
Concept explainers
a
Interpretation:
Expected completion time of project.
Concept Introduction: The critical path is the arrangement of project activities which gives an estimated time duration under which the project will be completed. The project activities may include float activities which can be delayed focusing on the shortest time duration.
a
Explanation of Solution
Calculate the estimated task time:
| Task | Immediate predecessors | Optimistic time | Most likely time | Pessimistic time | Estimated task time | Variance |
| A | None | 1 | 2 | 3 | 2 | 0.11 |
| B | A | 2 | 4 | 6 | 4 | 0.44 |
| C | None | 2 | 4 | 6 | 4 | 0.44 |
| D | B and C | 1 | 2 | 9 | 3 | 1.78 |
Calculate the estimated task time for task A:
It is calculated by dividing the value attained by adding optimistic time, pessimistic time and four times of most likely time with the value 6.
Hence, the estimated task time for task A is 2 hours.
Calculate the estimated task time for task B:
It is calculated by dividing the value attained by adding optimistic time, pessimistic time and four times of most likely time with the value 6.
Hence, the estimated task time for task B is 4 hours.
Calculation of estimated task time for Task C:
It is calculated by dividing the value attained by adding optimistic time, pessimistic time and four times of most likely time with the value 6.
Hence, the estimated task time for Task C is 4 hours.
Calculate the estimated task time for Task D:
It is calculated by dividing the value attained by adding optimistic time, pessimistic time and four times of most likely time with the value 6.
Hence, the estimated task time for task D is 3 hours.
Calculate the variance for Task A:
It is calculated by dividing the value attained subtracting the optimistic time from the pessimistic time with the value of 6. Then, square the attained value.
Calculate the variance for Task B:
It is calculated by dividing the value attained subtracting the optimistic time from the pessimistic time with the value of 6. Then, square the attained value.
Hence, the variance for task B is 0.44
Calculate the variance for Task C:
It is calculated by dividing the value attained subtracting the optimistic time from the pessimistic time with the value of 6. Then, square the attained value.
Hence, the variance for Task C is 0.44
Calculate the variance for Task D:
It is calculated by dividing the value attained subtracting the optimistic time from the pessimistic time with the value of 6. Then, square the attained value.
Hence, the variance for Task D is 1.78
Project network diagram for given information:
The below image shows the project network with the early start, early finish, late start and late finish:
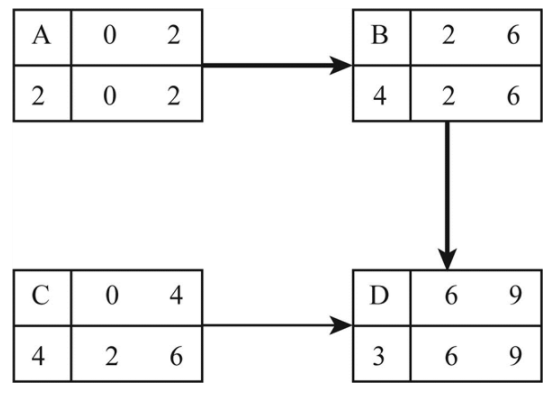
A
The critical path in the project network:
The paths in the given project network are as follows:
A-B-D
C-D
There are two paths in the project network.
Out of the above-mentioned path, the path has the equal early start and late start at the same time early finish and late finish are the critical path.
Hence, the critical path is A-B-D and the project completion time is 9 days.
b
Interpretation:
Time duration in the beginning of reconfiguration.
Concept Introduction: Early start time: The rule for the early start time of a task is that it is equal to the largest early finish time of the task’s immediate predecessors.
Early finish time: The early finish time of a task is the addition of both task time and early start time of the task.
b
Explanation of Solution
The late start time for activity C:
According to the project network, the late start time for activity C is 2 day.
c
Interpretation:
Probability that warehouse will finish the project.
Concept Introduction: Early start time: The rule for the early start time of a task is that it is equal to the largest early finish time of the task’s immediate predecessors.
Early finish time: The early finish time of a task is the addition of both task time and early start time of the task.
c
Explanation of Solution
The probability to finish the operation, which started at 1:00 a.m. and finished at 11:00 a.m. on the same day:
The value of Z should be calculated to find the probability to find the operation.
It is calculated by dividing the value attained by subtracting the completion time from the time (time gap from 1:00 a.m. to 11:00 a.m.) with the square root of the variance of critical path (sum of the variance of critical path).
Hence, the value of Z is 0.6551
For Z= 0.6551, the
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 7 Solutions
Practical Operations Management
- 1) View the video Alton Bridge (12.16 mins, Ctrl + Click on the link), and please answer the following questions: https://meida.gaspar.mheducation.com/GASPARPlayer/play.html?id=24qHEm8aNZExFciJtZQbqli a) According to the video, what are the various steps involved in managing projects? b) What were the different phases of the Alton Bridge project? c) What are the two widely used scheduling techniques, and under what phase of the Alton Bridge project are they discussed? Note: As a rough guideline, please try to keep the written submission to a paragraph or so for each of the questions. 2) The following is a table of activities associated with a mining project at Lunar Industries, their durations, and what activities each must precede: Activity Duration (weeks) Precedes A (start) 1 B, C B 1 E C 4 F E 2 F F (end) 2 - The AOM project diagram is as given below: a) What is the critical path (list all activities in the…arrow_forward1) View the video Alton Bridge (12.16 mins, Ctrl + Click on the link), and please answer the following questions: a) According to the video, what are the various steps involved in managing projects? b) What were the different phases of the Alton Bridge project? c) What are the two widely used scheduling techniques, and under what phase of the Alton Bridge project are they discussed? Note: As a rough guideline, please try to keep the written submission to a paragraph or so for each of the questions. 2) The following is a table of activities associated with a mining project at Lunar Industries, their durations, and what activities each must precede: Activity Duration (weeks) Precedes A (start) 1 B, C B 1 E C 4 F E 2 F F (end) 2 - The AOM project diagram is as given below:arrow_forwardWith all the problems companies are currently facing, why do so many choose to expand into international markets? What are the advantages of expanding beyond the domestic market?arrow_forward
- Perform resource leveling. Assume that each task can be performed independently of the other tasks.arrow_forwardher psychological test and interview while Ms. Domingo got a good score and good psychological result. Ms. Sabado’s father is your godfather and a good friend of yours. Ms. Sabado asked you a favor to consider her daughter and if possible she will be hired. He also added that every job can be learned through training and mentoring. The situation bothers you since it’s your duty to recommend to the higher authority whom to hire.Questions:1. As a supervisor how will you diced on this situation?2. It’s time to decide, who among the two (2) will be hired? Why?arrow_forwardHelp me solve part C.arrow_forward
- Boreki Enterprise has the following 10 items in inventory. Theodore Boreki asks you, a recent OM graduate, to divide these items into ABC classifications. Fill in the blanks and then answer the following questions. (Round dollar volume to the nearest whole number and percentage of dollar volume to two decimal places.) Dollar Item Annual Demand Cost/Unit Volume % of Total Dollar Volume A2 10 120 B8 4000 12 48,000 5.65 C7 1500 45 67,500 7.94 D1 2000 44 E9 1000 20 20,000 2.35 F3 25 40 G2 200 1500 300,000 35.29 H2 600 20 12,000 1.41 15 1000 300 J8 2500 5 12,500 1.47arrow_forwardBobby Flay is responsible for assigning steel workers to a structural steel infrastructure construction task. Having taken Project Management at the University of Portland, he understands the importance of managing risk. To ensure that the task takes place as scheduled, Bobby must ensure that there are at least 8 steel workers available at the start of the task. Based on analysis of similar tasks, he estimates that steel workers will show up for the task with probability 0.9. If Bobby wants to be 97% sure that there are enough tasks to begin as scheduled, he should assign ______ steel workers to the task.arrow_forwardMarcela Valladolid needs to assign resources to a task on a new high-tech development project at Jonathon's Pool Supplies. According to her estimates, the task's work content (in hours) is 408. Marcela needs help in determining an appropriate number of resources to allocate to the task. Marcela read somewhere that, when it comes to project staffing, more is not always better. Assuming that the direct labor rate per hour is $93, the indirect and over head rate per unit time is $73.62, assigned resources are dedicated to the task full time, and that 0.02 hours of communication per coordination are required per link per hour worked, help Marcela by determining the following: What is the minimum total cost: What resource allocation minimizes the total cost: What is the minimum duration: What is the duration minimizing number of resources: If Marcela assigns 12 FTEs to the task, the task metrics would be: Total Cost: Total Duration: Note: enter durations to 1 decimal place and costs…arrow_forward
- 1 point) Market Fresh Foods is looking to develop a new strategic plan. Guillermo Santiago has been developing a project plan and has identified the following tasks, precedence relations, normal task durations, and resource requirements. Guillermo has studied project management at the University of Portland and knows that the makespan of the project may be determined from the information in the table using the critical path method. Guillermo also learned a simple heuristic for evaluating resource sufficiency. Help Guillermo by answering the following related assuming 3 workers per week and a due date of 302.8: Project Work Content: Total Resource Capacity: Minimum due date for which 3 resources is sufficient: Minimum resource level that could make due date of 302.8 feasible:arrow_forwardHow an individual attending a university can help the development of a country?arrow_forwardWhat are the job description or role in Operations management? Please answer at your own easy words.arrow_forward
 Practical Management ScienceOperations ManagementISBN:9781337406659Author:WINSTON, Wayne L.Publisher:Cengage,
Practical Management ScienceOperations ManagementISBN:9781337406659Author:WINSTON, Wayne L.Publisher:Cengage,


