
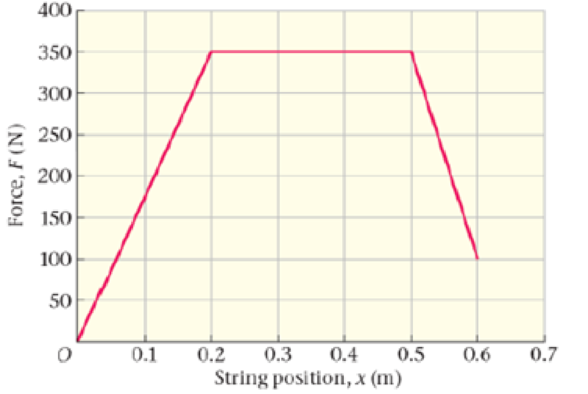
A Compound Bow A compound bow in archery allows the user to hold the bowstring at full draw with considerably less force than the maximum force exerted by the string. The draw force as a function of the string position x for a particular compound bow is shown in Figure 7-26.
(a) How much work does the archer do on the bow in order to draw the string from
x = 0
to
x = 0.60
m? (b) If all of this work becomes the kinetic energy of a 0 065-kg arrow, what is the speed of the arrow?
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Chapter 7 Solutions
EBK PHYSICS
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Laboratory Experiments in Microbiology (12th Edition) (What's New in Microbiology)
Cosmic Perspective Fundamentals
Chemistry: Structure and Properties (2nd Edition)
Genetic Analysis: An Integrated Approach (3rd Edition)
Introductory Chemistry (6th Edition)
Organic Chemistry (8th Edition)
- In Figure 5.5 (a)-(d), a block moves to the right in the positive x-direction through the displacement x while under the influence of a force with the same magnitude F. Which of the following is the correct order of the amount of work done by the force F, from most positive to most negative? (a) d, c, a, b (b) c, a, b, d (c) c, a, d, barrow_forwarda shopper in a supermarket pushes a cart with a force of 35 N directed at an angle of 25 below the horizontal. The force is just sufficient to overcome various frictional forces, so the cart moves at constant speed, (a) Find the work done by the shopper as she moves down a 50.0-m length aisle, (b) What is the net work done on the cart? Why? (c) The shopper goes down the next aisle, pushing horizontally and maintaining the same speed as before. If the work done by frictional forces doesnt change, would the shoppers applied force be larger, smaller, or the same? What about the work done on the cart by the shopper?arrow_forwardAs a simple pendulum swings back and forth, the forces acting on the suspended object are the force of gravity, the tension in the supporting cord, and air resistance, (a) Which of these forces, if any, does no work on the pendulum? (b) Which of these forces does negative work at all times during the pendulums motion? (c) Describe the work done by the force of gravity while the pendulum is swinging.arrow_forward
- As a mass tied to the end of a string strings from its highest point down to its lowest point, it is acted on by three forces: gravity, tension, and air resistance. Which force does (a) positive work? (b) negative work? (c) zero work?arrow_forwardA particle is subject to a force Fx that varies with position as shown in Figure P7.9. Find the work done by the force on the particle as it moves (a) from x = 0 to x = 5.00 m, (b) from x = 5.00 m to x = 10.0 m, and (c) from x = 10.0 m to x = 15.0 m. (d) What is the total work done by the force over the distance x = 0 to x = 15.0 m?arrow_forwardAlex and John are loading identical cabinets onto a truck. Alex lifts his cabinet straight up from the ground to the bed of the truck, whereas John slides his cabinet up a rough ramp to the truck. Which statement is correct about the work done on the cabinetEarth system? (a) Alex and John do the same amount of work. (b) Alex does more work than John. (c) John does more work than Alex. (d) None of those statements is necessarily true because the force of friction is unknown. (e) None of those statements is necessarily true because the angle of the incline is unknown.arrow_forward
- Alex and John are loading identical cabinets onto a truck. Alex lifts his cabinet straight up from the ground to the bed of the truck, whereas John slides his cabinet up a rough ramp to the truck. Which statement is correct about the work done on the cabinet-Earth system? (a) Alex and John do the same amount of work, (b) Alex does more work than John, (c) John does more work than Alex, (d) None of those statements is necessarily true because the force of friction is unknown, (e) None of those statements is necessarily true because the angle of the incline is unknown.arrow_forwardA jack-in-the-box is actually a system that consists of an object attached to the top of a vertical spring (Fig. P8.50). a. Sketch the energy graph for the potential energy and the total energy of the springobject system as a function of compression distance x from x = xmax to x = 0, where xmax is the maximum amount of compression of the spring. Ignore the change in gravitational potential energy. b. Sketch the kinetic energy of the system between these points the two distances in part (a)on the same graph (using a different color). FIGURE P8.50 Problems 50 and 79arrow_forwardA block of mass m = 5.00 kg is released from point and slides on the frictionless track shown in Figure P8.3. Determine (a) the blocks speed at points and and (b) the net work done by the gravitational force on the block as it moves from point to point . Figure P8.3arrow_forward
- A block slides at constant speed down a ramp while acted on by three forces: its weight, the normal force, and kinetic friction. Respond to each statement, true or false. (a) The combined net work done by all three forces on the block equals zero. (b) Each force does zero work on the block as it slides. (c) Each force does negative work on the block as it slides.arrow_forwardA book of mass in is projected with a speed v across a horizontal surface. The book slides until it stops due to the friction force between the book and the surface. The surface is now tilted 30, and the book is projected up the surface with the same initial speed v. When the book has come to rest, how does the decrease in mechanical energy of the book-Earth system compare with that when the book slid over the horizontal surface? (a) Its the same. (b) Its larger on the tilted surface. (c) Its smaller on the tilted surface. (d) More information is needed.arrow_forwardTwo toboggans (with riders) of the same mass are at rest on top of a steep hill. As they slide down the hill, toboggan A takes a straight path down the slope while toboggan B winds back and forth along a more gently sloping path. Toboggan A makes the trip in half the time of toboggan B. (a) Compare the work done by gravity on each toboggan. (b) Compare the average power delivered by gravity on the two toboggans.arrow_forward
 Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning





