shows a plot of potential energy U versus position x of a 0.200 kg particle that can... Problem 39P: GO Figure 8-50 shows a plot of potential energy U versus position x of a 0.90 kg particle that can... Problem 40P: The potential energy of a diatomic molecule a two-atom system like H2 or O2 is given by U=Ar12Br6,... Problem 41P: A single conservative force Fx acts on a 1.0 kg particle that moves along an x axis. The potential... Problem 42P: A worker pushed a 27 kg block 9.2 m along a level floor at constant speed with a force directed 32... Problem 43P: A collie drags its bed box across a floor by applying a horizontal force of 8.0 N. The kinetic... Problem 44P: A horizontal force of magnitude 35.0 N pushes a block of mass 4.00 kg across a floor where the... Problem 45P: SSM A rope is used to pull a 3.57 kg block at constant speed 4.06 m along a horizontal floor. The... Problem 46P: An outfielder throws a baseball with an initial speed of 81.8 mi/h. Just before an infielder catches... Problem 47P: A 75 g Frisbee is thrown from a point 1.1 m above the ground with a speed of 12 m/s. When it has... Problem 48P: In Fig. 8-51, a block slides down an incline. As it moves from point A to point B, which are 5.0 m... Problem 49P: SSM ILW A 25 kg bear slides, from rest, 12 m down a lodgepole pine tree, moving with a speed of 5.6... Problem 50P: A 60 kg skier leaves the end of a ski-jump ramp with a velocity of 24 m/s directed 25 above the... Problem 51P: During a rockslide, a 520 kg rock slides from rest down a hillside that is 500 m long and 300 m... Problem 52P: A large fake cookie sliding on a horizontal surface is attached to one end of a horizontal spring... Problem 53P: GO In Fig. 8-52, a 3.5 kg block is accelerated from rest by a compressed spring of spring constant... Problem 54P: A child whose weight is 267 N slides down a 6.1 m playground slide that makes an angle of 20 with... Problem 55P: ILW In Fig. 8-53, a block of mass m = 2.5 kg slides head on into a spring of spring constant k = 320... Problem 56P: You push a 2.0 kg block against a horizontal spring, compressing the spring by 15 cm. Then you... Problem 57P: GO In Fig. 8-54, a block slides along a track from one level to a higher level after passing through... Problem 58P: A cookie jar is moving up a 40 incline. At a point 55 cm from the bottom of the incline measured... Problem 59P: A stone with a weight of 5.29 N is launched vertically from ground level with an initial speed of... Problem 60P Problem 61P: When a click beetle is upside down on its back, it jumps upward by suddenly arching its back,... Problem 62P: GO In Fig. 8-55, a block slides along a path that is without friction until the block reaches the... Problem 63P: The cable of the 1800 kg elevator cab in Fig. 8-56 snaps when the cab is at rest at the first floor,... Problem 64P: GO In Fig. 8-57, a block is released from rest at height d = 40 cm and slides down a frictionless... Problem 65P: GO A particle can slide along a track with elevated ends and a flat central part, as shown in Fig.... Problem 66P: A 3.2 kg sloth hangs 3.0 m above the ground. a What is the gravitational potential energy of the... Problem 67P: SSM A spring k = 200 N/m is fixed at the top of a frictionless plane inclined at angle = 40 Fig.... Problem 68P: From the edge of a cliff, a 0.55 kg projectile is launched with an initial kinetic energy of 1550 J.... Problem 69P: SSM In Fig. 8-60, the pulley has negligible mass, and both it and the inclined plane are... Problem 70P: GO In Fig. 8-38, the string is L = 120 cm long, has a ball attached to one end, and is fixed at its... Problem 71P: SSM In Fig. 8-51, a block is sent sliding down a frictionless ramp. Its speeds at points A and B are... Problem 72P: Two snowy peaks are at heights H = 850 m and h = 750 m above the valley between them. A ski run... Problem 73P: SSM The temperature of a plastic cube is monitored while the cube is pushed 3.0 m across a floor at... Problem 74P: A skier weighing 600 N goes over a frictionless circular hill of radius R = 20 m Fig. 8-62. Assume... Problem 75P: SSM To form a pendulum, a 0.092 kg ball is attached to one end of a rod of length 0.62 m and... Problem 76P: We move a particle along an x axis, first outward from x = 1.0 m to x = 4.0 m and then back to x =... Problem 77P: SSM A conservative force Fx acts on a 2.00 kg particle that moves along an x axis. The potential... Problem 78P: At a certain factory, 300 kg crates are dropped vertically from a packing machine onto a conveyor... Problem 79P: SSM A 1500 kg car begins sliding down a 5.0 inclined road with a speed of 30 km/h. The engine is... Problem 80P: In Fig. 8-65, a 1400 kg block of granite is pulled up an incline at a constant speed of 1.34 m/s by... Problem 81P: A particle can move along only an x axis, where conservative forces act on it Fig. 8-66 and the... Problem 82P: For the arrangement of forces in Problem 81, a 2.00 kg particle is released at x = 5.00 m with an... Problem 83P: SSM A 15 kg block is accelerated at 2.0 m/s2 along a horizontal frictionless surface, with the speed... Problem 84P: A certain spring is found not to conform to Hookes law. The force in newtons it exerts when... Problem 85P: SSM Each second, 1200 m3 of water passes over a waterfall 100 m high. Three-fourths of the kinetic... Problem 86P: GO In Fig. 8-67, a small block is sent through point A with a speed of 7.0 m/s. Its path is without... Problem 87P: SSM A massless rigid rod of length L has a ball of mass m attached to one end Fig. 8-68. The other... Problem 88P: A 1.50 kg water balloon is shot straight up with an initial speed of 3.00 m/s. a What is the kinetic... Problem 89P: A 2.50 kg beverage can is thrown directly downward from a height of 4.00 m, with an initial speed of... Problem 90P: A constant horizontal force moves a 50 kg trunk 6.0 m up a 30 incline at constant speed. The... Problem 91P: GO Two blocks, of masses M = 2.0 kg and 2M, are connected to a spring of spring constant k = 200 N/m... Problem 92P: A volcanic ash flow is moving across horizontal ground when it encounters a 10 upslope. The front of... Problem 93P: A playground slide is in the form of an arc of a circle that has a radius of 12 m. The maximum... Problem 94P: The luxury liner Queen Elizabeth 2 has a diesel-electric power plant with a maximum power of 92 MW... Problem 95P: A factory worker accidentally releases a 180 kg crate that was being held at rest at the top of a... Problem 96P: If a 70 kg baseball player steals home by sliding into the plate with an initial speed of 10 m/s... Problem 97P: A 0.50 kg banana is thrown directly upward with an initial speed of 4.00 m/s and reaches a maximum... Problem 98P: A metal tool is sharpened by being held against the rim of a wheel on a grinding machine by a force... Problem 99P: A swimmer moves through the water at an average speed of 0.22 m/s. The average drag force is 110 N.... Problem 100P: An automobile with passengers has weight 16 400 N and is moving at 113 km/h when the driver brakes,... Problem 101P: A 0.63 kg ball thrown directly upward with an initial speed of 14 m/s reaches a maximum height of... Problem 102P: The summit of Mount Everest is 8850 m above sea level. a Flow much energy would a 90 kg climber... Problem 103P: A sprinter who weighs 670 N runs the first 7.0 m of a race in 1.6 s, starting from rest and... Problem 104P: A 20 kg object is acted on by a conservative force given by F = 3.0x 5.0x2, with F in newtons and x... Problem 105P: A machine pulls a 40 kg trunk 2.0 m up a 40 ramp at constant velocity, with the machines force on... Problem 106P Problem 107P: The only force acting on a particle is conservative force F. If the particle is at point A, the... Problem 108P: In 1981, Daniel Goodwin climbed 443 m up the exterior of the Sears Building in Chicago using suction... Problem 109P: A 60.0 kg circus performer slides 4.00 m down a pole to the circus floor, starting from rest. What... Problem 110P: A 5.0 kg block is projected at 5.0 m/s up a plane that is inclined at 30 with the horizontal. How... Problem 111P: A 9.40 kg projectile is fired vertically upward. Air drag decreases the mechanical energy of the... Problem 112P: A 70.0 kg man jumping from a window lands in an elevated fire rescue net 11.0 m below the window. He... Problem 113P: A 30 g bullet moving a horizontal velocity of 500 m/s comes to a stop 12 cm within a solid wall. a... Problem 114P: A 1500 kg car starts from rest on a horizontal road and gains a speed of 72 km/h in 30 s. a What is... Problem 115P: A 1.50 kg snowball is shot upward at an angle of 34.0 to the horizontal with an initial speed of... Problem 116P: A 68 kg sky diver falls at a constant terminal speed of 59 m/s. a At what rate is the gravitational... Problem 117P: A 20 kg block on a horizontal surface is attached to a horizontal spring of spring constant k = 4.0... Problem 118P: Resistance to the motion of an automobile consists of road friction, which is almost independent of... Problem 119P: SSM A 50 g ball is thrown from a window with an initial velocity of 8.0 m/s at an angle of 30 above... Problem 120P: A spring with a spring constant of 3200 N/m is initially stretched until the elastic potential... Problem 121P: A locomotive with a power capability of 1.5 MW can accelerate a train from a speed of 10 m/s to 25... Problem 122P: SSM A 0.42 kg shuffleboard disk is initially at rest when a player uses a cue to increase its speed... Problem 123P: A river descends 15 m through rapids. The speed of the water is 3.2 m/s upon entering the rapids and... Problem 124P: The magnitude of the gravitational force between a particle of mass m1 and one of mass m2 is given... Problem 125P: Approximately 5.5 106 kg of water falls 50 m over Niagara Falls each second. a What is the decrease... Problem 126P: To make a pendulum, a 300 g ball is attached to one end of a string that has a length of 1.4 m and... Problem 127P: In a circus act, a 60 kg clown is shot from a cannon with an initial velocity of 16 m/s at some... Problem 128P: A 70 kg firefighter slides, from rest, 4.3 m down a vertical pole. a If the firefighter holds onto... Problem 129P: The surface of the continental United States has an area of about 8 106 km2 and an average... Problem 130P: A spring with spring constant k = 200 N/m is suspended vertically with its upper end fixed to the... Problem 131P: Fasten one end of a vertical spring to a ceiling, attach a cabbage to the other end, and then slowly... Problem 132P: The maximum force you can exert on an object with one of your back teeth is about 750 N. Suppose... Problem 133P: Conservative force Fx acts on a particle that moves along an x axis. Figure 8-72 shows how the... Problem 134P: Figure 8-73a shows a molecule consisting of two atoms of masses m and M with m M and separation r.... Problem 135P: Repeat Problem 83, but now with the block accelerated up a frictionless plane inclined at 5.0 to the... Problem 136P: A spring with spring constant k = 620 N/m is placed in a vertical orientation with its lower end... format_list_bulleted

 University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University
University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning




