
Chemistry for Engineering Students
3rd Edition
ISBN: 9781285199023
Author: Lawrence S. Brown, Tom Holme
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 7, Problem 7.77PAE
7.69 Propene has the chemical formula 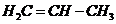 Describe the overall shape of the molecule by considering the geometry around each carbon atom.
Describe the overall shape of the molecule by considering the geometry around each carbon atom.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Can you please help me with drawing the Lewis structure of each molecular formula?I truly appreciate you!
Can you please help me with drawing the Lewis structure of each molecular formula?I truly appreciate you!
Please draw and explain
Chapter 7 Solutions
Chemistry for Engineering Students
Ch. 7 - List some factors influencing the biocompatibility...Ch. 7 - • use electron configurations to explain why...Ch. 7 - • describe die energy changes in the formation of...Ch. 7 - • define electronegativity and state how...Ch. 7 - • identify or predict polar, nonpolar, and ionic...Ch. 7 - • write Lewis electron structures for molecules or...Ch. 7 - • describe chemical bonding using a model based on...Ch. 7 - • explain how hybridization reconciles observed...Ch. 7 - • predict the geometry of a molecule from its,...Ch. 7 - • use models (real or software) to help visualize...
Ch. 7 - • explain the formation of multiple bonds in terms...Ch. 7 - • identify sigma and pi bonds in a molecule and...Ch. 7 - Define the term biocompatibility.Ch. 7 - List some properties associated with biomaterials...Ch. 7 - Prob. 7.3PAECh. 7 - Prob. 7.4PAECh. 7 - Prob. 7.5PAECh. 7 - Prob. 7.6PAECh. 7 - Why is the ion not found in nature?Ch. 7 - Why do nonmetals tend to form anions rather than...Ch. 7 - Prob. 7.9PAECh. 7 - 7.10 Arrange the members of each of the following...Ch. 7 - 7.11 Arrange the following sets of anions in order...Ch. 7 - 7.12 Which pair will form a compound with the...Ch. 7 - In a lattice, a positive ion is often surrounded...Ch. 7 - Use the concept of lattice energy to rationalize...Ch. 7 - 7.13 Figure 7-2 depicts the interactions of an ion...Ch. 7 - Mat type of bond is likely to form between one...Ch. 7 - 7.14 Describe the difference between a covalent...Ch. 7 - Prob. 7.18PAECh. 7 - Sketch a graph of the potential energy of two...Ch. 7 - Prob. 7.20PAECh. 7 - 7.17 Coulombic forces are often used to explain...Ch. 7 - 7.18 In terms of the strengths of the covalent...Ch. 7 - 7.19 If the formation of chemical bonds always...Ch. 7 - 7.20 Draw the Lewis dot symbol for each of the...Ch. 7 - 7.21 Theoretical models for the structure of...Ch. 7 - 7.22 Use Lewis dot symbols to explain why chlorine...Ch. 7 - 7.23 Define the term lone pair.Ch. 7 - 7.24 How many electrons are shared between two...Ch. 7 - 7.25 How does the bond energy of a double bond...Ch. 7 - 7.26 How is electronegativity defined?Ch. 7 - 7.27 Distinguish between electron affinity and...Ch. 7 - 7.28 Certain elements in the periodic table shown...Ch. 7 - 7.29 When two atoms with different...Ch. 7 - 7.30 The bond in HF is said to be polar, with the...Ch. 7 - 7.31 Why is a bond between two atoms with...Ch. 7 - Prob. 7.36PAECh. 7 - 7.33 In each group of three bonds, which bond is...Ch. 7 - Prob. 7.38PAECh. 7 - Prob. 7.39PAECh. 7 - 7.35 Which one of the following contains botb...Ch. 7 - Prob. 7.41PAECh. 7 - Prob. 7.42PAECh. 7 - 7.37 Draw the Lewis structure for each of the...Ch. 7 - 7.38 Draw a Lewis structure for each of the...Ch. 7 - Prob. 7.45PAECh. 7 - 7.40 Why is it impossible for hydrogen to be the...Ch. 7 - Prob. 7.47PAECh. 