
(a)
Interpretation:
The hybridization of the central atom of the molecules with the following molecular geometries has to be predicted.
- (a) Tetrahedral (b) trigonal planar (c) trigonal bipyramidal (d) linear (e) octahedral
Concept Introduction:
Hybridization is a hypothetical concept. It refers to overlapping of atomic orbitals and the resultant orbitals formed are known as hybrid orbitals. An orbital that doesn’t involve in hybridization is termed as unhybridized orbital. After hybridization, the orbitals cannot be distinguished individually. The orientation of the orbitals while overlapping impacts the nature of the bond forms. By knowing the hybridization of central atom in the molecule its geometry can be predicted and vice-versa.
(a)
Answer to Problem 7.52QP
| Molecular Geometry | Hybridization of the central atom | |
| (a) | Tetrahedral |
|
Explanation of Solution
Tetrahedral
A molecule having tetrahedral geometry has the empirical formula
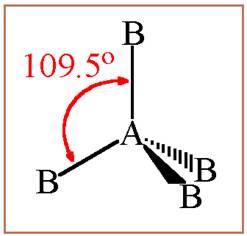
Figure 1
The bond angle between two atoms in a tetrahedral molecule is
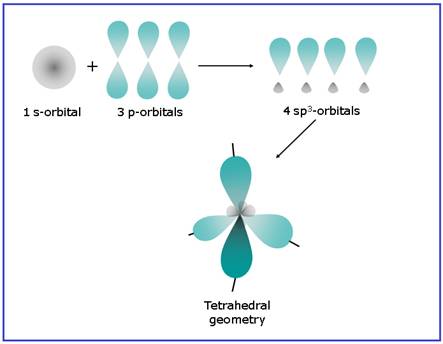
Figure 2
Thus a molecule having tetrahedral geometry has central atom with
(b)
Interpretation:
The hybridization of the central atom of the molecules with the following molecular geometries has to be predicted.
- (a) Tetrahedral (b) trigonal planar (c) trigonal bipyramidal (d) linear (e) octahedral
Concept Introduction:
Hybridization is a hypothetical concept. It refers to overlapping of atomic orbitals and the resultant orbitals formed are known as hybrid orbitals. An orbital that doesn’t involve in hybridization is termed as unhybridized orbital. After hybridization, the orbitals cannot be distinguished individually. The orientation of the orbitals while overlapping impacts the nature of the bond forms. By knowing the hybridization of central atom in the molecule its geometry can be predicted and vice-versa.
(b)
Answer to Problem 7.52QP
| Molecular Geometry | Hybridization of the central atom | |
| (b) | Trigonal planar |
|
Explanation of Solution
Trigonal planar
A molecule having trigonal planar geometry has the empirical formula
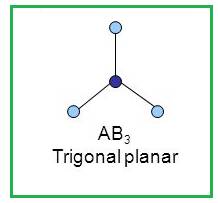
Figure 3
The bond angle between two atoms in a trigonal planar molecule is
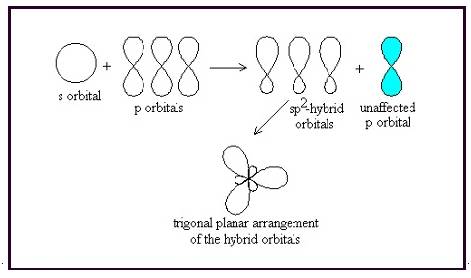
Figure 4
Thus a molecule having trigonal planar geometry has central atom with
(c)
Interpretation:
The hybridization of the central atom of the molecules with the following molecular geometries has to be predicted.
- (a) Tetrahedral (b) trigonal planar (c) trigonal bipyramidal (d) linear (e) octahedral
Concept Introduction:
Hybridization is a hypothetical concept. It refers to overlapping of atomic orbitals and the resultant orbitals formed are known as hybrid orbitals. An orbital that doesn’t involve in hybridization is termed as unhybridized orbital. After hybridization, the orbitals cannot be distinguished individually. The orientation of the orbitals while overlapping impacts the nature of the bond forms. By knowing the hybridization of central atom in the molecule its geometry can be predicted and vice-versa.
