Concept explainers
(a)
Find the energy stored in the element at time
(a)
Answer to Problem 68E
The energy stored in the element at time
Explanation of Solution
Given data:
Write a general expression to calculate the energy stored in an inductor.
Here,
Given data:
Refer to Figure 7.82 in the textbook.
The value of initial current through inductor
Calculation:
Substitute
Substitute
Simplify the above equation to find
Conclusion:
Thus, the energy stored in the element at time
(b)
Determine the value of
(b)
Answer to Problem 68E
The value of
Explanation of Solution
Calculation:
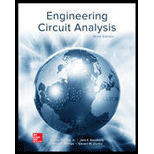
Create the new schematic in LTspice with series connected resistor and inductor of given circuit as shown in Figure 1.
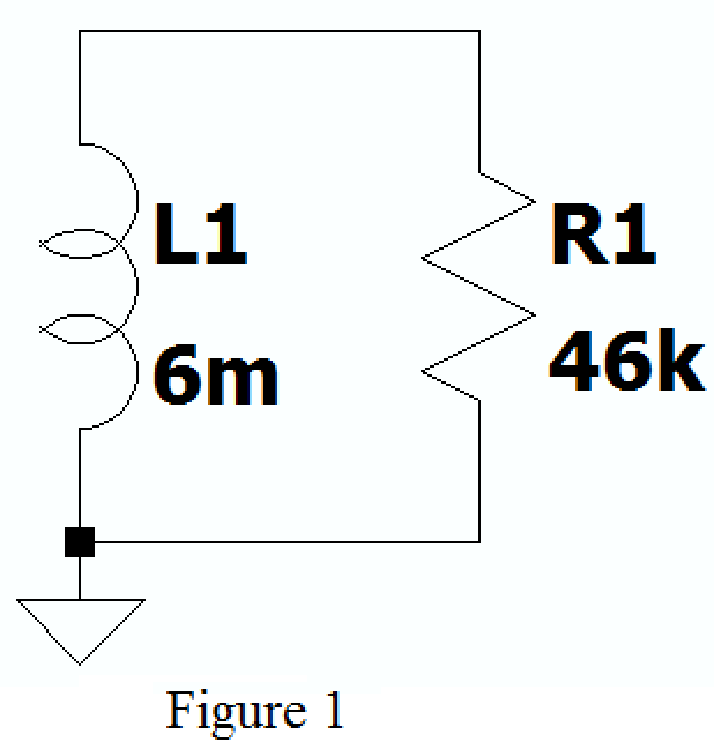
Using SPICE Directive mention the command .ic I(L1)=1m as shown in Figure 2.
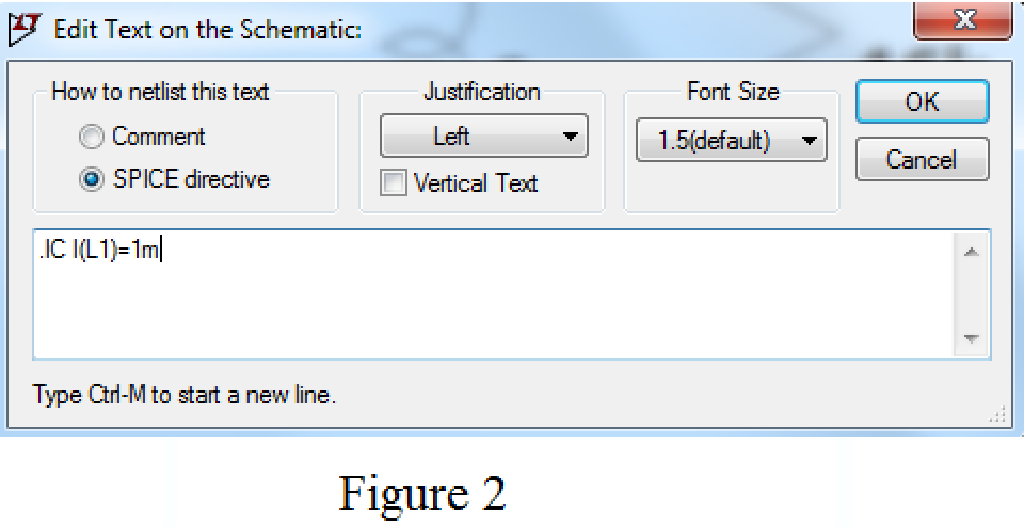
Enter the stop time as 500ns, time to start saving data as 0, and maximum Timestep as 25ns in Edit simulation Cmd as shown in Figure 3.
