
To calculate: The rate of crossover for two projects and sketch the NPV profile.
Introduction:
The
Answer to Problem 11QP
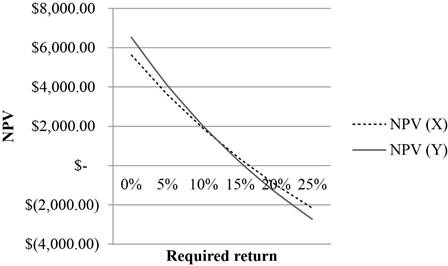
The crossover rate for the two projects is 11.95%. The NPV profiles shows that both projects have a higher NPV for the rate of discount below 11.95% and have a lower NPV for the rate above 11.95%.
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The details of 2 projects are provided. The cash flows of Project X for year 1, year 2, and year 3, are $10,800, $8,630, and $5,210 respectively. The initial investment is -$19,000. The Project Y cash flows for 4 years are $6,840, $9,410, $9,300 respectively and the initial investment is -$19,000.
Note:
- NPV is the difference between the present values of the cash inflows and the
present value of the cash outflows. - The IRR is the rate of interest, which makes the project’s NPV equals zero. Hence, using the available information, assume that NPV is equal to zero and form an equation to compute the IRR.
Equation of NPV to compute IRR assuming that NPV is equal to zero:
Compute IRR for Project X using a spreadsheet:
Step 1:
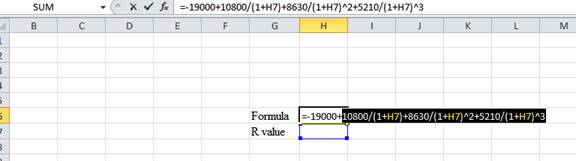
- Type the equation of NPV in H6 in the spreadsheet and consider the IRR value as H7.
Step 2:
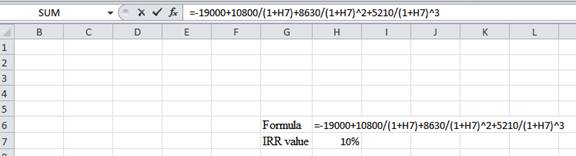
- Assume the IRR value as 10%.
Step 3:
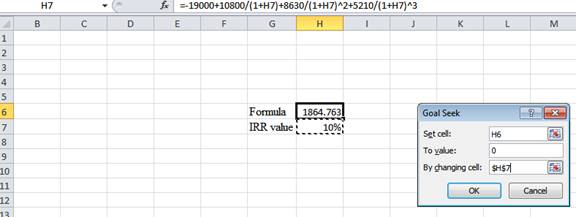
- In the spreadsheet, go to data and select the What-if analysis
- In What-if analysis, select Goal Seek.
- In “Set cell”, select H6 (the formula).
- The “To value” is considered as 0 (the assumption value for NPV).
- The H7 cell is selected for “By changing cell”.
Step 4:
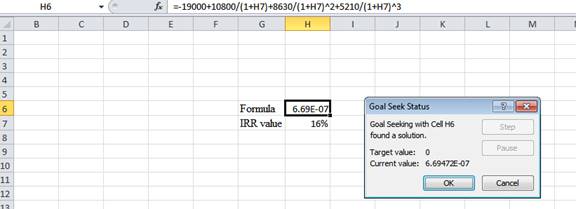
- Following the previous step, click OK in the Goal Seek Status. The Goal Seek Status appears with the IRR value.
Step 5:
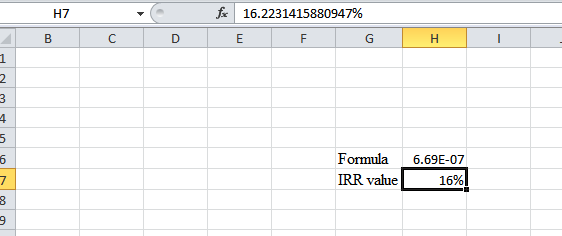
- The value appears to be 16.2231415880947%.
Hence, the IRR value is 16.22%.
Equation of NPV to compute IRR assuming that NPV is equal to zero:
Compute IRR for Project Y using a spreadsheet:
Step 1:
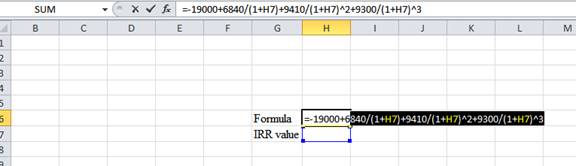
- Type the equation of NPV in H6 in the spreadsheet and consider the IRR value as H7.
Step 2:
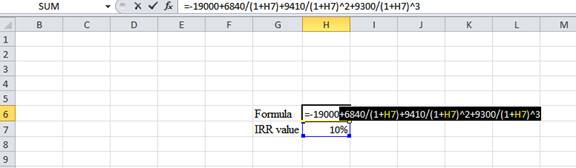
- Assume the IRR value as 10%.
