
Subpart (a):
Subpart (a):
Explanation of Solution
The equilibrium
We have given the supply equation and the demand equations and we can equate them in order to obtain the equilibrium price as follows:
Thus, the equilibrium price is $100. Now we can calculate the equilibrium quantity by substituting the equilibrium price in the equations as follows:
Thus, the equilibrium quantity is 200 units.
Concept introduction:
Equilibrium: It is the
Subpart (b):
Equilibrium price.
Subpart (b):
Explanation of Solution
We have given the supply equation and the demand equation changes due to the tax on consumers and the new demand equation is
Thus, the price received by the producers is
Thus, the quantity is now
Concept introduction:
Equilibrium: It is the market equilibrium which is determined by equating the supply to the demand. At this equilibrium point, the supply will be equal to the demand and there will be no excess demand or excess supply in the economy. Thus, the economy will be at equilibrium.
Subpart (c):
Total tax revenue.
Subpart (c):
Explanation of Solution
We have given that the tax revenue equals to the tax rate multiplied with the quantity. The quantity is calculated in part b as
This relation between the tax revenue can be illustrated as follows:
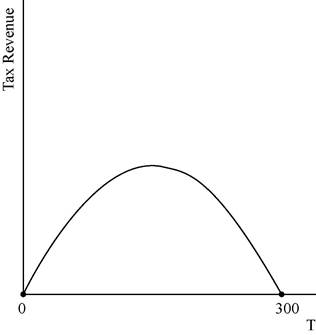
The graph depicts that the tax revenue will be zero at the tax levels of T = $0 and also at the tax rate of T = $300.
Concept introduction:
Tax: It is the unilateral payment made by the public towards the government. There are many different types of taxes in the economy which include the income tax, property tax and professional tax and so forth.
Tax revenue: Tax revenue refers to the total revenue earned by the government through imposing tax.
Subpart (d):
Subpart (d):
Explanation of Solution
We have given that deadweight loss is the area of the triangle between the demand and supply curves. The following diagram shows, the area of the triangle (laid on its side) that represents the deadweight loss is 1/2 × base × height, where the base is the change in the price, which is the size of the tax (T) and the height is the amount of the decline in quantity (
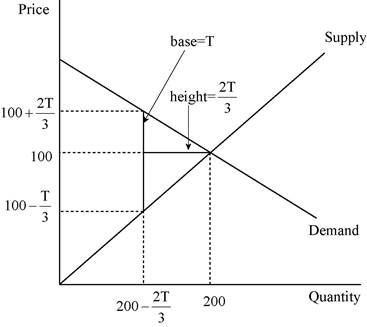
The deadweight loss can be calculated as follows:
Thus, the deadweight loss is equal to
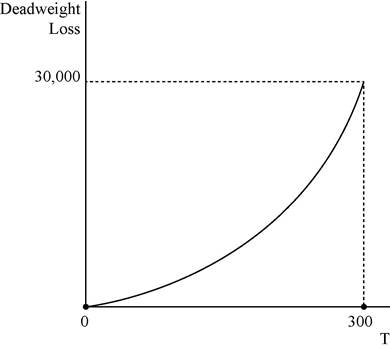
In the above diagram horizontal axis measures quantity and vertical axis measures deadweight loss.
Concept introduction:
Tax: It is the unilateral payment made by the public towards the government. There are many different types of taxes in the economy which include the income tax, property tax and professional tax and so forth.
Deadweight loss: It is the reduction in the units where the marginal benefit to the consumer is higher than the marginal cost of production of the unit.
Subpart (e):
Determine the tax amount.
Subpart (e):
Explanation of Solution
A tax of $200 will not turn out to be a good policy because the tax revenue decreases when the tax rate reaches to $300 where the tax revenue is zero. The tax revenue is at its maximum at the middle of the tax rate of $0 and $300 which is $150. Thus, in order to increase the tax revenue, the government should reduce the tax rate to $150 from $200 which will be the good alternative policy.
Concept introduction:
Tax: It is the unilateral payment made by the public towards the government. There are many different types of taxes in the economy which include the income tax, property tax and professional tax and so forth.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 8 Solutions
Essentials of Economics (MindTap Course List)
- how commond economies relate to principle Of Economics ?arrow_forwardCritically analyse the five (5) characteristics of Ubuntu and provide examples of how they apply to the National Health Insurance (NHI) in South Africa.arrow_forwardCritically analyse the five (5) characteristics of Ubuntu and provide examples of how they apply to the National Health Insurance (NHI) in South Africa.arrow_forward
- Outline the nine (9) consumer rights as specified in the Consumer Rights Act in South Africa.arrow_forwardIn what ways could you show the attractiveness of Philippines in the form of videos/campaigns to foreign investors? Cite 10 examples.arrow_forwardExplain the following terms and provide an example for each term: • Corruption • Fraud • Briberyarrow_forward
- In what ways could you show the attractiveness of a country in the form of videos/campaigns?arrow_forwardWith the VBS scenario in mind, debate with your own words the view that stakeholders are the primary reason why business ethics must be implemented.arrow_forwardThe unethical decisions taken by the VBS management affected the lives of many of their clients who trusted their business and services You are appointed as an ethics officer at Tyme Bank. Advise the management regarding the role of legislation in South Africa in providing the legal framework for business operations.arrow_forward
 Microeconomics: Principles & PolicyEconomicsISBN:9781337794992Author:William J. Baumol, Alan S. Blinder, John L. SolowPublisher:Cengage Learning
Microeconomics: Principles & PolicyEconomicsISBN:9781337794992Author:William J. Baumol, Alan S. Blinder, John L. SolowPublisher:Cengage Learning








