
Organic Chemistry (8th Edition)
8th Edition
ISBN: 9780134042282
Author: Paula Yurkanis Bruice
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 8, Problem 109P
The experiment shown next and discussed in Section 8.13 shows that the proximity of the chloride ion to C-2 in the transition state causes the 1,2·addition product to form more rapidly than the 1,4-addition product.
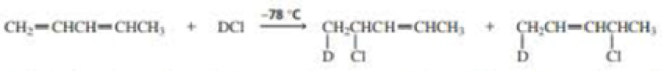
- a. Why was it important for the investigators to know that the preceding reaction was being carried out under kinetic control?
- b. How could the investigators know that the reaction was being carried out under kinetic control?
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Using the following two half-reactions, determine the pH range in which $NO_2^-\ (aq)$ cannot be found as the predominant chemical species in water.* $NO_3^-(aq)+10H^+(aq)+8e^-\rightarrow NH_4^+(aq)+3H_2O(l),\ pE^{\circ}=14.88$* $NO_2^-(aq)+8H^+(aq)+6e^-\rightarrow NH_4^+(aq)+2H_2O(l),\ pE^{\circ}=15.08$
Indicate characteristics of oxodec acid.
What is the final product when hexanedioic acid reacts with 1º PCl5 and 2º NH3.
Chapter 8 Solutions
Organic Chemistry (8th Edition)
Ch. 8.1 - Prob. 1PCh. 8.1 - Prob. 2PCh. 8.4 - Prob. 3PCh. 8.5 - Prob. 4PCh. 8.5 - Prob. 6PCh. 8.6 - a. Predict the relative bond lengths of the three...Ch. 8.6 - Prob. 8PCh. 8.6 - Prob. 9PCh. 8.6 - Prob. 10PCh. 8.7 - Prob. 11P
Ch. 8.7 - Prob. 12PCh. 8.7 - Prob. 13PCh. 8.8 - Prob. 14PCh. 8.8 - Prob. 15PCh. 8.8 - Prob. 16PCh. 8.9 - Which member of each pair is the stronger acid?Ch. 8.9 - Which member of each pair is the stronger base? a....Ch. 8.9 - Rank the following compounds from strongest acid...Ch. 8.10 - Prob. 20PCh. 8.10 - Which acid in each of the following pairs is...Ch. 8.10 - Prob. 23PCh. 8.11 - Prob. 24PCh. 8.11 - Prob. 26PCh. 8.12 - Prob. 27PCh. 8.12 - Prob. 28PCh. 8.12 - Prob. 29PCh. 8.12 - Prob. 30PCh. 8.12 - Prob. 31PCh. 8.12 - Prob. 32PCh. 8.13 - Prob. 33PCh. 8.13 - Prob. 34PCh. 8.13 - Prob. 35PCh. 8.13 - What are the major 1,2- and 1,4-addition products...Ch. 8.13 - Prob. 38PCh. 8.14 - Prob. 39PCh. 8.14 - Prob. 40PCh. 8.14 - Prob. 41PCh. 8.14 - Prob. 42PCh. 8.14 - Prob. 43PCh. 8.14 - Prob. 44PCh. 8.14 - Prob. 46PCh. 8.15 - Prob. 47PCh. 8.17 - Prob. 48PCh. 8.17 - Prob. 49PCh. 8.18 - Prob. 50PCh. 8.18 - Prob. 52PCh. 8.18 - Prob. 53PCh. 8.18 - Prob. 54PCh. 8.19 - Prob. 55PCh. 8.20 - Prob. 56PCh. 8.20 - What orbitals contain the electrons represented as...Ch. 8.20 - Prob. 59PCh. 8.20 - Prob. 60PCh. 8 - Prob. 61PCh. 8 - Prob. 62PCh. 8 - Prob. 63PCh. 8 - Prob. 64PCh. 8 - Prob. 65PCh. 8 - Prob. 66PCh. 8 - Prob. 67PCh. 8 - Prob. 68PCh. 8 - Prob. 69PCh. 8 - Prob. 70PCh. 8 - Prob. 71PCh. 8 - Prob. 72PCh. 8 - Prob. 73PCh. 8 - Which compound is the strongest base?Ch. 8 - Prob. 75PCh. 8 - Prob. 76PCh. 8 - a. The A ring (Section 3.16) of cortisone (a...Ch. 8 - Prob. 78PCh. 8 - Prob. 79PCh. 8 - Prob. 80PCh. 8 - Prob. 81PCh. 8 - Purine is a heterocyclic compound with four...Ch. 8 - Prob. 83PCh. 8 - Why is the delocalization energy of pyrrole (21...Ch. 8 - Prob. 85PCh. 8 - Prob. 86PCh. 8 - Prob. 87PCh. 8 - A student obtained two products from the reaction...Ch. 8 - Prob. 89PCh. 8 - a. How could each of the following compounds be...Ch. 8 - Draw the products obtained from the reaction of...Ch. 8 - How would the following substituents affect the...Ch. 8 - Prob. 93PCh. 8 - The acid dissociation