Step 3:
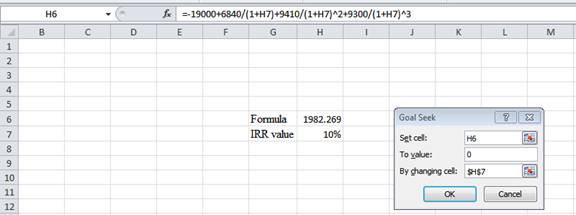
- In the spreadsheet, go to data and select the What-if analysis.
- In What-if analysis, select Goal Seek.
- In “Set cell”, select H6 (the formula).
- The “To value” is considered as 0 (the assumption value for NPV).
- The H7 cell is selected for “By changing cell”.
Step 4:
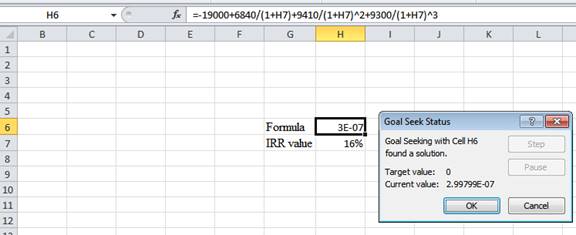
- Following the previous step, click OK in the Goal Seek Status. The Goal Seek Status appears with the IRR value.
Step 5:
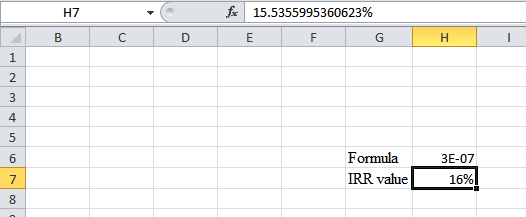
- The value appears to be 15.5355995360623%.
Hence, the IRR value is 15.53%.
Formula to compute the crossover rate:
Equation of crossover rate to compute R:
Where,
“R” denotes the crossover rate.
Compute R using a spreadsheet:
Step 1:
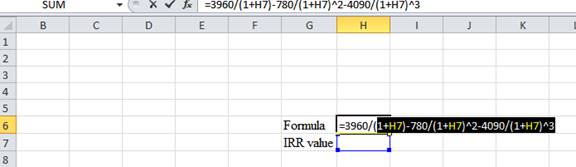
- Type the equation of NPV in H6 in the spreadsheet and consider the IRR value as H7.
Step 2:
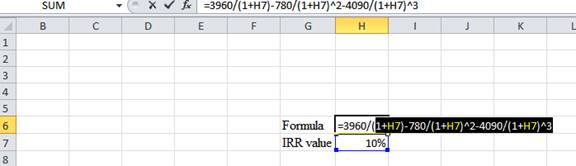
- Assume the IRR value as 10%.
Step 3:
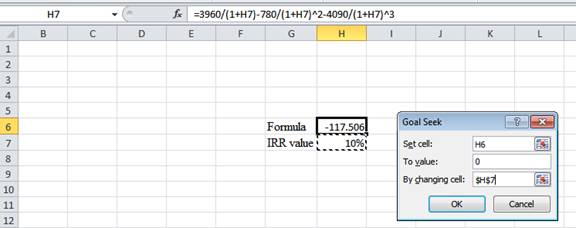
- In the spreadsheet, go to data and select the What-if analysis.
- In What-if analysis, select Goal Seek.
- In “Set cell”, select H6 (the formula).
- The “To value” is considered as 0 (the assumption value for NPV).
- The H7 cell is selected for “By changing cell”.
Step 4:
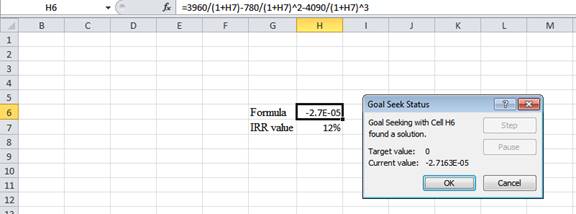
- Following the previous step, click OK in the Goal Seek Status. The Goal Seek Status appears with the IRR value.
Step 5:
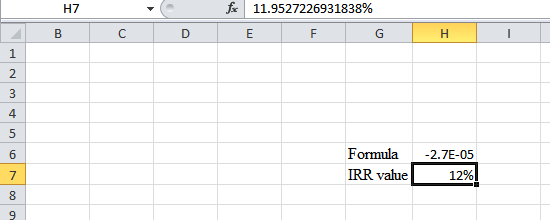
- The value appears to be 11.9527226931838%.
Hence, the R-value is 11.95%.
Formula to calculate the NPV:
Note: As the discount rate is over a range of 0% to 25%, calculate NPV for 0%, 5%, 10%, 15%, 20%, and 25%.
Compute the NPV with the discount rate of 0% for Project X:
Compute the NPV with the discount rate of 0% for Project Y:
Hence, the NPV for Project X and Y at 0% are $5,640 and $6,550 respectively.
