
Concept explainers
a)
To draw: A process flow diagram and determine the processing capacity of the whole process.
Process capacity:
Process capacity is the maximum level of output can be possibly obtained through a specific machine of the production line.
a)
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
Hours = 8 per day
Days = 5 per week.
Cost of purchasing parts:
Part A = 40 cents per piece.
Part B = 35 cents per piece
Part C = 15 cents per piece.
Production output:
Assembly line 1 = 140 components per hour.
Operational drill machines = 3
Drilling Part C = 50 parts per hour.
Final assembly line = 160 components per hour.
Cost of production:
Assembly labor = 30 cents per part.
Drilling labor = 15 cents per part.
Cost of electricity = 1 cent per part.
Total overhead cost = $1,200 per week,
Process flow diagram:
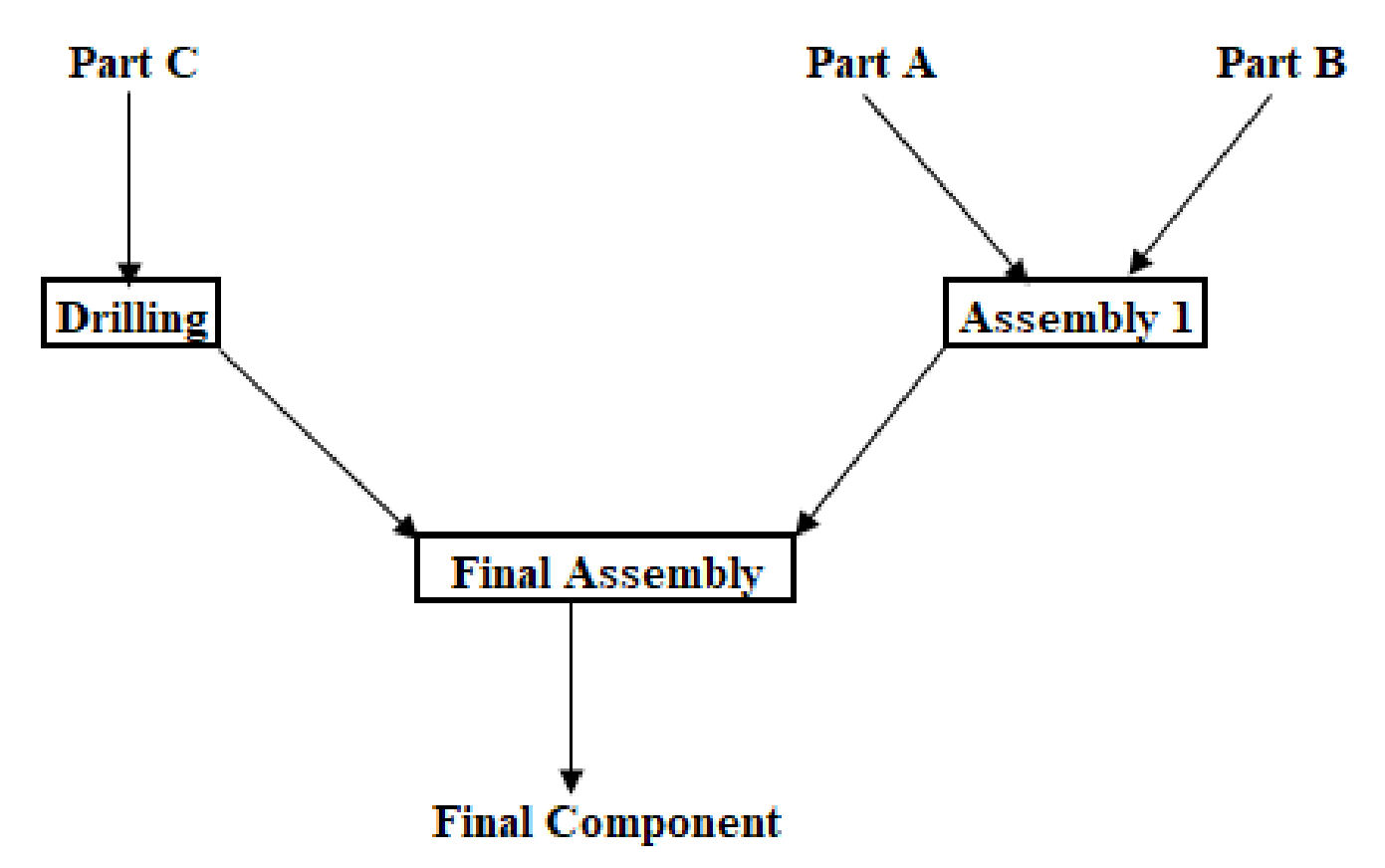
Calculation of capacity:
The overall capacity of the process will be equal to the activity with the lowest individual capacity.
Hence, the capacity of the process is 5,600 units per week.
b)
To calculate: The new process capacity and identify the operation that limits the capacity.
b)
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
Hours = 16 per day
Days = 5 per week.
Number of shifts = 2 per day
Cost of purchasing parts:
Part A = 40 cents per piece.
Part B = 35 cents per piece
Part C = 15 cents per piece.
Production output:
Assembly line 1 = 140 components per hour.
Operational drill machines = 4
Drilling hours = 8 per day
Drilling Part C = 50 parts per hour.
Final assembly line = 160 components per hour.
Cost of production:
Assembly labor = 30 cents per part.
Drilling labor = 15 cents per part.
Cost of electricity = 1 cent per part.
Total overhead cost = $1,200 per week,
Depreciation cost for equipment = $30 per week
Calculation of capacity:
The overall capacity of the process will be equal to the activity with the lowest individual capacity. The capacity of the process is 8,000 units per week.
The drilling operation only works for 8 hours in a day limiting the overall capacity.
c)
To calculate: The new process capacity and identify the operation that limits the capacity.
c)
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
Hours for assembly line 1 = 16 per day
Hours of Final assembly line = 12 per day
Days = 5 per week.
Number of shifts = 2 per day
Cost of purchasing parts:
Part A = 40 cents per piece.
Part B = 35 cents per piece
Part C = 15 cents per piece.
Production output:
Assembly line 1 = 140 components per hour.
Operational drill machines = 5
Drilling hours = 8 per day
Drilling Part C = 50 parts per hour.
Final assembly line = 160 components per hour.
Cost of production:
Assembly labor = 30 cents per part.
Drilling labor = 15 cents per part.
Cost of electricity = 1 cent per part.
Total overhead cost = $1,200 per week,
Depreciation cost for equipment = $30 per week
Calculation of capacity:
The overall capacity of the process will be equal to the activity with the lowest individual capacity. The capacity of the process is 9,600 units per week.
The final assembly line only works for 4 hours in the second shift limiting the overall capacity.
d)
To calculate: The cost per unit for the previous two calculated capacities.
d)
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
Hours for assembly line 1 = 16 per day
Hours of Final assembly line = 12 per day
Days = 5 per week.
Number of shifts = 2 per day
Cost of purchasing parts:
Part A = 40 cents per piece.
Part B = 35 cents per piece
Part C = 15 cents per piece.
Production output:
Assembly line 1 = 140 components per hour.
Operational drill machines = 5
Drilling hours = 8 per day
Drilling Part C = 50 parts per hour.
Final assembly line = 160 components per hour.
Cost of production:
Assembly labor = 30 cents per part.
Drilling labor = 15 cents per part.
Cost of electricity = 1 cent per part.
