
CONNECT FOR THERMODYNAMICS: AN ENGINEERI
9th Edition
ISBN: 9781260048636
Author: CENGEL
Publisher: MCG
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 7.13, Problem 51P
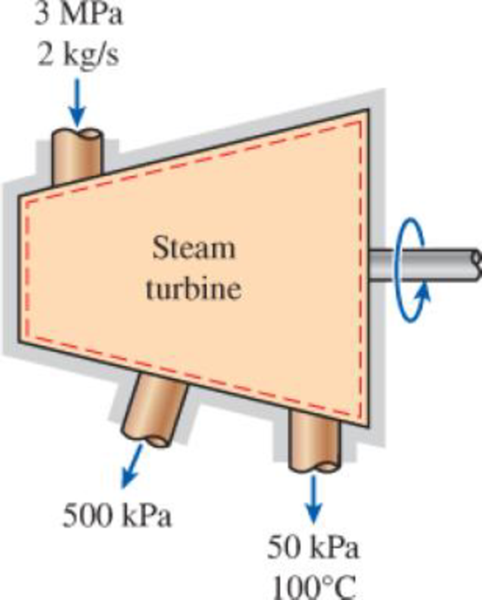
An isentropic steam turbine processes 2 kg/s of steam at 3 MPa, which is exhausted at 50 kPa and 100°C. Five percent of this flow is diverted for feedwater heating at 500 kPa.
FIGURE P7–51
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
12)
A particle is moving along a circular path having a radius of
6 in. such that its position as a function of time is given by
0 = sin 3t, where 0 is in radians, the argument for the sine are
in radians, and t is in seconds. Determine the acceleration of
the particle at 0 = 30°. The particle starts from rest at
0 = 0°.
6)
==
The particle travels along the path defined by the parabola
y 0.5x2. If the component of velocity along the x axis is
Vx =
(5t) ft/s, where t is in seconds, determine the particle's
distance from the origin O and the magnitude of its
acceleration when t = 1s. When t 0, x = 0, y = 0.
=
7)
Determine the minimum initial velocity vo and the
corresponding angle 00 at which the ball must be kicked in
order for it to just cross over the 3-m high fence.
VO
θα
6 m
3 m
Chapter 7 Solutions
CONNECT FOR THERMODYNAMICS: AN ENGINEERI
Ch. 7.13 - Does a cycle for which Q 0 violate the Clausius...Ch. 7.13 - Does the cyclic integral of heat have to be zero...Ch. 7.13 - Is a quantity whose cyclic integral is zero...Ch. 7.13 - Prob. 4PCh. 7.13 - Prob. 5PCh. 7.13 - How do the values of the integral 12Q/T compare...Ch. 7.13 - Prob. 7PCh. 7.13 - The entropy of a hot baked potato decreases as it...Ch. 7.13 - When a system is adiabatic, what can be said about...Ch. 7.13 - Prob. 10P
Ch. 7.13 - A pistoncylinder device contains helium gas....Ch. 7.13 - A pistoncylinder device contains nitrogen gas....Ch. 7.13 - A pistoncylinder device contains superheated...Ch. 7.13 - The entropy of steam will (increase, decrease,...Ch. 7.13 - During a heat transfer process, the entropy of a...Ch. 7.13 - Steam is accelerated as it flows through an actual...Ch. 7.13 - Heat is transferred at a rate of 2 kW from a hot...Ch. 7.13 - A completely reversible air conditioner provides...Ch. 7.13 - Heat in the amount of 100 kJ is transferred...Ch. 7.13 - In Prob. 719, assume that the heat is transferred...Ch. 7.13 - During the isothermal heat addition process of a...Ch. 7.13 - Prob. 22PCh. 7.13 - During the isothermal heat rejection process of a...Ch. 7.13 - Air is compressed by a 40-kW compressor from P1 to...Ch. 7.13 - Refrigerant-134a enters the coils of the...Ch. 7.13 - A rigid tank contains an ideal gas at 40C that is...Ch. 7.13 - A rigid vessel is filled with a fluid from a...Ch. 7.13 - A rigid vessel filled with a fluid is allowed to...Ch. 7.13 - Prob. 29PCh. 7.13 - One lbm of R-134a is expanded isentropically in a...Ch. 7.13 - Two lbm of water at 300 psia fill a weighted...Ch. 7.13 - A well-insulated rigid tank contains 3 kg of a...Ch. 7.13 - Using the relation ds = (Q/T)int rev for the...Ch. 7.13 - The radiator of a steam heating system has a...Ch. 7.13 - A rigid tank is divided into two equal parts by a...Ch. 7.13 - Prob. 36PCh. 7.13 - An insulated pistoncylinder device contains 5 L of...Ch. 7.13 - Onekg of R-134a initially at 600 kPa and 25C...Ch. 