After adding the Spice directives the circuit shows as in Figure 4.
Now run the simulation and place the probe at inductor, the plot of the current through inductor with respect to time is shown as shown in Figure 5.
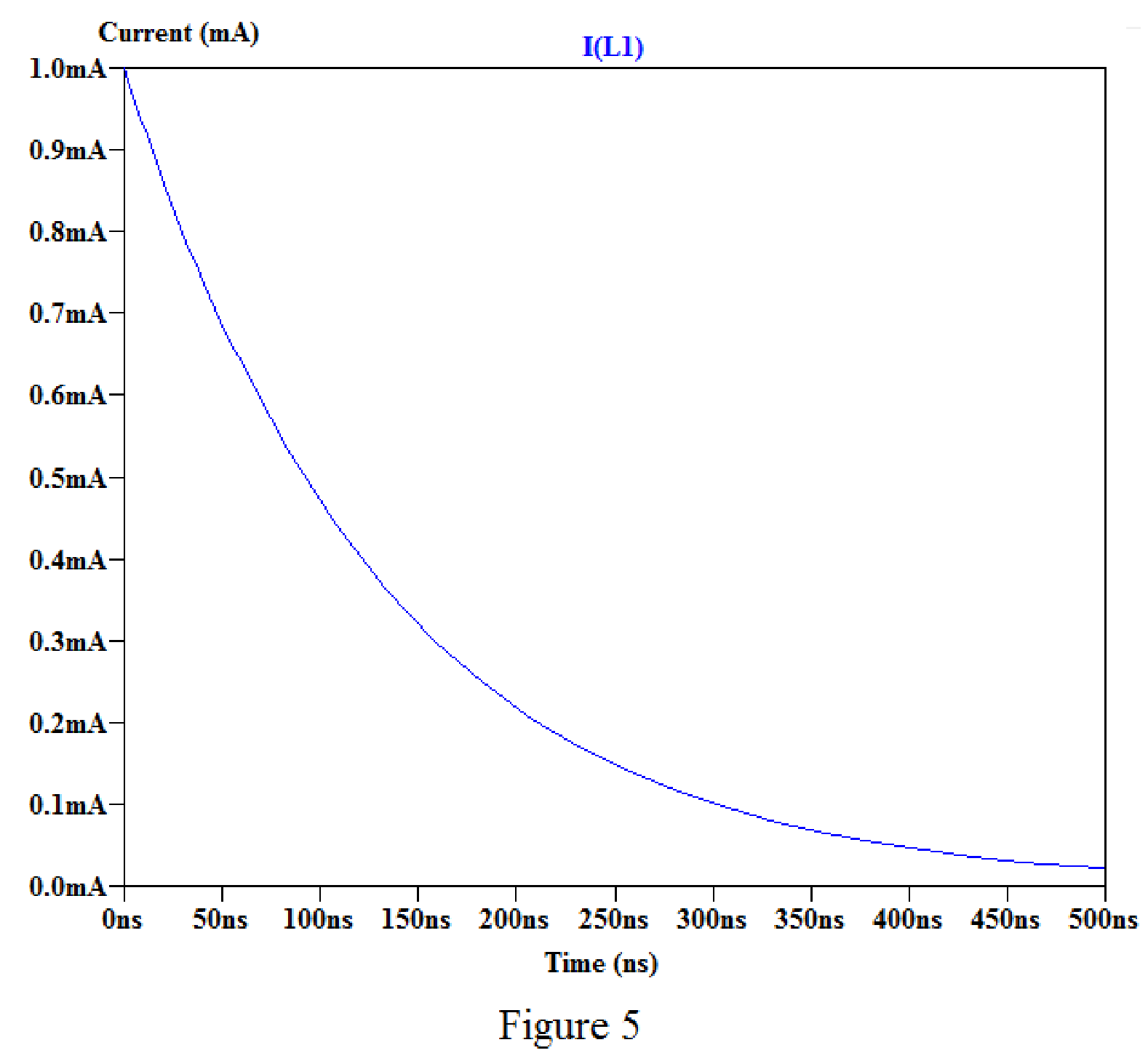
By placing the cursor on the graph, we obtain the current values for different time as shown in below.
