
EBK CAMPBELL BIOLOGY IN FOCUS
2nd Edition
ISBN: 8220101459299
Author: Reece
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 7, Problem 8TYU
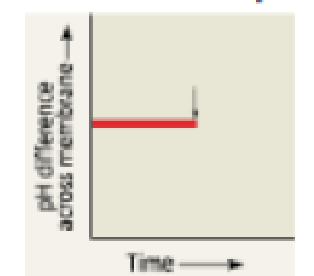
DRAW IT The graph here shows the pH difference across the inner mitochondrial membrane over time in an actively respiring cell. At the time indicated by the vertical arrow, a
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Please help me to draw this by hand. In as much detail as possible, hand draw a schematic diagram of the hypothalamic-pituitary-gonad (HPG) axis in the human female. Be sure to include all the relevant structures and hormones. You must define all abbreviations the first time you use them. Please include (and explain) the feedback loops.
Please refer below
AaBbCc X AaBbCc individuals are crossed.
What is the probability of their offspring having a genotype AABBCC?
Chapter 7 Solutions
EBK CAMPBELL BIOLOGY IN FOCUS
Ch. 7.1 - Compare and contrast aerobic and anaerobic...Ch. 7.1 - Name and describe the two ways in which ATP is...Ch. 7.1 - Prob. 3CCCh. 7.2 - During step 6 in Figure 7.9, which molecule acts...Ch. 7.3 - Name the molecules that conserve most of the...Ch. 7.3 - Prob. 2CCCh. 7.4 - Prob. 1CCCh. 7.4 - Prob. 2CCCh. 7.4 - MAKE CONNECTIONS Membranes must be fluid to...Ch. 7.5 - Prob. 1CC
Ch. 7.5 - WHAT IF? A glucose-fed yeast cell is moved from an...Ch. 7.6 - MAKE CONNECTIONS Compare the structure of a fat...Ch. 7.6 - Prob. 2CCCh. 7.6 - WHAT IF? During intense exercise, can a muscle...Ch. 7 - The immediate energy source that drives ATP...Ch. 7 - Which metabolic pathway is common to both...Ch. 7 - In mitochondria, exergonic redox reactions A. are...Ch. 7 - The final electron acceptor of the electron...Ch. 7 - What is the oxidizing agent in the following...Ch. 7 - When electrons flow along the electron transport...Ch. 7 - Most co, from catabolism is released during A....Ch. 7 - DRAW IT The graph here shows the pH difference...Ch. 7 - INTERPRET THE DATA Phosphofructokinase is an...Ch. 7 - Prob. 10TYUCh. 7 - FOCUS ON EVOLUTION ATP synthases are found in the...Ch. 7 - Prob. 12TYUCh. 7 - Prob. 13TYU
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
1. Rub your hands together vigorously. What happens? Discuss the energy transfers and transformations that take...
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (3rd Edition)
Single penny tossed 20 times and counting heads and tails: Probability (prediction): _______/20 heads ________/...
Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & Physiology
How does the removal of hydrogen atoms from nutrient molecules result in a loss of energy from the nutrient mol...
SEELEY'S ANATOMY+PHYSIOLOGY
The validity of a scientific law.
Physical Universe
An obese 55-year-old woman consults her physician about minor chest pains during exercise. Explain the physicia...
Biology: Life on Earth with Physiology (11th Edition)
Choose the best answer to each of the following. Explain your reasoning. If Earth were twice as far as it actua...
Cosmic Perspective Fundamentals
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- circle a nucleotide in the imagearrow_forward"One of the symmetry breaking events in mouse gastrulation requires the amplification of Nodal on the side of the embryo opposite to the Anterior Visceral Endoderm (AVE). Describe one way by which Nodal gets amplified in this region." My understanding of this is that there are a few ways nodal is amplified though I'm not sure if this is specifically occurs on the opposite side of the AVE. 1. pronodal cleaved by protease -> active nodal 2. Nodal -> BMP4 -> Wnt-> nodal 3. Nodal-> Nodal, Fox1 binding site 4. BMP4 on outside-> nodal Are all of these occuring opposite to AVE?arrow_forwardIf four babies are born on a given day What is the chance all four will be girls? Use genetics lawsarrow_forward
- Explain each punnet square results (genotypes and probabilities)arrow_forwardGive the terminal regression line equation and R or R2 value: Give the x axis (name and units, if any) of the terminal line: Give the y axis (name and units, if any) of the terminal line: Give the first residual regression line equation and R or R2 value: Give the x axis (name and units, if any) of the first residual line : Give the y axis (name and units, if any) of the first residual line: Give the second residual regression line equation and R or R2 value: Give the x axis (name and units, if any) of the second residual line: Give the y axis (name and units, if any) of the second residual line: a) B1 Solution b) B2 c)hybrid rate constant (λ1) d)hybrid rate constant (λ2) e) ka f) t1/2,absorb g) t1/2, dist h) t1/2, elim i)apparent central compartment volume (V1,app) j) total AUC (short cut method) k) apparent volume of distribution based on AUC (VAUC,app) l)apparent clearance (CLapp) m) absolute bioavailability of oral route (need AUCiv…arrow_forwardYou inject morpholino oligonucleotides that inhibit the translation of follistatin, chordin, and noggin (FCN) at the 1 cell stage of a frog embryo. What is the effect on neurulation in the resulting embryo? Propose an experiment that would rescue an embryo injected with FCN morpholinos.arrow_forward
- Participants will be asked to create a meme regarding a topic relevant to the department of Geography, Geomatics, and Environmental Studies. Prompt: Using an online art style of your choice, please make a meme related to the study of Geography, Environment, or Geomatics.arrow_forwardPlekhg5 functions in bottle cell formation, and Shroom3 functions in neural plate closure, yet the phenotype of injecting mRNA of each into the animal pole of a fertilized egg is very similar. What is the phenotype, and why is the phenotype so similar? Is the phenotype going to be that there is a disruption of the formation of the neural tube for both of these because bottle cell formation is necessary for the neural plate to fold in forming the neural tube and Shroom3 is further needed to close the neural plate? So since both Plekhg5 and Shroom3 are used in forming the neural tube, injecting the mRNA will just lead to neural tube deformity?arrow_forwardWhat are some medical issues or health trends that may have a direct link to the idea of keeping fat out of diets?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Human Physiology: From Cells to Systems (MindTap ...BiologyISBN:9781285866932Author:Lauralee SherwoodPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Physiology: From Cells to Systems (MindTap ...BiologyISBN:9781285866932Author:Lauralee SherwoodPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning Concepts of BiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168116Author:Samantha Fowler, Rebecca Roush, James WisePublisher:OpenStax College
Concepts of BiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168116Author:Samantha Fowler, Rebecca Roush, James WisePublisher:OpenStax College BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305577206Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. GrishamPublisher:Cengage Learning
BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305577206Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. GrishamPublisher:Cengage Learning

Human Physiology: From Cells to Systems (MindTap ...
Biology
ISBN:9781285866932
Author:Lauralee Sherwood
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Biology 2e
Biology
ISBN:9781947172517
Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann Clark
Publisher:OpenStax

Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)
Biology
ISBN:9781305389892
Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillan
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Concepts of Biology
Biology
ISBN:9781938168116
Author:Samantha Fowler, Rebecca Roush, James Wise
Publisher:OpenStax College

Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:9781305577206
Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. Grisham
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Mitochondrial mutations; Author: Useful Genetics;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=GvgXe-3RJeU;License: CC-BY