7.13 - Refrigerant-134a is expanded isentropically from...Ch. 7.13 - Refrigerant-134a at 320 kPa and 40C undergoes an...Ch. 7.13 - A rigid tank contains 5 kg of saturated vapor...Ch. 7.13 - A 0.5-m3 rigid tank contains refrigerant-134a...Ch. 7.13 - Steam enters a steady-flow adiabatic nozzle with a...Ch. 7.13 - Steam enters an adiabatic diffuser at 150 kPa and...Ch. 7.13 - R-134a vapor enters into a turbine at 250 psia and...Ch. 7.13 - Refrigerant-134a enters an adiabatic compressor as...Ch. 7.13 - The compressor in a refrigerator compresses...Ch. 7.13 - An isentropic steam turbine processes 2 kg/s of...Ch. 7.13 - Prob. 52PCh. 7.13 - Twokg of saturated water vapor at 600 kPa are...Ch. 7.13 - A pistoncylinder device contains 5 kg of steam at...Ch. 7.13 - Prob. 55PCh. 7.13 - In Prob. 755, the water is stirred at the same...Ch. 7.13 - Prob. 57PCh. 7.13 - Prob. 58PCh. 7.13 - Determine the total heat transfer for the...Ch. 7.13 - Calculate the heat transfer, in kJ/kg. for the...Ch. 7.13 - Prob. 61PCh. 7.13 - An adiabatic pump is to be used to compress...Ch. 7.13 - Prob. 63PCh. 7.13 - Prob. 64PCh. 7.13 - A 30-kg aluminum block initially at 140C is...Ch. 7.13 - A 50-kg copper block initially at 140C is dropped...Ch. 7.13 - A 30-kg iron block and a 40-kg copper block, both...Ch. 7.13 - Prob. 69PCh. 7.13 - Prob. 70PCh. 7.13 - Can the entropy of an ideal gas change during an...Ch. 7.13 - An ideal gas undergoes a process between two...Ch. 7.13 - Prob. 73PCh. 7.13 - Air is expanded from 200 psia and 500F to 100 psia...Ch. 7.13 - Prob. 75PCh. 7.13 - Air is expanded isentropically from 100 psia and...Ch. 7.13 - Which of the two gaseshelium or nitrogenhas the...Ch. 7.13 - Which of the two gasesneon or airhas the lower...Ch. 7.13 - A 1.5-m3 insulated rigid tank contains 2.7 kg of...Ch. 7.13 - An insulated pistoncylinder device initially...Ch. 7.13 - A pistoncylinder device contains 0.75 kg of...Ch. 7.13 - A mass of 25 lbm of helium undergoes a process...Ch. 7.13 - One kg of air at 200 kPa and 127C is contained in...Ch. 7.13 - An insulated rigid tank is divided into two equal...Ch. 7.13 - Air at 27C and 100 kPa is contained in a...Ch. 7.13 - Air at 3.5 MPa and 500C is expanded in an...Ch. 7.13 - Air is compressed in a pistoncylinder device from...Ch. 7.13 - Helium gas is compressed from 90 kPa and 30C to...Ch. 7.13 - Nitrogen at 120 kPa and 30C is compressed to 600...Ch. 7.13 - Five kg of air at 427C and 600 kPa are contained...Ch. 7.13 - Prob. 92PCh. 7.13 - Prob. 93PCh. 7.13 - Prob. 94PCh. 7.13 - The well-insulated container shown in Fig. P 795E...Ch. 7.13 - An insulated rigid tank contains 4 kg of argon gas...Ch. 7.13 - Prob. 97PCh. 7.13 - Prob. 98PCh. 7.13 - Prob. 99PCh. 7.13 - It is well known that the power consumed by a...Ch. 7.13 - Calculate the work produced, in kJ/kg, for the...Ch. 7.13 - Prob. 102PCh. 7.13 - Prob. 103PCh. 7.13 - Saturated water vapor at 150C is compressed in a...Ch. 7.13 - Liquid water at 120 kPa enters a 7-kW pump where...Ch. 7.13 - Water enters the pump of a steam power plant as...Ch. 7.13 - Consider a steam power plant that operates between...Ch. 7.13 - Saturated refrigerant-134a vapor at 15 psia is...Ch. 7.13 - Helium gas is compressed from 16 psia and 85F to...Ch. 7.13 - Nitrogen gas is compressed from 80 kPa and 27C to...Ch. 7.13 - Describe the ideal process