Total overhead cost = $1,200 per week,
Depreciation cost for equipment = $30 per week
Calculation of cost per unit when the capacity is 8,000 and 9,600 units:
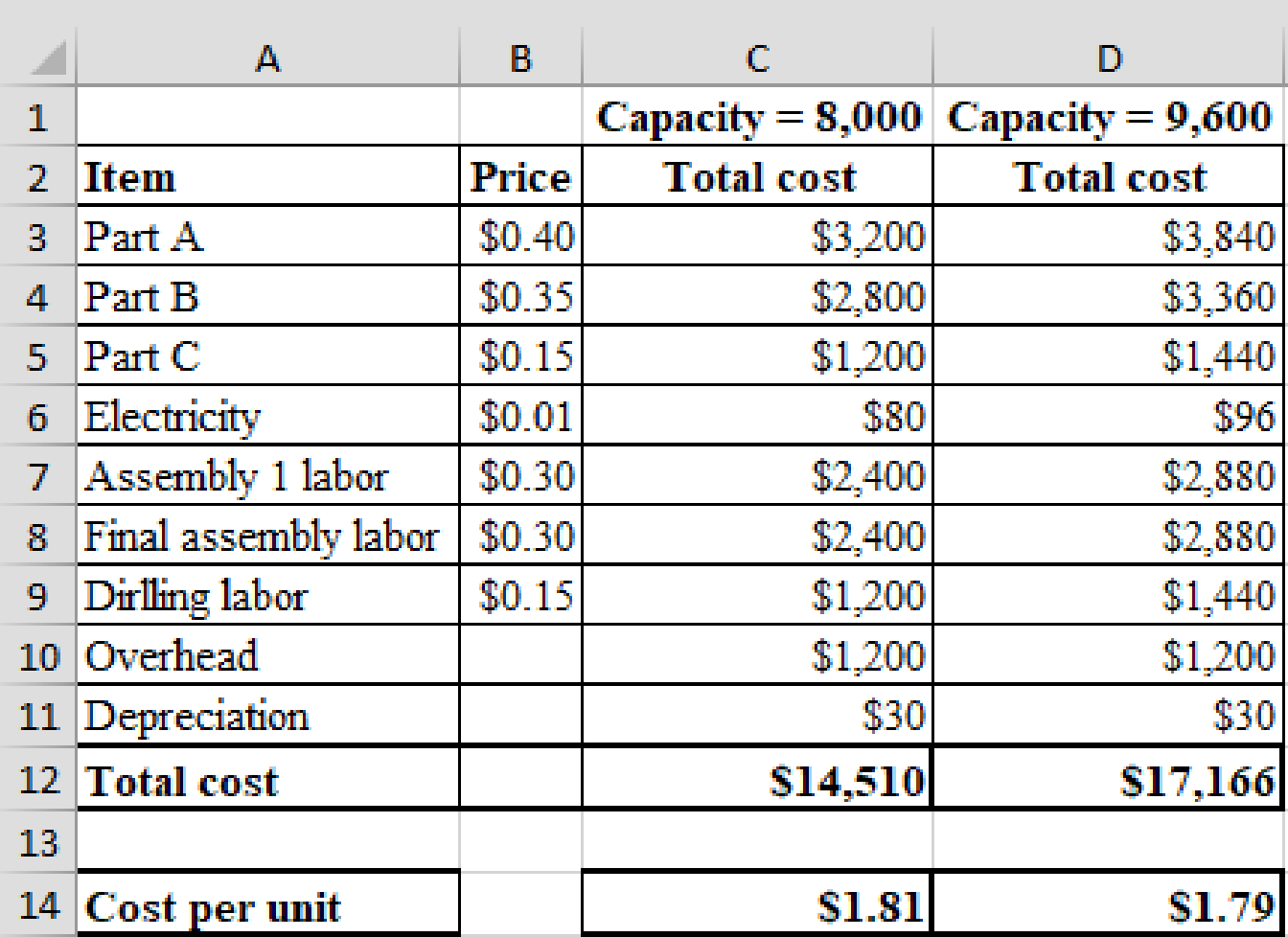
Formula:
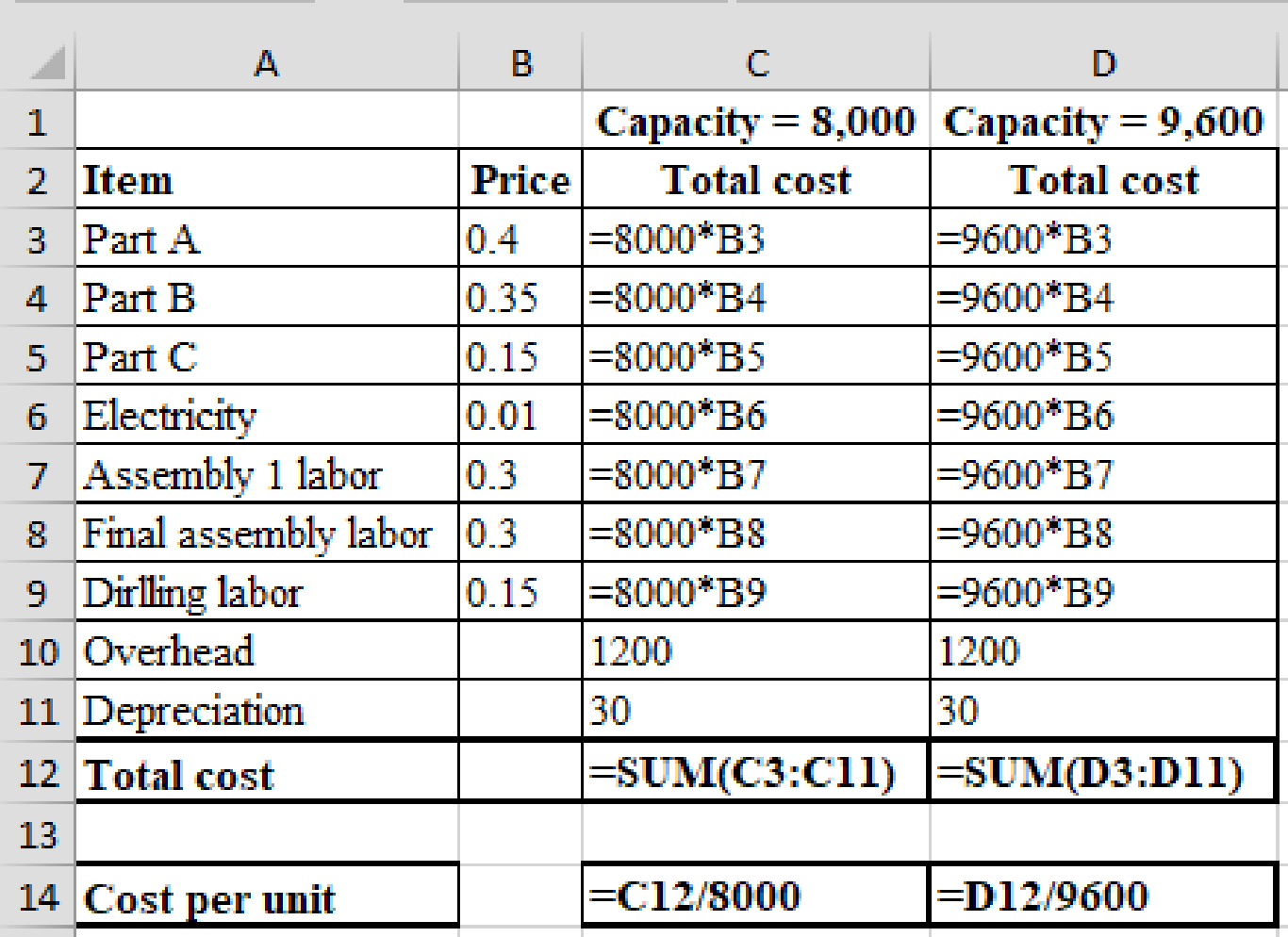
e)
To calculate: The break-even number of units.
e)
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
Product selling price = $4 per unit.
Fixed cost per drilling machine = $30,000
Output per week = 8,000 parts
Number of drilling machines = 4
Product buying price = $3 per unit
Calculation of break-even number of units:
Let ‘x’ be the number of units each option will produce.
The cost of buying the unit becomes
When the firm decides to manufacture the part, it incurs a fixed for each of the drilling machines which will be:
The cost per unit for manufacturing as calculated before is $1.81.
