1 Physics And Measurement 2 Motion In One Dimension 3 Vectors 4 Motion In Two Dimensions 5 The Laws Of Motion 6 Circular Motion And Other Applications Of Newton's Laws 7 Energy Of A System 8 Conservation Of Energy 9 Linear Momentum And Collisions 10 Rotation Of A Rigid Object About A Fixed Axis 11 Angular Momentum 12 Static Equilibrium And Elasticity 13 Universal Gravitation 14 Fluid Mechanics 15 Oscillatory Motion 16 Wave Motion 17 Sound Waves 18 Superposition And Standing Waves 19 Temperature 20 The First Law Of Thermodynamics 21 The Kinetic Theory Of Gases 22 Heat Engines, Entropy, And The Second Law Of Thermodynamics 23 Electric Fields 24 Gauss’s Law 25 Electric Potential 26 Capacitance And Dielectrics 27 Current And Resistance 28 Direct-current Circuits 29 Magnetic Fields 30 Sources Of The Magnetic Field 31 Faraday's Law 32 Inductance 33 Alternating-current Circuits 34 Electromagnetic Waves 35 The Nature Of Light And The Principles Of Ray Optics 36 Image Fonnation 37 Wave Optics 38 Diffraction Patterns And Polarization 39 Relativity 40 Introduction To Quantum Physics 41 Quantum Mechanics 42 Atomic Physics 43 Molecules And Solids 44 Nuclear Structure 45 Applications Of Nuclear Physics 46 Particle Physics And Cosmology expand_more
7.1 Systems And Environments 7.2 Work Done By A Constant Force 7.3 The Scalar Product Of Two Vectors 7.4 Work Done By A Varying Force 7.5 Kinetic Energy And The Work-kinetic Energy Theorem 7.6 Potential Energy Of A System 7.7 Conservative And Nonconservative Forces 7.8 Relationship Between Conservative Forces And Potential Energy 7.9 Energy Diagrams And Equilibrium Of A System Chapter Questions expand_more
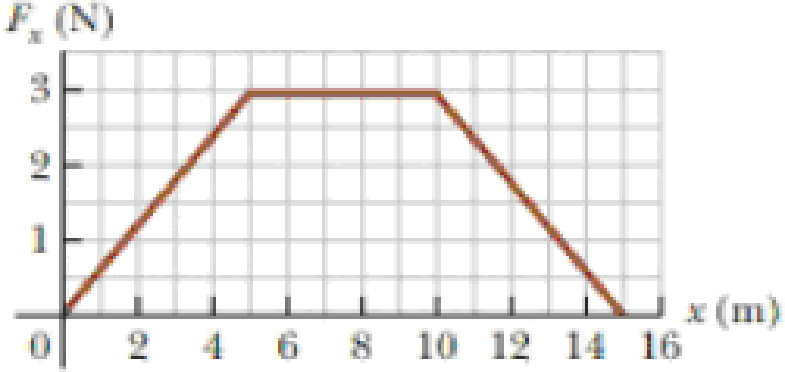
Problem 1OQ Problem 2OQ: If the net work done by external forces on a particle is zero, which of the following statements... Problem 3OQ Problem 4OQ: A cart is set rolling across a level table, at the same speed on every trial. If it runs into a... Problem 5OQ: Let N represent the direction horizontally north, NE represent northeast (halfway between north and... Problem 6OQ Problem 7OQ Problem 8OQ: As a simple pendulum swings back and forth, the forces acting on the suspended object arc (a) the... Problem 9OQ: Bullet 2 has twice the mass of bullet 1. Both are fired so that they have the same speed. If the... Problem 10OQ Problem 11OQ: If the speed of a particle is doubled, what happens to its kinetic energy? (a) It becomes four times... Problem 12OQ Problem 13OQ Problem 14OQ: A certain spring that obeys Hookes law is stretched by an external agent. The work done in... Problem 15OQ: A cart is set rolling across a level table, at the same speed on every trial. If it runs into a... Problem 16OQ Problem 1CQ: Can a normal force do work? If not, why not? If so, give an example. Problem 2CQ: Object 1 pushes on object 2 as the objects move together, like a bulldozer pushing a stone. Assume... Problem 3CQ Problem 4CQ: (a) For what values of the angle u between two vectors is their scalar product positive? (b) For... Problem 5CQ Problem 6CQ: Discuss the work done by a pitcher throwing a baseball. What is the approximate distance through... Problem 7CQ Problem 8CQ Problem 9CQ Problem 10CQ Problem 11CQ Problem 12CQ Problem 13CQ Problem 14CQ: Cite two examples in which a force is exerted on an object without doing any work on the object. Problem 1P: A shopper in a supermarket pushes a cart with a force of 35.0 N directed at an angle of 25.0 below... Problem 2P Problem 3P: In 1990, Walter Arfeuille of Belgium lifted a 281.5-kg object through a distance of 17.1 cm using... Problem 4P: The record number of boat lifts, including the boat and its ten crew members, was achieved by Sami... Problem 5P: A block of mass m = 2.50 kg is pushed a distance d = 2.20 m along a frictionless, horizontal table... Problem 6P: Spiderman, whose mass is 80.0 kg, is dangling on the free end of a 12.0-m-long rope, the other end... Problem 7P Problem 8P: Vector A has a magnitude of 5.00 units, and vector B has a magnitude of 9.00 units. The two vectors... Problem 9P Problem 10P: Find the scalar product of the vectors in Figure P7.7. Figure P7.7 Problem 11P Problem 12P: Using the definition of the scalar product, find the angles between (a) A=3i2j and B=4i4j, (b)... Problem 13P Problem 14P Problem 15P: A particle is subject to a force Fx that varies with position as shown in Figure P7.9. Find the work... Problem 16P: In a control system, an accelerometer consists of a 4.70-g object sliding on a calibrated horizontal... Problem 17P: When a 4.00-kg object is hung vertically on a certain light spring that obeys Hookes law, the spring... Problem 18P Problem 19P Problem 20P Problem 21P Problem 22P Problem 23P Problem 24P Problem 25P: A small particle of mass m is pulled to the top of a friction less half-cylinder (of radius R) by a... Problem 26P: The force acting on a particle is Fx = (8x 16), where F is in newtons and x is in meters. (a) Make... Problem 27P: When different loads hang on a spring, the spring stretches to different lengths as shown in the... Problem 28P Problem 29P Problem 30P: Review. The graph in Figure P7.20 specifies a functional relationship between the two variables u... Problem 31P Problem 32P Problem 33P: A 0.600-kg particle has a speed of 2.00 m/s at point and kinetic energy of 7.50 J at point . What... Problem 34P: A 4.00-kg particle is subject to a net force that varies with position as shown in Figure P7.9. The... Problem 35P: A 2 100-kg pile driver is used to drive a steel I-beam into the ground. The pile driver falls 5.00 m... Problem 36P: Review. In an electron microscope, there is an electron gun that contains two charged metallic... Problem 37P: Review. You can think of the workkinetic energy theorem as a second theory of motion, parallel to... Problem 38P Problem 39P: Review. A 5.75-kg object passes through the origin at time t = 0 such that its x component of... Problem 40P: A 1 000-kg roller coaster car is initially at the top of a rise, at point . It then moves 135 ft, at... Problem 41P: A 0.20-kg stone is held 1.3 m above the top edge of a water well and then dropped into it. The well... Problem 42P Problem 43P: A 4.00-kg particle moves from the origin to position , having coordinates x = 5.00 m and y = 5.00 m... Problem 44P Problem 45P: A force acting on a particle moving in the xy plane is given by F=(2yi+x2j), where F is in newtons... Problem 46P Problem 47P Problem 48P Problem 49P Problem 50P Problem 51P Problem 52P: For the potential energy curve shown in Figure P7.38, (a) determine whether the force Fx is... Problem 53P: A right circular cone can theoretically be balanced on a horizontal surface in three different ways.... Problem 54AP: The potential energy function for a system of particles is given by U(x) = x3 + 2x2 + 3x, where x is... Problem 55AP Problem 56AP: A particle moves along the xaxis from x = 12.8 m to x = 23.7 m under the influence of a force... Problem 57AP Problem 58AP Problem 59AP Problem 60AP: Why is the following situation impossible? In a new casino, a supersized pinball machine is... Problem 61AP Problem 62AP Problem 63AP: An inclined plane of angle = 20.0 has a spring of force constant k = 500 N/m fastened securely at... Problem 64AP Problem 65AP Problem 66CP: A particle of mass m = 1.18 kg is attached between two identical springs on a frictionless,... Problem 67CP format_list_bulleted


 Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University
University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University