for an (a) adiabatic...Ch. 7.13 - Is the isentropic process a suitable model for...Ch. 7.13 - On a T-s diagram, does the actual exit state...Ch. 7.13 - Argon gas enters an adiabatic turbine at 800C and...Ch. 7.13 - Steam at 100 psia and 650F is expanded...Ch. 7.13 - Combustion gases enter an adiabatic gas turbine at...Ch. 7.13 - Steam at 4 MPa and 350C is expanded in an...Ch. 7.13 - Prob. 120PCh. 7.13 - Prob. 121PCh. 7.13 - Refrigerant-134a enters an adiabatic compressor as...Ch. 7.13 - The adiabatic compressor of a refrigeration system...Ch. 7.13 - Prob. 125PCh. 7.13 - Argon gas enters an adiabatic compressor at 14...Ch. 7.13 - Prob. 127PCh. 7.13 - Air enters an adiabatic nozzle at 45 psia and 940F...Ch. 7.13 - An adiabatic diffuser at the inlet of a jet engine...Ch. 7.13 - Hot combustion gases enter the nozzle of a...Ch. 7.13 - The exhaust nozzle of a jet engine expands air at...Ch. 7.13 - Prob. 133PCh. 7.13 - Refrigerant-134a is expanded adiabatically from...Ch. 7.13 - A frictionless pistoncylinder device contains...Ch. 7.13 - Prob. 136PCh. 7.13 - Steam enters an adiabatic turbine steadily at 7...Ch. 7.13 - Prob. 138PCh. 7.13 - Oxygen enters an insulated 12-cm-diameter pipe...Ch. 7.13 - Water at 20 psia and 50F enters a mixing chamber...Ch. 7.13 - Prob. 141PCh. 7.13 - Prob. 142PCh. 7.13 - In a dairy plant, milk at 4C is pasteurized...Ch. 7.13 - Steam is to be condensed in the condenser of a...Ch. 7.13 - An ordinary egg can be approximated as a...Ch. 7.13 - Prob. 146PCh. 7.13 - In a production facility, 1.2-in-thick, 2-ft 2-ft...Ch. 7.13 - Prob. 148PCh. 7.13 - Prob. 149PCh. 7.13 - Prob. 150PCh. 7.13 - Prob. 151PCh. 7.13 - Prob. 152PCh. 7.13 - Prob. 153PCh. 7.13 - Liquid water at 200 kPa and 15C is heated in a...Ch. 7.13 - Prob. 155PCh. 7.13 - Prob. 157PCh. 7.13 - Prob. 158PCh. 7.13 - Prob. 159PCh. 7.13 - Prob. 160PCh. 7.13 - The compressed-air requirements of a plant are met...Ch. 7.13 - Prob. 162PCh. 7.13 - The space heating of a facility is accomplished by...Ch. 7.13 - Prob. 164PCh. 7.13 - Prob. 165PCh. 7.13 - Prob. 166PCh. 7.13 - Prob. 167RPCh. 7.13 - A refrigerator with a coefficient of performance...Ch. 7.13 - What is the minimum internal energy that steam can...Ch. 7.13 - Prob. 170RPCh. 7.13 - What is the maximum volume that 3 kg of oxygen at...Ch. 7.13 - A 100-lbm block of a solid material whose specific...Ch. 7.13 - Prob. 173RPCh. 7.13 - A pistoncylinder device initially contains 15 ft3...Ch. 7.13 - A pistoncylinder device contains steam that...Ch. 7.13 - Prob. 176RPCh. 7.13 - Prob. 177RPCh. 7.13 - Prob. 178RPCh. 7.13 - A 0.8-m3 rigid tank contains carbon dioxide (CO2)...Ch. 7.13 - Air enters the evaporator section of a window air...Ch. 7.13 - Prob. 181RPCh. 7.13 - Prob. 182RPCh. 7.13 - Prob. 183RPCh. 7.13 - Prob. 184RPCh. 7.13 - Helium gas is throttled steadily from 400 kPa and...Ch. 7.13 - Determine the work input and entropy generation...Ch. 7.13 - Prob. 187RPCh. 7.13 - Reconsider Prob. 7187. Determine the change in the...Ch. 7.13 - Prob. 189RPCh. 7.13 - Air enters a two-stage compressor at 100 kPa and...Ch. 7.13 - Three kg of helium gas at 100 kPa and 27C are...Ch. 7.13 - Steam at 6 MPa and 500C enters a two-stage...Ch. 7.13 - Prob. 193RPCh. 7.13 - Prob. 194RPCh. 7.13 - Refrigerant-134a enters a compressor as a...Ch. 7.13 - Prob. 196RPCh. 7.13 - Prob. 197RPCh. 7.13 - Prob. 198RPCh. 7.13 - Prob. 199RPCh. 7.13 - Prob. 200RPCh. 7.13 - Prob. 201RPCh. 7.13 - Prob. 202RPCh. 7.13 - Prob. 203RPCh. 7.13 - Prob. 204RPCh. 7.13 - Prob. 205RPCh. 7.13 - Prob. 206RPCh. 7.13 - Prob. 207RPCh. 7.13 - Prob. 208RPCh. 7.13 - (a) Water flows through a shower head steadily at...Ch. 7.13 - Prob. 211RPCh. 7.13 - Prob. 212RPCh. 7.13 - Prob. 213RPCh. 7.13 - Consider the turbocharger of an internal...Ch. 7.13 - Prob. 215RPCh. 7.13 - Prob. 216RPCh. 7.13 - A 5-ft3 rigid tank initially contains...Ch. 7.13 - Prob. 218RPCh. 7.13 - Show that the difference between the reversible...Ch. 7.13 - Demonstrate the validity of the Clausius...Ch. 7.13 - Consider two bodies of identical mass m and...Ch. 7.13 - Consider a three-stage isentropic compressor with...Ch. 7.13 - Prob. 223RPCh. 7.13 - Prob. 224RPCh. 7.13 - Prob. 225RPCh. 7.13 - The polytropic or small stage efficiency of a...Ch. 7.13 - Steam is condensed at a constant temperature of...Ch. 7.13 - Steam is compressed from 6 MPa and 300C to 10 MPa...Ch. 7.13 - An apple with a mass of 0.12 kg and average...Ch. 7.13 - A pistoncylinder device contains 5 kg of saturated...Ch. 7.13 - Argon gas expands in an adiabatic turbine from 3...Ch. 7.13 - A unit mass of a substance undergoes an...Ch. 7.13 - A unit mass of an ideal gas at temperature T...Ch. 7.13 - Heat is lost through a plane wall steadily at a...Ch. 7.13 - Air is compressed steadily and adiabatically from...Ch. 7.13 - Argon gas expands in an adiabatic turbine steadily...Ch. 7.13 - Water enters a pump steadily at 100 kPa at a rate...Ch. 7.13 - Air is to be compressed steadily and...Ch. 7.13 - Helium gas enters an adiabatic nozzle steadily at...Ch. 7.13 - Combustion gases with a specific heat ratio of 1.3...Ch. 7.13 - Steam enters an adiabatic turbine steadily at 400C...Ch. 7.13 - Liquid water enters an adiabatic piping system at...Ch. 7.13 - Liquid water is to be compressed by a pump whose...Ch. 7.13 - Steam enters an adiabatic turbine at 8 MPa and...Ch. 7.13 - Helium gas is compressed steadily from 90 kPa and...Ch. 7.13 - Helium gas is compressed from 1 atm and 25C to a...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 11) = If a particle moves along a path such that r = (2 cost) ft and (t/2) rad, where t is in seconds, plot the path r = f(0) and determine the particle's radial and transverse components of velocity and acceleration.arrow_forward9) The car travels around the circular track having a radius of r = 300 m such that when it is at point A it has a velocity of 5 m/s, which is increasing at the rate of v = (0.06t) m/s², where t is in seconds. Determine the magnitudes of its velocity and acceleration when it has traveled one-third the way around the track.arrow_forward15) Two boats leave the pier P at the same time and travel in the directions shown. If v = 40 ft/s and vB = 30 ft/s, VA determine the velocity of boat A relative to boat B. How long after leaving the pier will the boats be 1500 ft apart? =40 ft/s UB=30 ft/s 30° 45°arrow_forward
- 14) Determine the time needed for the load at B to attain a speed of 10 m/s, starting from rest, if the cable is drawn into the motor with an acceleration of 3 m/s². C Barrow_forward13) Starting from rest, the cable can be wound onto the drum of the motor at a rate of v₁ = (31²) m/s, where t is in seconds. Determine the time needed to lift the load 7 m. 40 D A C Barrow_forward13) Starting from rest, the cable can be wound onto the drum of the motor at a rate of v₁ = (31²) m/s, where t is in seconds. Determine the time needed to lift the load 7 m.arrow_forward
- 10) At a given instant the train engine at E has a speed of 20 m/s and an acceleration of 14 m/s² acting in the direction shown. Determine the rate of increase in the train's speed and the radius of curvature p of the path. Ans. a 14 m/s² E v = 20 m/sarrow_forward8) The satellite S travels around the earth in a circular path with a constant speed of 20 Mm/h. If the acceleration is 2.5 m/s², determine the altitude h. Assume the earth's diameter to be 12 713 km.arrow_forward5) A particle, originally at rest and located at point (3 ft, 2 ft, 5 ft), is subjected to an acceleration a = {6ti 12 k} ft/s². Determine the particle's position (x, y, z) when t=2s.arrow_forward
- 4) A sandbag is dropped from a balloon which is ascending vertically at a constant speed of 6 m/s. If the bag is released with the same upward velocity of 6 m/s when t = O and hits the ground when t = 8 s, determine the speed of the bag as it hits the ground and the altitude of the balloon at this instant.arrow_forward3) A ball A is thrown vertically upward from the top of a 30-m-high building with an initial velocity of 5 m/s. At the same instant another ball B is thrown upward from the ground with an initial velocity of 20 m/s. Determine the height from the ground and the time at which they pass.arrow_forward1) = - The position of a particle along a straight line is given by (1.5t3 13.52 + 22.5t) ft, where t is in seconds. Determine the position of the particle when t = 6s and the total distance it travels during the 6-s time interval. Hint: Plot the path to determine the total distance traveled.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Refrigeration and Air Conditioning Technology (Mi...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305578296Author:John Tomczyk, Eugene Silberstein, Bill Whitman, Bill JohnsonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Refrigeration and Air Conditioning Technology (Mi...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305578296Author:John Tomczyk, Eugene Silberstein, Bill Whitman, Bill JohnsonPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Heat Transfer (Activate Learning wi...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305387102Author:Kreith, Frank; Manglik, Raj M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Heat Transfer (Activate Learning wi...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305387102Author:Kreith, Frank; Manglik, Raj M.Publisher:Cengage Learning

Refrigeration and Air Conditioning Technology (Mi...
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781305578296
Author:John Tomczyk, Eugene Silberstein, Bill Whitman, Bill Johnson
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Heat Transfer (Activate Learning wi...
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781305387102
Author:Kreith, Frank; Manglik, Raj M.
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Power Plant Explained | Working Principles; Author: RealPars;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=HGVDu1z5YQ8;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY