
(a)
To prove: The sequence of equations
Also, give the reason behind the negative square root chosen in the last equation.
(b)
To prove: The formula
(c)
To prove: The elliptical integral
(d)
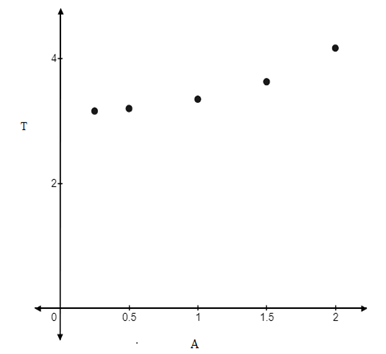
The values of
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 7 Solutions
DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS-NEXTGEN WILEYPLUS
- answer number 2arrow_forward4. Linear Regression - Model Assumptions and Interpretation A real estate analyst is studying how house prices (Y) are related to house size in square feet (X). A simple linear regression model is proposed: The analyst fits the model and obtains: • Ŷ50,000+150X YBoB₁X + € • R² = 0.76 • Residuals show a fan-shaped pattern when plotted against fitted values. Questions: a) Interpret the slope coefficient in context. b) Explain what the R² value tells us about the model's performance. c) Based on the residual pattern, what regression assumption is likely violated? What might be the consequence? d) Suggest at least two remedies to improve the model, based on the residual analysis.arrow_forward5. Probability Distributions – Continuous Random Variables A factory machine produces metal rods whose lengths (in cm) follow a continuous uniform distribution on the interval [98, 102]. Questions: a) Define the probability density function (PDF) of the rod length.b) Calculate the probability that a randomly selected rod is shorter than 99 cm.c) Determine the expected value and variance of rod lengths.d) If a sample of 25 rods is selected, what is the probability that their average length is between 99.5 cm and 100.5 cm? Justify your answer using the appropriate distribution.arrow_forward
- 2. Hypothesis Testing - Two Sample Means A nutritionist is investigating the effect of two different diet programs, A and B, on weight loss. Two independent samples of adults were randomly assigned to each diet for 12 weeks. The weight losses (in kg) are normally distributed. Sample A: n = 35, 4.8, s = 1.2 Sample B: n=40, 4.3, 8 = 1.0 Questions: a) State the null and alternative hypotheses to test whether there is a significant difference in mean weight loss between the two diet programs. b) Perform a hypothesis test at the 5% significance level and interpret the result. c) Compute a 95% confidence interval for the difference in means and interpret it. d) Discuss assumptions of this test and explain how violations of these assumptions could impact the results.arrow_forward1. Sampling Distribution and the Central Limit Theorem A company produces batteries with a mean lifetime of 300 hours and a standard deviation of 50 hours. The lifetimes are not normally distributed—they are right-skewed due to some batteries lasting unusually long. Suppose a quality control analyst selects a random sample of 64 batteries from a large production batch. Questions: a) Explain whether the distribution of sample means will be approximately normal. Justify your answer using the Central Limit Theorem. b) Compute the mean and standard deviation of the sampling distribution of the sample mean. c) What is the probability that the sample mean lifetime of the 64 batteries exceeds 310 hours? d) Discuss how the sample size affects the shape and variability of the sampling distribution.arrow_forwardAn airplane flies due west at an airspeed of 428 mph. The wind blows in the direction of 41° south of west at 50 mph. What is the ground speed of the airplane? What is the bearing of the airplane? 428 mph 41° 50 mph a. The ground speed of the airplane is b. The bearing of the airplane is mph. south of west.arrow_forward
- Rylee's car is stuck in the mud. Roman and Shanice come along in a truck to help pull her out. They attach one end of a tow strap to the front of the car and the other end to the truck's trailer hitch, and the truck starts to pull. Meanwhile, Roman and Shanice get behind the car and push. The truck generates a horizontal force of 377 lb on the car. Roman and Shanice are pushing at a slight upward angle and generate a force of 119 lb on the car. These forces can be represented by vectors, as shown in the figure below. The angle between these vectors is 20.2°. Find the resultant force (the vector sum), then give its magnitude and its direction angle from the positive x-axis. 119 lb 20.2° 377 lb a. The resultant force is (Tip: omit degree notations from your answers; e.g. enter cos(45) instead of cos(45°)) b. It's magnitude is lb. c. It's angle from the positive x-axis isarrow_forwardComplete the table below. For solutions, round to the nearest whole number.arrow_forwardA biologist is investigating the effect of potential plant hormones by treating 20 stem segments. At the end of the observation period he computes the following length averages: Compound X = 1.18 Compound Y = 1.17 Based on these mean values he concludes that there are no treatment differences. 1) Are you satisfied with his conclusion? Why or why not? 2) If he asked you for help in analyzing these data, what statistical method would you suggest that he use to come to a meaningful conclusion about his data and why? 3) Are there any other questions you would ask him regarding his experiment, data collection, and analysis methods?arrow_forward
- Businessarrow_forwardAnswer first questionarrow_forwardLet the universal set be whole numbers 1 through 20 inclusive. That is, U = {1, 2, 3, 4, . . ., 19, 20}. Let A, B, and C be subsets of U. Let A be the set of all prime numbers: A = {2, 3, 5, 7, 11, 13, 17, 19} Let B be the set of all odd numbers: B = {1,3,5,7, . . ., 17, 19} Let C be the set of all square numbers: C = {1,4,9,16}arrow_forward
 Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)TrigonometryISBN:9781337278461Author:Ron LarsonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)TrigonometryISBN:9781337278461Author:Ron LarsonPublisher:Cengage Learning
