
Concept explainers
Interpretation:Whether in the model of 1,2-dimethylcyclopentane, the molecule in the left box is same as the molecule in the right box or not needs to be determined.
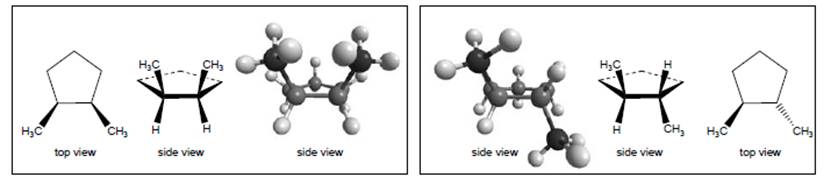
Concept Introduction:
The cis and trans isomerism concept will be applied here. Any molecule will be called cis if it follows the conditions for itthat is the same groups attached either above the plane or below the plane.For trans isomer,same groups are attached where one is above the plane and other group is below the plane or vice versa.
Answer to Problem 1CTQ
The given both structures of isomers of 1,2 dimethylcyclopentane are similar to each other. This is because when the bonds of the groups interchanges with each other, the bond’s spatial character changes. As a result of which these structures can be converted to each other without breaking of bonds.
Explanation of Solution
It is given that the left box and right box contain two molecules of 1,2-dimethylcyclopentane.Thus, it is very easy to conclude that the 2 different molecules are isomers of 1,2-dimethylcyclopentane. This is because both the molecules have same number of atoms in it.
Both the molecules are similar toeach other. Thiscan be explained as, if the interchanging of bonds takes place, similar structure can be obtained. In the interchanging of structure in left box and right box, there is no breaking of bonds takes place. For example, if the methyl group attached to the bond below the planeis interchanged with other group attached to the same atom, then the position of methyl group will be converted to above the plane from below the plane. In this process, no breaking of bond takes place then similar structure will be obtained.
Thus, the structure on the left box is similar to that on the right box.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 7 Solutions
Custom eBook for Organic Chemistry
- The temperature on a sample of pure X held at 1.25 atm and -54. °C is increased until the sample boils. The temperature is then held constant and the pressure is decreased by 0.42 atm. On the phase diagram below draw a path that shows this set of changes. pressure (atm) 2 0 0 200 400 temperature (K) Xarrow_forwardQUESTION: Answer Question 5: 'Calculating standard error of regression' STEP 1 by filling in all the empty green boxes *The values are all provided in the photo attached*arrow_forwardpressure (atm) 3 The pressure on a sample of pure X held at 47. °C and 0.88 atm is increased until the sample condenses. The pressure is then held constant and the temperature is decreased by 82. °C. On the phase diagram below draw a path that shows this set of changes. 0 0 200 temperature (K) 400 аarrow_forward
- er your payment details | bar xb Home | bartleby x + aleksogi/x/isl.exe/1o u-lgNskr7j8P3jH-1Qs_pBanHhviTCeeBZbufuBYT0Hz7m7D3ZcW81NC1d8Kzb4srFik1OUFhKMUXzhGpw7k1 O States of Matter Sketching a described thermodynamic change on a phase diagram 0/5 The pressure on a sample of pure X held at 47. °C and 0.88 atm is increased until the sample condenses. The pressure is then held constant and the temperature is decreased by 82. °C. On the phase diagram below draw a path that shows this set of changes. pressure (atm) 1 3- 0- 0 200 Explanation Check temperature (K) 400 X Q Search L G 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved Terms of Use Privacy Cearrow_forward5.arrow_forward6.arrow_forward
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
