
(a)
Interpretation:
The bond which can be easily broken for the conversion of compound 6 to 7 and 8 needs to be determined.
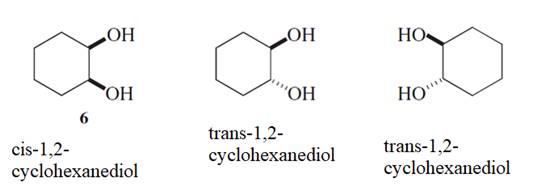
Concept Introduction :
Stereoisomers are the isomers with different spatial arrangement of the atoms, instead of order of atomic connectivity. It has the same molecular formula and the similar connectivity except for the procedure within 2D or 3D space. Like cis- and trans-but-2-ene both have two CH3 groups 2-H and a C=C but connectivity is different in the space.
(b)
Interpretation:
The value of
Concept Introduction :
Stereoisomers are the isomers with different spatial arrangement of the atoms, instead of order of atomic connectivity. It has the same molecular formula and the similar connectivity except for the procedure within 2D or 3D space. Like cis- and trans-but-2-ene both have two CH3 groups 2-H and a C=C but connectivity is different in the space.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 7 Solutions
EBK EXPERIMENTAL ORGANIC CHEMISTRY: A M
- What is the name of the following compound? SiMe3arrow_forwardK Draw the starting structure that would lead to the major product shown under the provided conditions. Drawing 1. NaNH2 2. PhCH2Br 4 57°F Sunny Q Searcharrow_forward7 Draw the starting alkyl bromide that would produce this alkyne under these conditions. F Drawing 1. NaNH2, A 2. H3O+ £ 4 Temps to rise Tomorrow Q Search H2arrow_forward
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