constant (Ka) for loss of a...Ch. 8 - Protonated cyclohexylamine has a Ka = 1 1011...Ch. 8 - Draw the product or products that would be...Ch. 8 - Prob. 97PCh. 8 - Prob. 98PCh. 8 - Prob. 99PCh. 8 - Prob. 100PCh. 8 - Prob. 101PCh. 8 - a. Propose n mechanism for the following reaction:...Ch. 8 - Prob. 103PCh. 8 - As many as 18 different Diels-Alder products can...Ch. 8 - Prob. 105PCh. 8 - Prob. 106PCh. 8 - Prob. 107PCh. 8 - Prob. 108PCh. 8 - The experiment shown next and discussed in Section...Ch. 8 - Prob. 110PCh. 8 - Prob. 111PCh. 8 - Prob. 112PCh. 8 - Prob. 1PCh. 8 - Prob. 2PCh. 8 - Prob. 3PCh. 8 - Prob. 4PCh. 8 - Prob. 5PCh. 8 - Prob. 6PCh. 8 - Prob. 7PCh. 8 - Prob. 8PCh. 8 - Prob. 9PCh. 8 - Prob. 10PCh. 8 - Prob. 11PCh. 8 - Prob. 12P
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- What is the final product when D-galactose reacts with hydroxylamine?arrow_forwardIndicate the formula of the product obtained by reacting methyl 5-chloro-5-oxopentanoate with 1 mole of 4-penten-1-ylmagnesium bromide.arrow_forwardIn the two chair conformations of glucose, the most stable is the one with all the OH groups in the equatorial position. Is this correct?arrow_forward
- please help me with my homeworkarrow_forwardhelparrow_forwardThe temperature on a sample of pure X held at 1.25 atm and -54. °C is increased until the sample boils. The temperature is then held constant and the pressure is decreased by 0.42 atm. On the phase diagram below draw a path that shows this set of changes. pressure (atm) 2 0 0 200 400 temperature (K) Xarrow_forward
- QUESTION: Answer Question 5: 'Calculating standard error of regression' STEP 1 by filling in all the empty green boxes *The values are all provided in the photo attached*arrow_forwardpressure (atm) 3 The pressure on a sample of pure X held at 47. °C and 0.88 atm is increased until the sample condenses. The pressure is then held constant and the temperature is decreased by 82. °C. On the phase diagram below draw a path that shows this set of changes. 0 0 200 temperature (K) 400 аarrow_forwarder your payment details | bar xb Home | bartleby x + aleksogi/x/isl.exe/1o u-lgNskr7j8P3jH-1Qs_pBanHhviTCeeBZbufuBYT0Hz7m7D3ZcW81NC1d8Kzb4srFik1OUFhKMUXzhGpw7k1 O States of Matter Sketching a described thermodynamic change on a phase diagram 0/5 The pressure on a sample of pure X held at 47. °C and 0.88 atm is increased until the sample condenses. The pressure is then held constant and the temperature is decreased by 82. °C. On the phase diagram below draw a path that shows this set of changes. pressure (atm) 1 3- 0- 0 200 Explanation Check temperature (K) 400 X Q Search L G 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved Terms of Use Privacy Cearrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry: A Guided Inquiry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780618974122
Author:Andrei Straumanis
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305580350
Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. Foote
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Enzymes - Effect of cofactors on enzyme; Author: Tutorials Point (India) Ltd;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=AkAbIwxyUs4;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY
Enzyme Catalysis Part-I; Author: NPTEL-NOC IITM;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=aZE740JWZuQ;License: Standard Youtube License