
System Dynamics
3rd Edition
ISBN: 9780073398068
Author: III William J. Palm
Publisher: MCG
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 7, Problem 7.38P
(a) Determine the capacitance of a spherical tank of radius R, shown in
Figure P7.38.
(b) Obtain a model of the pressure at the bottom of the tank, given the mass flow rate qmi.
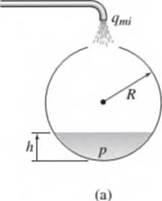
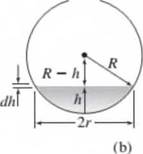

Figure P7.38 A spherical tank.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
The 120 kg wheel has a radius of gyration of 0.7 m. A force P with a magnitude of 50 N is applied at the edge of the wheel as seen in the diagram. The coefficient of static friction is 0.3, and the coefficient of kinetic friction is 0.25. Find the acceleration and angular acceleration of the wheel.
Auto Controls
Using MATLAB , find the magnitude and phase plot of the compensators
NO COPIED SOLUTIONS
4-81 The corner shown in Figure P4-81 is initially uniform at 300°C and then suddenly
exposed to a convection environment at 50°C with h 60 W/m². °C. Assume the
=
2
solid has the properties of fireclay brick. Examine nodes 1, 2, 3, 4, and 5 and deter-
mine the maximum time increment which may be used for a transient numerical
calculation.
Figure P4-81
1
2
3
4
1 cm
5
6
1 cm
2 cm
h, T
+
2 cm
Chapter 7 Solutions
System Dynamics
Ch. 7 - Prob. 7.1PCh. 7 - Refer to the water storage and supply system shown...Ch. 7 - Prob. 7.3PCh. 7 - In Figure P7.4 the piston of area A is connected...Ch. 7 - Refer to Figure 7.1.4a. and suppose that p\ — p2=...Ch. 7 - Pure water flows into a mixing tank of volume V =...Ch. 7 - Consider the mixing tank treated in Problem 7.6....Ch. 7 - Derive the expression for the fluid capacitance of...Ch. 7 - Prob. 7.9PCh. 7 - Prob. 7.10P
Ch. 7 - 7.11 Derive the expression for the capacitance of...Ch. 7 - Air flows in a certain cylindrical pipe 1 m long...Ch. 7 - Derive the expression for the linearized...Ch. 7 - Consider the cylindrical container treated in...Ch. 7 - A certain tank has a bottom area A = 20 m2. The...Ch. 7 - A certain tank has a circular bottom area A = 20...Ch. 7 - The water inflow rate to a certain tank was kept...Ch. 7 - Prob. 7.18PCh. 7 - Prob. 7.19PCh. 7 - In the liquid level system shown in Figure P7.20,...Ch. 7 - The water height in a certain tank was measured at...Ch. 7 - Derive the model for the system shown in Figure...Ch. 7 - (a) Develop a model of the two liquid heights in...Ch. 7 - Prob. 7.24PCh. 7 - Design a piston-type damper using an oil with a...Ch. 7 - Prob. 7.26PCh. 7 - 7.27 An electric motor is sometimes used to move...Ch. 7 - Prob. 7.28PCh. 7 - Prob. 7.29PCh. 7 - Figure P7.3O shows an example of a hydraulic...Ch. 7 - Prob. 7.31PCh. 7 - Prob. 7.32PCh. 7 - Prob. 7.33PCh. 7 - Prob. 7.34PCh. 7 - Prob. 7.35PCh. 7 - Prob. 7.36PCh. 7 - Prob. 7.37PCh. 7 - (a) Determine the capacitance of a spherical tank...Ch. 7 - Obtain the dynamic model of the liquid height It...Ch. 7 - Prob. 7.40PCh. 7 - Prob. 7.41PCh. 7 - Prob. 7.42PCh. 7 - Prob. 7.43PCh. 7 - Prob. 7.44PCh. 7 - Prob. 7.45PCh. 7 - The copper shaft shown in Figure P7.46 consists of...Ch. 7 - A certain radiator wall is made of copper with a...Ch. 7 - A particular house wall consists of three layers...Ch. 7 - A certain wall section is composed of a 12 in. by...Ch. 7 - Prob. 7.50PCh. 7 - Prob. 7.51PCh. 7 - A steel tank filled with water has a volume of...Ch. 7 - Prob. 7.53PCh. 7 - Prob. 7.54PCh. 7 - Prob. 7.55P
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Auto Controls A union feedback control system has the following open loop transfer function where k>0 is a variable proportional gain i. for K = 1 , derive the exact magnitude and phase expressions of G(jw). ii) for K = 1 , identify the gaincross-over frequency (Wgc) [where IG(jo))| 1] and phase cross-overfrequency [where <G(jw) = - 180]. You can use MATLAB command "margin" to obtain there quantities. iii) Calculate gain margin (in dB) and phase margin (in degrees) ·State whether the closed-loop is stable for K = 1 and briefly justify your answer based on the margin . (Gain marginPhase margin) iv. what happens to the gain margin and Phase margin when you increase the value of K?you You can use for loop in MATLAB to check that.Helpful matlab commands : if, bode, margin, rlocus NO COPIED SOLUTIONSarrow_forwardAuto Controls Hand sketch the root Focus of the following transfer function How many asymptotes are there ?what are the angles of the asymptotes?Does the system remain stable for all values of K NO COPIED SOLUTIONSarrow_forward-400" 150" in Datum 80" 90" -280"arrow_forward
- 7) Please draw the front, top and side view for the following object. Please cross this line outarrow_forwardA 10-kg box is pulled along P,Na rough surface by a force P, as shown in thefigure. The pulling force linearly increaseswith time, while the particle is motionless att = 0s untilit reaches a maximum force of100 Nattimet = 4s. If the ground has staticand kinetic friction coefficients of u, = 0.6 andHU, = 0.4 respectively, determine the velocityof the A 1 0 - kg box is pulled along P , N a rough surface by a force P , as shown in the figure. The pulling force linearly increases with time, while the particle is motionless at t = 0 s untilit reaches a maximum force of 1 0 0 Nattimet = 4 s . If the ground has static and kinetic friction coefficients of u , = 0 . 6 and HU , = 0 . 4 respectively, determine the velocity of the particle att = 4 s .arrow_forwardCalculate the speed of the driven member with the following conditions: Diameter of the motor pulley: 4 in Diameter of the driven pulley: 12 in Speed of the motor pulley: 1800 rpmarrow_forward
- 4. In the figure, shaft A made of AISI 1010 hot-rolled steel, is welded to a fixed support and is subjected to loading by equal and opposite Forces F via shaft B. Stress concentration factors K₁ (1.7) and Kts (1.6) are induced by the 3mm fillet. Notch sensitivities are q₁=0.9 and qts=1. The length of shaft A from the fixed support to the connection at shaft B is 1m. The load F cycles from 0.5 to 2kN and a static load P is 100N. For shaft A, find the factor of safety (for infinite life) using the modified Goodman fatigue failure criterion. 3 mm fillet Shaft A 20 mm 25 mm Shaft B 25 mmarrow_forwardPlease sovle this for me and please don't use aiarrow_forwardPlease sovle this for me and please don't use aiarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY
Intro to Compressible Flows — Lesson 1; Author: Ansys Learning;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=OgR6j8TzA5Y;License: Standard Youtube License