7 - 7.42 Draw resonance structure for (a) (b) and (c)Ch. 7 - Prob. 7.49PAECh. 7 - Prob. 7.50PAECh. 7 - Prob. 7.51PAECh. 7 - 7.46 Consider the nitrogen-oxygen bond lengths in...Ch. 7 - 7.47 Which of the species listed has a Lewis...Ch. 7 - 7.48 Identify what is incorrect in the Lewis...Ch. 7 - 7.49 Identify what is incorrect in the Lewis...Ch. 7 - 7.50 Chemical species are said to be isoelectronic...Ch. 7 - 7.51 Explain the concept of wave interference in...Ch. 7 - Distinguish between constructive and destructive...Ch. 7 - How is the concept of orbital overlap related to...Ch. 7 - 7.52 How does orbital overlap explain the buildup...Ch. 7 - 7.53 How do sigma and pi bonds differ? How are...Ch. 7 - 7.54 CO , CO2 , CH3OH , and CO32 , all contain...Ch. 7 - 7.55 Draw the Lewis dot structure of the following...Ch. 7 - 7.56 Draw the Lewis dot structures of the...Ch. 7 - 7.57 What observation about molecules compels us...Ch. 7 - Prob. 7.66PAECh. 7 - 7.59 What type of hybrid orbital is generated by...Ch. 7 - Considering only s and p atomic orbitals, list all...Ch. 7 - 7.61 What hybrid orbitals would be expected for...Ch. 7 - 7.62 What type of hybridization would you expect...Ch. 7 - 7.63 What physical concept forms the premise of...Ch. 7 - 7.64 Predict the geometry of the following...Ch. 7 - Prob. 7.73PAECh. 7 - Prob. 7.74PAECh. 7 - Prob. 7.75PAECh. 7 - 7.68 Give approximate values for the indicated...Ch. 7 - 7.69 Propene has the chemical formula Describe the...Ch. 7 - Prob. 7.78PAECh. 7 - Describe what happens to the shape about the...Ch. 7 - Prob. 7.80PAECh. 7 - Prob. 7.81PAECh. 7 - 7.72 How does an MSN differ from amorphous silica...Ch. 7 - Prob. 7.83PAECh. 7 - Prob. 7.84PAECh. 7 - Prob. 7.85PAECh. 7 - Prob. 7.86PAECh. 7 - 7.91 A Lewis structure for the oxalate ion is...Ch. 7 - Prob. 7.88PAECh. 7 - 7.93 An unknown metal M forms a chloride with the...Ch. 7 - Prob. 7.90PAECh. 7 - Prob. 7.91PAECh. 7 - 7.96 Consider the hydrocarbons whose structures...Ch. 7 - 7.97 Consider the structure shown below for as...Ch. 7 - Prob. 7.94PAECh. 7 - Prob. 7.95PAECh. 7 - Prob. 7.96PAECh. 7 - 7.101 Lead selenide nanocrystals may provide a...Ch. 7 - Prob. 7.98PAECh. 7 - Prob. 7.99PAECh. 7 - 7.104 Hydrogen azide, HN3 , is a liquid that...Ch. 7 - Prob. 7.101PAECh. 7 - Prob. 7.102PAECh. 7 - 7.107 How do the Lewis symbols for C, Si, and Ge...Ch. 7 - Prob. 7.104PAECh. 7 - Prob. 7.105PAE
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Describe each highlighted bond in terms of the overlap of atomic orbitals. (a) Н Н H H [References] HIC H H C H H-C-CC-N: H σ character n character (b) HIC H H H H-C-C-C HIC H Н H O-H σ character n character Submit Answer Try Another Version 3 item attempts remainingarrow_forward11 Naming and drawing alcohols Write the systematic (IUPAC) name for each of the following organic molecules: structure OH HO OH Explanation Check name ☐arrow_forwardwhat is the drawn mechanism for diethyl carbonate and 4 - bromo - N, N -dimethylaniline to create crystal violet?arrow_forward
- Which of the following compounds are constitutional isomers of each other? I and II O II and III O III and IV OI and IV O II and IV CI H CI H CI H H CI H-C-C-CI C-C-C-CI H-C-C-CI H-C-C-CI H CI Ĥ ĆI A A Ĥ ĆI || IVarrow_forwardPlease correct answer and don't used hand raitingarrow_forwardQ1: Curved Arrows, Bronsted Acids & Bases, Lewis Acids & Bases Considering the following reactions: a) Predict the products to complete the reactions. b) Use curved electron-pushing arrows to show the mechanism for the reaction in the forward direction. Redraw some of the compounds to explicitly illustrate all bonds that are broken and all bonds that are formed. c) Label Bronsted acids and bases in the left side of the reactions. Label conjugate acids and bases in the right side of the reactions. d) Label Lewis acids and bases, nucleophiles and electrophiles in the left side of the reactions. A. + OH CH30: OH B. + HBr C. H₂SO4 D. CF 3. CH 3 + HCI N H fluoxetine antidepressant 1↓ JDownloadarrow_forward
