
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
An oxygen-binding curve for a hypothetical two subunit hemoglobin with
Concept introduction:
Hill equation is represented as follows:
Here, Y- fractional saturation
n − a measure of the degree of cooperativity in ligand binding.
P50 − partial pressure of oxygen at which hemoglobin is half saturated.
The Hill plot of log(Y/1-Y) versus log(P50) should be a linear graph with slope of n.
Answer to Problem 14P
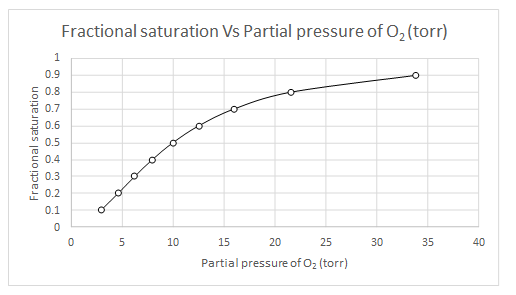
Explanation of Solution
The values of
| Y | log(Y/(1-Y) | log(Y/(1-Y)-n log (P50) | log (pO2) | pO2 |
| 0.1 | -0.95424251 | 0.845757491 | 0.469865 | 2.950294 |
| 0.2 | -0.60205999 | 1.197940009 | 0.665522 | 4.629374 |
| 0.3 | -0.36797679 | 1.432023215 | 0.795568 | 6.245518 |
| 0.4 | -0.17609126 | 1.623908741 | 0.902172 | 7.983099 |
| 0.5 | 0 | 1.8 | 1 | 10 |
| 0.6 | 0.176091259 | 1.976091259 | 1.097828 | 12.52646 |
| 0.7 | 0.367976785 | 2.167976785 | 1.204432 | 16.01148 |
| 0.8 | 0.602059991 | 2.402059991 | 1.334478 | 21.60119 |
| 0.9 | 0.954242509 | 2.754242509 | 1.530135 | 33.89493 |
(b)
Interpretation:
An oxygen-binding curve for shypothetical two subunit hemoglobin with
Concept introduction:
Concerted model equation is written as follows:
Here, Y − fractional saturation
a − ratio between the substrate concentration and the dissociation constant for a ligand binding to a single site in R state.
L − The ratio of the concentrations of the T and R states with no ligands bound
c − the ratio between the dissociation constant for a ligand binding to a single site in R state and that of T state.
n − number of binding sites
Also, the ratio can be calculated as follows:
Here,
pO2 − partial pressure of oxygen
KR - the dissociation constant for a ligand binding to a single site in R state.
Answer to Problem 14P
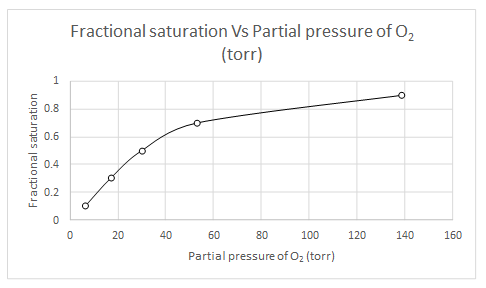
Explanation of Solution
When
Likewise, partial pressure of oxygen for several fractional saturation values are calculated and a plot of fractional saturation versus oxygen partial pressure is drawn.
| Y | pO2 |
| 0.1 | 6.55 |
| 0.3 | 17.09 |
| 0.5 | 30.15 |
| 0.7 | 53.21 |
| 0.9 | 138.91 |
Want to see more full solutions like this?
- Which type of enzyme catalyses the following reaction? oxidoreductase, transferase, hydrolase, lyase, isomerase, or ligase.arrow_forward+NH+ CO₂ +P H₂N + ATP H₂N NH₂ +ADParrow_forwardWhich type of enzyme catalyses the following reaction? oxidoreductase, transferase, hydrolase, lyase, isomerase, or ligase.arrow_forward
- Which features of the curves in Figure 30-2 indicates that the enzyme is not consumed in the overall reaction? ES is lower in energy that E + S and EP is lower in energy than E + P. What does this tell you about the stability of ES versus E + S and EP versus E + P.arrow_forwardLooking at the figure 30-5 what intermolecular forces are present between the substrate and the enzyme and the substrate and cofactors.arrow_forwardprovide short answers to the followings Urgent!arrow_forward
- Pyruvate is accepted into the TCA cycle by a “feeder” reaction using the pyruvatedehydrogenase complex, resulting in acetyl-CoA and CO2. Provide a full mechanismfor this reaction utilizing the TPP cofactor. Include the roles of all cofactors.arrow_forwardB- Vitamins are converted readily into important metabolic cofactors. Deficiency inany one of them has serious side effects. a. The disease beriberi results from a vitamin B 1 (Thiamine) deficiency and ischaracterized by cardiac and neurological symptoms. One key diagnostic forthis disease is an increased level of pyruvate and α-ketoglutarate in thebloodstream. How does this vitamin deficiency lead to increased serumlevels of these factors? b. What would you expect the effect on the TCA intermediates for a patientsuffering from vitamin B 5 deficiency? c. What would you expect the effect on the TCA intermediates for a patientsuffering from vitamin B 2 /B 3 deficiency?arrow_forwardDraw the Krebs Cycle and show the entry points for the amino acids Alanine,Glutamic Acid, Asparagine, and Valine into the Krebs Cycle - (Draw the Mechanism). How many rounds of Krebs will be required to waste all Carbons of Glutamic Acidas CO2?arrow_forward
 BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305577206Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. GrishamPublisher:Cengage Learning
BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305577206Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. GrishamPublisher:Cengage Learning BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305961135Author:Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Owen M. McDougalPublisher:Cengage Learning
BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305961135Author:Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Owen M. McDougalPublisher:Cengage Learning Human Physiology: From Cells to Systems (MindTap ...BiologyISBN:9781285866932Author:Lauralee SherwoodPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Physiology: From Cells to Systems (MindTap ...BiologyISBN:9781285866932Author:Lauralee SherwoodPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning





