
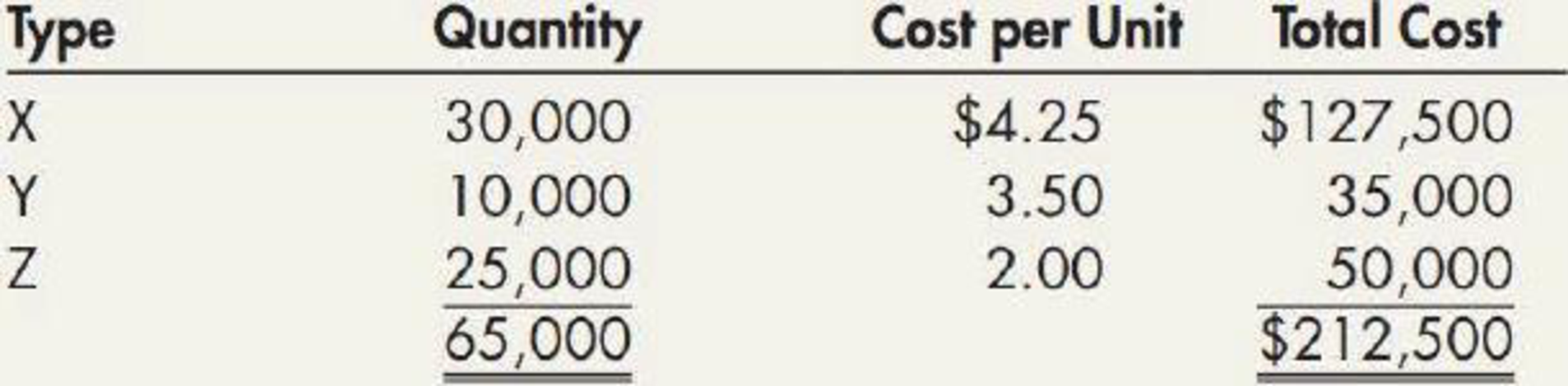
Webster Company adopted do liar-value LIFO on January 1, 2019. Webster produces three products: X, Y, and Z. Webster’s beginning inventory consisted of the following:
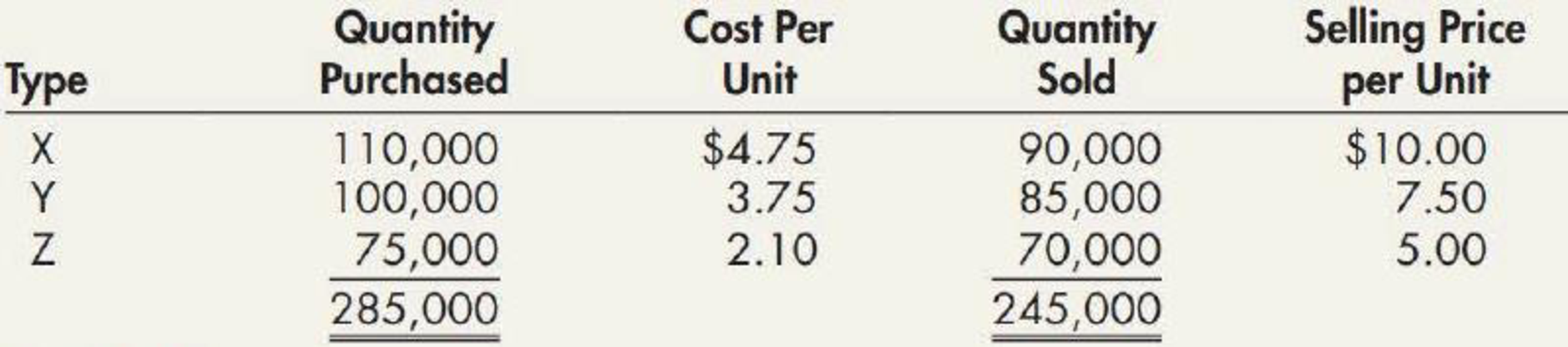
During 2019, Webster had the following purchases and sales:
Required:
- 1. Compute the LIFO cost of the ending inventory assuming Webster uses a single inventory pool. Round cost index to 4 decimal places.
- 2. Compute the LIFO cost of the ending inventory assuming Webster uses three inventory pools. Round cost indexes to 4 decimal places.
1.
Calculate the ending inventory for LIFO cost if single inventory pool is used.
Explanation of Solution
Cost index:
Cost index refer to the index which relates the inventory cost of current year with the base year. The cost index is usually prepared with a sample from the total inventory.
Double-extension method:
Under the double-extension method of cost index, the ending inventory of the current year are valued at the current year costs and related with the base year’s cost.
Calculate the ending inventory in units:
| Particulars | Product X | Product Y | Product Z |
| Beginning inventory | 30,000 | 10,000 | 25,000 |
| Add: Net Purchases | 110,000 | 100,000 | 75,000 |
| Units available for sale | 140,000 | 110,000 | 100,000 |
| Less: Sales | (90,000) | (85,000) | (70,000) |
| Ending inventory | 50,000 | 25,000 | 30,000 |
Table (1)
Calculate the cost index:
Calculate the ending inventory at the Base year cost:
Calculate the increase in inventory at the Base year cost:
Calculate the layer increase in inventory at the Current year cost:
Calculate the LIFO ending inventory cost:
Thus, the ending inventory for LIFO cost if single inventory pool is used is $374,033.
2.
Calculate the ending inventory for LIFO cost if three inventory pools are used.
Explanation of Solution
Calculate the cost index for Product X:
Calculate the ending inventory at the Base year cost for Product X:
Calculate the increase in inventory at the Base year cost for Product X:
Calculate the layer increase in inventory at the Current year cost for Product X:
Calculate the LIFO ending inventory cost for Product X:
Thus, the ending inventory for LIFO cost for Product X if three inventory pools are used is $222,500.
Calculate the cost index for Product Y:
Calculate the ending inventory at the Base year cost for Product Y:
Calculate the increase in inventory at the Base year cost for Product Y:
Calculate the layer increase in inventory at the Current year cost for Product Y:
Calculate the LIFO ending inventory cost for Product Y:
Thus, the ending inventory for LIFO cost for Product Y if three inventory pools are used is $91,252.
Calculate the cost index for Product Z:
Calculate the ending inventory at the Base year cost for Product Z:
Calculate the increase in inventory at the Base year cost for Product Z:
Calculate the layer increase in inventory at the Current year cost for Product Z:
Calculate the LIFO ending inventory cost for Product Z:
Thus, the ending inventory for LIFO cost for Product Z if three inventory pools are used is $60,500.
Calculate the LIFO ending inventory cost:
Thus, the ending inventory for LIFO cost if three inventory pools are used is $374,252.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 7 Solutions
Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And Analysis
 Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And AnalysisAccountingISBN:9781337788281Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald PagachPublisher:Cengage LearningPrinciples of Accounting Volume 1AccountingISBN:9781947172685Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College
Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And AnalysisAccountingISBN:9781337788281Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald PagachPublisher:Cengage LearningPrinciples of Accounting Volume 1AccountingISBN:9781947172685Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College