- Don't used Ai solutionarrow_forwardPart 3: AHm,system Mass of 1.00 M HCI Vol. of 1.00 M HCI Mass of NaOH(s) Total Mass in Calorimeter Mole product if HCI limiting reactant Trial 1 62.4009 1.511g Mole product if NaOH limiting reactant Limiting reactant Initial Temperature Final Temperature 23.8°C 37.6°C Change in Temperature AHm,system (calculated) Average AHm,system (calculated) (calculated) (calculated) Trial 2 64.006g 1.9599 (calculated) (calculated) (calculated) (calculated) (calculated) (calculated) 24.7°C 41.9°C (calculated) (calculated) (2 pts. each)arrow_forwardDon't used Ai solutionarrow_forward
- What is the numerical value of the slope using the equation y=-1.823x -0.0162 please show calculationsarrow_forwardDon't used hand raitingarrow_forward1.) Using the graph below (including the line equation of y = -1.823x - 0.0162) What is the numerical value for the slope shown? 2.) What are the Unit(s) associated with the slope of the line shown? for we all remember that numerical data always has units. 3.) What would be a good title for this graph and explain your choice. 0.00 0.0 02 0.4 10.6 08 10 12 -0.20 -0.40 -0.60 -0.80 Temp, freezing, in degrees Celcius 5-1.00 -1.20 -1.40 -1:60 y=-1.823x-0.0162 -180 -2.00 Concentration of Sucrose (m)arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Chemistry for Engineering StudentsChemistryISBN:9781337398909Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom HolmePublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
Chemistry for Engineering StudentsChemistryISBN:9781337398909Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom HolmePublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning
General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning
World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry for Engineering Students
Chemistry
ISBN:9781337398909
Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom Holme
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry: Matter and Change
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078746376
Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl Wistrom
Publisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co

General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305580343
Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; Darrell
Publisher:Cengage Learning

World of Chemistry, 3rd edition
Chemistry
ISBN:9781133109655
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning

General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781285853918
Author:H. Stephen Stoker
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079250
Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed Peters
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Stoichiometry - Chemistry for Massive Creatures: Crash Course Chemistry #6; Author: Crash Course;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=UL1jmJaUkaQ;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY
Bonding (Ionic, Covalent & Metallic) - GCSE Chemistry; Author: Science Shorts;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=p9MA6Od-zBA;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY
General Chemistry 1A. Lecture 12. Two Theories of Bonding.; Author: UCI Open;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=dLTlL9Z1bh0;License: CC-BY