For time
For time
For time
For time
Conclusion:
Thus, the value of
(c)
Find the value of initial energy remains in the inductor at time
(c)
Answer to Problem 68E
The value of initial energy remains in the inductor at time
Explanation of Solution
Calculation:
Refer to part (b), the value of current at time
Substitute
Substitute
Simplify the above equation to find
Substitute
Substitute
Simplify the above equation to find
Conclusion:
Thus, the value of initial energy remains in the inductor at time
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 7 Solutions
Engineering Circuit Analysis
- find inverse LT for the following functions 1- [0.2s+1.4] s2+1.96. 2. L-1 5s+1 Ls2-25. 4s+32 3. L- L(s2-16).arrow_forwardQ Figurel shows the creation of the Frequency Reuse Pattern Using the Cluster Size K (A) illustrates how i and j can be used to locate a co-channel cell. Juster Cluster CB Cluster 2 X=7(i=2,j=1)arrow_forwardDon't use ai to answer I will report you answerarrow_forward
- Q2. For the transformer shown in Fig. 1. A. Plot the winding connection for the transformer and justify your answer. (4M) B. If the transformer is adopted in 12 pulse diode rectifier, where two-series connected bridge rectifiers are used to supply a highly inductive load with 100 A. (i) Select a suitable turns ratio for the transformer (ii) Plot the line current of each winding ( secondary + primary) showing the current magnitude at each interval (iii) Use Fourier Page 1 of 3 analysis to obtain the Fourier series of all line currents then calculate the THD of the input current. (8=0° (16M) (Y) = 30° Fig. 1 P. I v Iarrow_forwardQ2. For the transformer shown in Fig.1, A. Find the phase shift between the primary and star-connected secondary. B. If the transformer is adopted in a 12-pulse diode rectifier, where a two-series connected bridge rectifier is connected in series and supplies a highly inductive load (i) Select a suitable turns ratio for the transformer (ii) Plot the line current of each winding (secondary + primary). (iii)Using Fourier analysis to obtain the Fourier series of all line currents, then calculate the THD of the input current. (iv) Draw the output voltage of the first and second rectifiers and give the relation of the total output voltage. N2 B C Fig. 1 N3 aarrow_forwardQ2.A. It is planned to use the transformer shown in Fig. 1, a 12-pulse rectifier. Each secondary is connected to three phase controlled bridge rectifier. The two rectifiers are connected in series to supply a highly inductive load. 1. Based on the phasor relationship between different windings. If suitable turns ratio is selected, is it possible to use this transformer to produce 12 pulse output voltage? Show the reason behind your answer. 2. Assuming this arrangement is possible to be used in 12-pulse rectifier, draw the output voltage of the 1st and 2nd rectifier and give the relation of the total output voltage. 3. Use the Fourier analysis to show the harmonics in all line currents of the transformer. A B in C Fig. 1 b la a 2 b.arrow_forward
 Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON
Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON
Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,





