
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation: The name of the given structure needs to be determined.
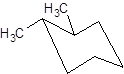
Concept Introduction: Chair conformation is the most stable conformation of cyclohexane. It is represented as follows:
Here, the substituted groups in the chair conformation are represented as follows:
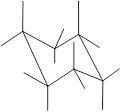
The groups showing in straight upward and downward directions are axial and the groups bend slightly right or left are equatorial.
The axial and equatorial groups are represented in the chair conformation as A and E:
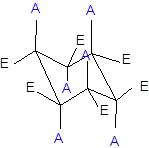
(b)
Interpretation: The given structure on the right needs to be completed which is obtained by chair flip.
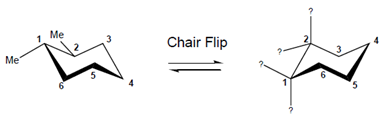
Concept Introduction:After a chair flip, all the axial bonds become equatorial and all the equatorial bonds become axial. But, the groups in the up direction remains upward and groups in down direction remain downward.
Also, if the molecule is cis, it remains cis even after chair flip. The same is the case with trans molecule.
(c)
Interpretation: The name of the structure formed after the chair flip in part (b) needs to be determined.
Concept Introduction: Chair conformation is the most stable conformation of cyclohexane. It is represented as follows:
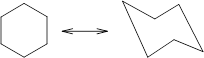
Here, the substituted groups in the chair conformation are represented as follows:
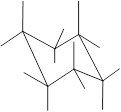
The groups showing in straight upward and downward directions are axial and the groups bend slightly right or left are equatorial.
The axial and equatorial groups are represented in the chair conformation as A and E:
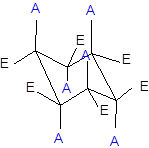
(d)
Interpretation: Whether the two structures are consistent with the given facts about chair flip or not needs to be determined.
Concept Introduction:
The chair conformation of cyclohexane is represented as follows:
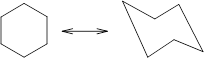
During the flipping, no bond is break. The numbering in the chair form is represented as follows:
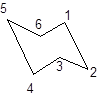
During ring flipping, mirror image of the chair conformation is formed.
It is represented as follows:
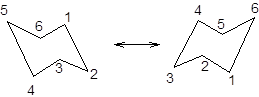
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Chapter 7 Solutions
Custom eBook for Organic Chemistry
- Synthesize 2-Ethyl-3-methyloxirane from dimethyl(propyl)sulfonium iodide using the necessary organic or inorganic reagents. Draw the structures of the compounds.arrow_forwardSynthesize 2-Hydroxy-2-phenylacetonitrile from phenylmethanol using the necessary organic or inorganic reagents. Draw the structures of the compounds.arrow_forwardSynthesize N-Methylcyclohexylamine from cyclohexanol using the necessary organic or inorganic reagents. Draw the structures of the compounds.arrow_forward
- Synthesize N-Methylcyclohexylamine from cyclohexanol using the necessary organic or inorganic reagents. Draw the structures of the compounds.arrow_forwardIf possible, please provide the formula of the compound 3,3-dimethylbut-2-enal.arrow_forwardSynthesize 1,4-dibromobenzene from acetanilide (N-phenylacetamide) using the necessary organic or inorganic reagents. Draw the structures of the compounds.arrow_forward
- Indicate the products obtained by mixing (3-oxo-3-phenylpropyl)triphenylphosphonium bromide with sodium hydride.arrow_forwardWe mix N-ethyl-2-hexanamine with excess methyl iodide and followed by heating with aqueous Ag2O. Indicate the major products obtained.arrow_forwardIndicate the products obtained by mixing acetophenone with iodine and NaOH.arrow_forward
- Indicate the products obtained by mixing 2-Propanone and ethyllithium and performing a subsequent acid hydrolysis.arrow_forwardIndicate the products obtained if (E)-2-butenal and 3-oxo-butanenitrile are mixed with sodium ethoxide in ethanol.arrow_forwardQuestion 3 (4 points), Draw a full arrow-pushing mechanism for the following reaction Please draw all structures clearly. Note that this intramolecular cyclization is analogous to the mechanism for halohydrin formation. COH Br + HBr Brarrow_forward
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