Compute the NPV with the discount rate of 5% for Project X:
Compute the NPV with the discount rate of 5% for Project Y:
Hence, the NPV for Project X and Y at 5% are $3,613.972 and $4,083.12 respectively.
Compute the NPV with the discount rate of 10% for Project X:
Compute the NPV with the discount rate of 10% for Project Y:
Hence, the NPV for Project X and Y at 10% are $1,864.76 and $1,982.26 respectively.
Compute the NPV with the discount rate of 15% for Project X:
Compute the NPV with the discount rate of 15% for Project Y:
Hence, the NPV for Project X and Y at 15% are $342.48 and $178.03 respectively.
Compute the NPV with the discount rate of 20% for Project X:
Compute the NPV with the discount rate of 20% for Project Y:
Hence, the NPV for Project X and Y at 20% are -$991.89 and -$1,383.33 respectively.
Compute the NPV with the discount rate of 25% for Project X:
Compute the NPV with the discount rate of 25% for Project Y:
Hence, the NPV for Project X and Y at 25% are -$2,169.28 and -$2,744 respectively.
NPV profile:
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 8 Solutions
Essentials of Corporate Finance
- An accounts payable period decrease would increase the length of a firm's cash cycle. Consider each in isolation. Question 6 options: True Falsearrow_forwardWhich of the following is the best definition of cash budget? Question 10 options: Costs that rise with increases in the level of investment in current assets. A forecast of cash receipts and disbursements for the next planning period. A secured short-term loan that involves either the assignment or factoring of the receivable. The time between sale of inventory and collection of the receivable. The time between receipt of inventory and payment for it.arrow_forwardShort-term financial decisions are typically defined to include cash inflows and outflows that occur within __ year(s) or less. Question 9 options: Four Two Three Five Onearrow_forward
- A national firm has sales of $575,000 and cost of goods sold of $368,000. At the beginning of the year, the inventory was $42,000. At the end of the year, the inventory balance was $45,000. What is the inventory turnover rate? Question 8 options: 8.46 times 13.22 times 43.14 times 12.78 times 28.56 timesarrow_forwardThe formula (Cash cycle + accounts payable period) correctly defines the operating cycle. Question 7 options: False Truearrow_forwardAn accounts payable period decrease would increase the length of a firm's cash cycle. Consider each in isolation. Question 6 options: True Falsearrow_forward
- Which of the following issues is/are NOT considered a part of short-term finance? Question 5 options: The amount of credit that should be extended to customers The firm determining whether to issue commercial paper or obtain a bank loan The amount of the firms current income that should be paid out as dividends The amount the firm should borrow short-term A reasonable level of cash for the firm to maintainarrow_forwardLiberal credit terms for customers is associated with a restrictive short-term financial policy. Question 3 options: True Falsearrow_forwardAn increase in fixed assets is a source of cash. Question 2 options: True Falsearrow_forward
- If the initial current ratio for a firm is greater than one, then using cash to purchase marketable securities will decrease net working capital. True or falsearrow_forwardwhat is going to be the value of American put option that expires in one year modeled with a binomial tree of 3 months step with year to expiry? assume the underlying is oil future with RF of 5% and vol of oil is 30%. Strike is 70 and price is 60 of oil. 13.68 13.44 13.01arrow_forwardhello tutor need step by step approach.arrow_forward
 Essentials Of InvestmentsFinanceISBN:9781260013924Author:Bodie, Zvi, Kane, Alex, MARCUS, Alan J.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Essentials Of InvestmentsFinanceISBN:9781260013924Author:Bodie, Zvi, Kane, Alex, MARCUS, Alan J.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,

 Foundations Of FinanceFinanceISBN:9780134897264Author:KEOWN, Arthur J., Martin, John D., PETTY, J. WilliamPublisher:Pearson,
Foundations Of FinanceFinanceISBN:9780134897264Author:KEOWN, Arthur J., Martin, John D., PETTY, J. WilliamPublisher:Pearson, Fundamentals of Financial Management (MindTap Cou...FinanceISBN:9781337395250Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Joel F. HoustonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Fundamentals of Financial Management (MindTap Cou...FinanceISBN:9781337395250Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Joel F. HoustonPublisher:Cengage Learning Corporate Finance (The Mcgraw-hill/Irwin Series i...FinanceISBN:9780077861759Author:Stephen A. Ross Franco Modigliani Professor of Financial Economics Professor, Randolph W Westerfield Robert R. Dockson Deans Chair in Bus. Admin., Jeffrey Jaffe, Bradford D Jordan ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Corporate Finance (The Mcgraw-hill/Irwin Series i...FinanceISBN:9780077861759Author:Stephen A. Ross Franco Modigliani Professor of Financial Economics Professor, Randolph W Westerfield Robert R. Dockson Deans Chair in Bus. Admin., Jeffrey Jaffe, Bradford D Jordan ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