Therefore the total cost of manufacturing the part is:
The total cost of buying and manufacturing is equated to each other to calculate the break-even units as shown below:
The break-even units are 100,840 units.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 7 Solutions
Operations and Supply Chain Management
- Negotiators can gain several benefits from using the strategy of multiple equivalent simultaneous offers. By offering multiple options it reduces the chance of rejection. It also improves the chances of reaching reaching an agreement. By presenting multiple offers, it shows you are flexible. disagree with this post or add on to the postarrow_forwardThe strategy of Multiple Equivalent Simultaneous Offers involves presenting several equally valuable options to the other party during negotiations. This approach benefits negotiators by creating flexibility and increasing the chances of finding a mutually agreeable solution. By offering multiple options, negotiators show that they are open to compromise, which can build trust and make the negotiation process smoother. It also helps avoid getting stuck on one issue, as the other party can choose from several alternatives that meet their needs. In my experience, using MESOs in a work negotiation helped both parties reach an agreement more quickly because each option was carefully thought out to address different needs, and this made it easier for us to settle on one that worked for both sides. This strategy can also reveal what is most important to the other party, helping negotiators understand their priorities better. agree or disagree with the postarrow_forwardExamine the conflicts between improving customer service levels and controlling costs in sales. Strategies to Balance Both customer service levels and controlling costs in sales 1.Outsourcing and workforce optimization 2. AI-driven customer supportarrow_forward
- how can you gain trust in a negotiation setting?arrow_forward✓ Custom $€ .0 .on File Home Insert Share Page Layout Formulas Data Review View Help Draw Arial 10 B B14 ✓ X✓ fx 1400 > 甘く 曲 > 冠 > Comments Editing ✓ . . . P Q R S T 3 A Production cost ($/unit) B с D E F G H J K L M N $74.00 4 Inventory holding cost ($/unit) $1.50 5 Lost sales cost ($/unit) $82.00 6 Overtime cost ($/unit) $6.80 7 Undertime cost ($/unit) $3.20 8 Rate change cost ($/unit) $5.00 9 Normal production rate (units) 2,000 10 Ending inventory (previous Dec.) 800 11 Cumulative 12 13 Month Demand Cumulative Demand Product Production Availability Ending Inventory Lost Cumulative Cumulative Product Sales 14 January 1,400 1,475 15 FUERANZ222222223323333BRUINE 14 February 1,000 2,275 Month January February Demand Demand Production Availability Ending Inventory Lost Sales 1,400 #N/A 1,475 #N/A #N/A #N/A 1,000 #N/A 2,275 #N/A #N/A #N/A 16 March 1,800 2,275 March 1,800 #N/A 2,275 #N/A #N/A #N/A 17 April 2,700 2,275 April 2,700 #N/A 2,275 #N/A #N/A #N/A 18 May 3,000 2,275 May 3,000 #N/A…arrow_forwardFollow guidelines and summarize in a paragrapharrow_forward
 Practical Management ScienceOperations ManagementISBN:9781337406659Author:WINSTON, Wayne L.Publisher:Cengage,
Practical Management ScienceOperations ManagementISBN:9781337406659Author:WINSTON, Wayne L.Publisher:Cengage, Operations ManagementOperations ManagementISBN:9781259667473Author:William J StevensonPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Operations ManagementOperations ManagementISBN:9781259667473Author:William J StevensonPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Operations and Supply Chain Management (Mcgraw-hi...Operations ManagementISBN:9781259666100Author:F. Robert Jacobs, Richard B ChasePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Operations and Supply Chain Management (Mcgraw-hi...Operations ManagementISBN:9781259666100Author:F. Robert Jacobs, Richard B ChasePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
 Purchasing and Supply Chain ManagementOperations ManagementISBN:9781285869681Author:Robert M. Monczka, Robert B. Handfield, Larry C. Giunipero, James L. PattersonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Purchasing and Supply Chain ManagementOperations ManagementISBN:9781285869681Author:Robert M. Monczka, Robert B. Handfield, Larry C. Giunipero, James L. PattersonPublisher:Cengage Learning Production and Operations Analysis, Seventh Editi...Operations ManagementISBN:9781478623069Author:Steven Nahmias, Tava Lennon OlsenPublisher:Waveland Press, Inc.
Production and Operations Analysis, Seventh Editi...Operations ManagementISBN:9781478623069Author:Steven Nahmias, Tava Lennon OlsenPublisher:Waveland Press, Inc.