(c)
Answer to Problem 7.52QP
| S.No | Molecular Geometry | Hybridization of the central atom |
| (c) | Trigonal bipyramidal |
|
Explanation of Solution
Trigonal bipyramidal
A molecule having trigonal bipyramidal geometry has the empirical formula
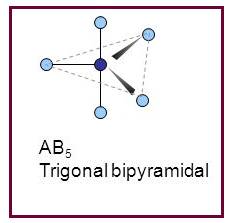
Figure 5
Trigonal bipyramidal molecule has two set of bonds – two axial bonds and three equatorial bonds. The two axial bonds are
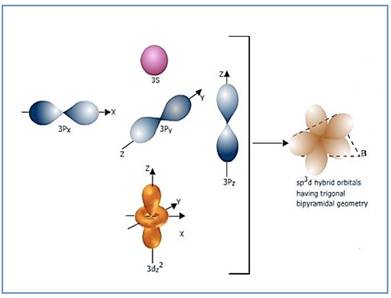
Figure 6
If the d-orbital of the
(d)
Interpretation:
The hybridization of the central atom of the molecules with the following molecular geometries has to be predicted.
- (a) Tetrahedral (b) trigonal planar (c) trigonal bipyramidal (d) linear (e) octahedral
Concept Introduction:
Hybridization is a hypothetical concept. It refers to overlapping of atomic orbitals and the resultant orbitals formed are known as hybrid orbitals. An orbital that doesn’t involve in hybridization is termed as unhybridized orbital. After hybridization, the orbitals cannot be distinguished individually. The orientation of the orbitals while overlapping impacts the nature of the bond forms. By knowing the hybridization of central atom in the molecule its geometry can be predicted and vice-versa.
(d)
Answer to Problem 7.52QP
| S.No | Molecular Geometry | Hybridization of the central atom |
| (d) | Linear |
|
Explanation of Solution
Linear
A molecule having linear geometry has the empirical formula
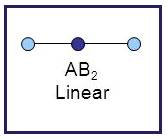
Figure 7
The bond angle between two atoms in linear molecule is
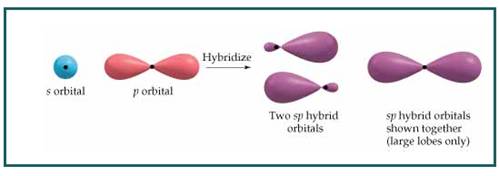
Figure 8
Thus a molecule having linear geometry has central atom with
(e)
Interpretation:
The hybridization of the central atom of the molecules with the following molecular geometries has to be predicted.
- (a) Tetrahedral (b) trigonal planar (c) trigonal bipyramidal (d) linear (e) octahedral
Concept Introduction:
Hybridization is a hypothetical concept. It refers to overlapping of atomic orbitals and the resultant orbitals formed are known as hybrid orbitals. An orbital that doesn’t involve in hybridization is termed as unhybridized orbital. After hybridization, the orbitals cannot be distinguished individually. The orientation of the orbitals while overlapping impacts the nature of the bond forms. By knowing the hybridization of central atom in the molecule its geometry can be predicted and vice-versa.
(e)
Answer to Problem 7.52QP
| S.No | Molecular Geometry | Hybridization of the central atom |
| (e) | Octahedral |
|
Explanation of Solution
Octahedral
A molecule having octahedral geometry has the empirical formula
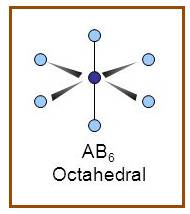
Figure 9
The bond angle between two atoms in octahedral molecule is
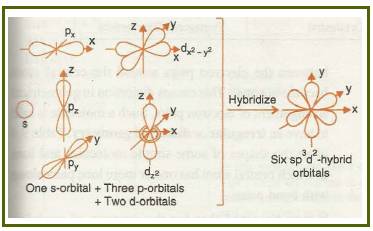
Figure 10
If the d-orbital of the
The hybridization of the central atom of the molecules with the given molecular geometries has been predicted.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 7 Solutions
Chemistry: Atoms First V1
- Use the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation to calculate pH of a buffer containing 0.050M benzoic acidand 0.150M sodium benzoate. The Ka of benzoic acid is 6.5 x 10-5arrow_forwardA. Draw the structure of each of the following alcohols. Then draw and name the product you would expect to produce by the oxidation of each. a. 4-Methyl-2-heptanol b. 3,4-Dimethyl-1-pentanol c. 4-Ethyl-2-heptanol d. 5,7-Dichloro-3-heptanolarrow_forwardWhat is the pH of a 1.0 L buffer made with 0.300 mol of HF (Ka = 6.8 × 10⁻⁴) and 0.200 mol of NaF to which 0.160 mol of NaOH were added?arrow_forward
- Can I please get help with this.arrow_forwardDetermine if the following salt is neutral, acidic or basic. If acidic or basic, write the appropriate equilibrium equation for the acid or base that exists when the salt is dissolved in aqueous solution. If neutral, simply write only NR. Be sure to include the proper phases for all species within the reaction. N₂H₅ClO₄arrow_forwardPlease help me with identifying these.arrow_forward
 Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co





