
Concept explainers
a.
Record the given events in the
a.
Explanation of Solution
Record the given events in accounting equation.
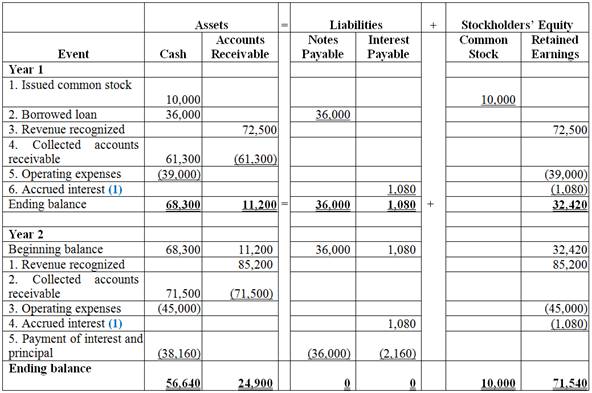
Table (1)
Working note 1: Calculate the amount of Accrued interest:
b.
Calculate the amount of net cash flow from operating activities that would be reported on 2018 Statement of
b.
Explanation of Solution
Cash flows from operating activities refer to the cash received or cash paid in day-to-day operating activities of a company.
Calculate the cash flow from operating activities.
| Enterprise M | ||
| Statement of cash flow | ||
| Particulars | Amount ($) | Amount ($) |
| Cash flow from operating activities | ||
| Cash collected from revenue | $61,300 | |
| Cash paid for operating expenses | ($39,000) | |
| Net cash flow from operating activities | $22,300 | |
Table (2)
Thus, the amount of net cash flow from operating activities that would be reported on 2018 Statement of cash flows is $22,300.
c.
Calculate the amount of interest expense that would be reported on 2018 income statement.
c.
Explanation of Solution
Interest expense refers to the cost of debt which is incurred during a particular accounting period. The interest amount is a fixed interest rate payable on the principal amount of debt.
Calculate the amount of interest expense.
Hence, the amount of interest expense that would be reported on 2018 income statement is $1,080.
d.
Calculate the amount of total liabilities that would be reported on December 31, 2018
d.
Explanation of Solution
Total liabilities are the sum of financial obligations and debt owed by business.
Calculate the total liabilities.
| Particulars | Amount ($) | Amount ($) |
| Notes payable | 36,000 | |
| Interest payable | 1,080 | |
| Total liabilities | 37,080 |
Table (3)
Thus, the amount of total liabilities that would be reported on December 31, 2018 balance sheet is $37,080.
e.
Calculate the amount of
e.
Explanation of Solution
Retained earnings are the portion of earnings kept by the business for the purpose of reinvestments, payment of debts, or for future growth.
Calculate the amount of retained earnings.
Hence, the amount of retained earnings that would be reported on December 31, 2018 balance sheet is $32,420.
f.
Calculate the amount net cash flow from financing activities that would be reported on 2018 statement of cash flows.
f.
Explanation of Solution
Cash flow from financing activities: This section of cash flows statement provides information about the
Calculate the amount net cash flow from financing activities.
| Enterprise M | ||
| Statement of cash flow | ||
| Particulars | Amount ($) | Amount ($) |
| Cash flow from financing activities | ||
| Issued common stock | $10,000 | |
| Loan borrowed | $36,000 | |
| Net cash flow from operating activities | $46,000 | |
Table (4)
Thus, the amount of cash flow from financing activities that would be reported on 2018 statement of cash flow is $46,000.
g.
Calculate the amount of interest expense that would be reported on 2019 income statement.
g.
Explanation of Solution
Interest expense refers to the cost of debt which is incurred during a particular accounting period. The interest amount is a fixed interest rate payable on the principal amount of debt.
Calculate the amount of interest expense.
Hence, the amount of interest expense that would be reported on 2019 income statement is $1,080.
h.
Calculate the amount of net cash flow from operating activities that would be reported on the 2019 Statement of cash flows.
h.
Explanation of Solution
Cash flows from operating activities refer to the cash received or cash paid in day-to-day operating activities of a company.
Calculate the cash flow from operating activities.
| Enterprise M | ||
| Statement of cash flow | ||
| Particulars | Amount ($) | Amount ($) |
| Cash flow from operating activities | ||
| Cash collected from accounts receivable | $71,500 | |
| Cash paid for operating expenses | ($45,000) | |
| Cash paid for interest | ($2,160) | |
| Net cash flow from operating activities | $24,340 | |
Table (5)
Thus, the cash flow operating activities that would be reported on 2019 statement of cash flows is $24,340.
i.
Calculate the amount of total assets that would be reported on 2019 balance sheet.
i.
Explanation of Solution
Calculate the total assets.
| Particulars | Amount ($) | Amount ($) |
| Cash | 56,640 | |
| Accounts receivable | 24,900 | |
| Total assets | 81,540 |
Table (6)
Thus, the amount of total assets that would be reported on 2019 balance sheet is $81,540.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 7 Solutions
Survey Of Accounting
- Please help me solve this general accounting question using the right accounting principles.arrow_forwardIf a business has revenue of $677,000, cost of goods sold of $214,000, operating expenses of $157,000, and pays $70,000 in taxes, what is the net income?arrow_forwardGiven the solution and general accounting questionarrow_forward
- The current sections of Kingbird Inc.'s balance sheets at December 31, 2024 and 2025, are presented here. Kingbird's net income for 2025 was $107,100. Depreciation expense was $18,900. 2025 2024 Current assets Cash $73,500 $ 69,300 Accounts receivable 56,000 62,300 Inventory 117,600 120,400 Prepaid expenses 18,900 15,400 Total current assets $266,000 $267,400 Current liabilities Accrued expenses payable $10,500 $3,500 Accounts payable 59,500 64,400 Total current liabilities $70,000 $ 67,900 Prepare the operating activities section of the company's statement of cash flows for the year ended December 31, 2025, using the indirect method. (Show amounts that decrease cash flow with either a - sign e.g.-15,000 or in parenthesis e.g. (15,000).)arrow_forwardPlease provide problem with accounting questionarrow_forwardI need help with this financial accounting question using standard accounting techniques.arrow_forward
- On July 1, the accounts receivable account balance was $77,500. During July, $335,000 was collected from customers on account. Assuming the July 31 balance was $75,400, determine the fees billed to customers on account during July.arrow_forwardCan you solve this financial accounting problem using appropriate financial principles?arrow_forwardPlease explain the solution to this general accounting problem with accurate principles.arrow_forward
 Financial Accounting: The Impact on Decision Make...AccountingISBN:9781305654174Author:Gary A. Porter, Curtis L. NortonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Financial Accounting: The Impact on Decision Make...AccountingISBN:9781305654174Author:Gary A. Porter, Curtis L. NortonPublisher:Cengage Learning Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And AnalysisAccountingISBN:9781337788281Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald PagachPublisher:Cengage Learning
Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And AnalysisAccountingISBN:9781337788281Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald PagachPublisher:Cengage Learning College Accounting, Chapters 1-27AccountingISBN:9781337794756Author:HEINTZ, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
College Accounting, Chapters 1-27AccountingISBN:9781337794756Author:HEINTZ, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Cornerstones of Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337690881Author:Jay Rich, Jeff JonesPublisher:Cengage Learning
Cornerstones of Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337690881Author:Jay Rich, Jeff JonesPublisher:Cengage Learning Corporate Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305653535Author:Carl Warren, James M. Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning
Corporate Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305653535Author:Carl Warren, James M. Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning





