
Concept explainers
(a)
Sketch the voltage waveform of capacitor.
(a)
Explanation of Solution
Given data:
Value of capacitor is
Formula used:
Refer to FIGURE 7.44 in the textbook.
The expression for the voltage across the capacitor is:
Here,
Calculation:
Refer to the FIGURE 7.43 (a).
Substitute the limits
The equation for the current waveform for time period
Substitute
Here,
Substitute
Since initial value of voltage at
Therefore,
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Since initial value of voltage at
Therefore,
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Since initial value of voltage at
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Since initial value of voltage at
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
The expression for the voltage across capacitor for time period
Substitute
The labeled sketch of voltage waveform for
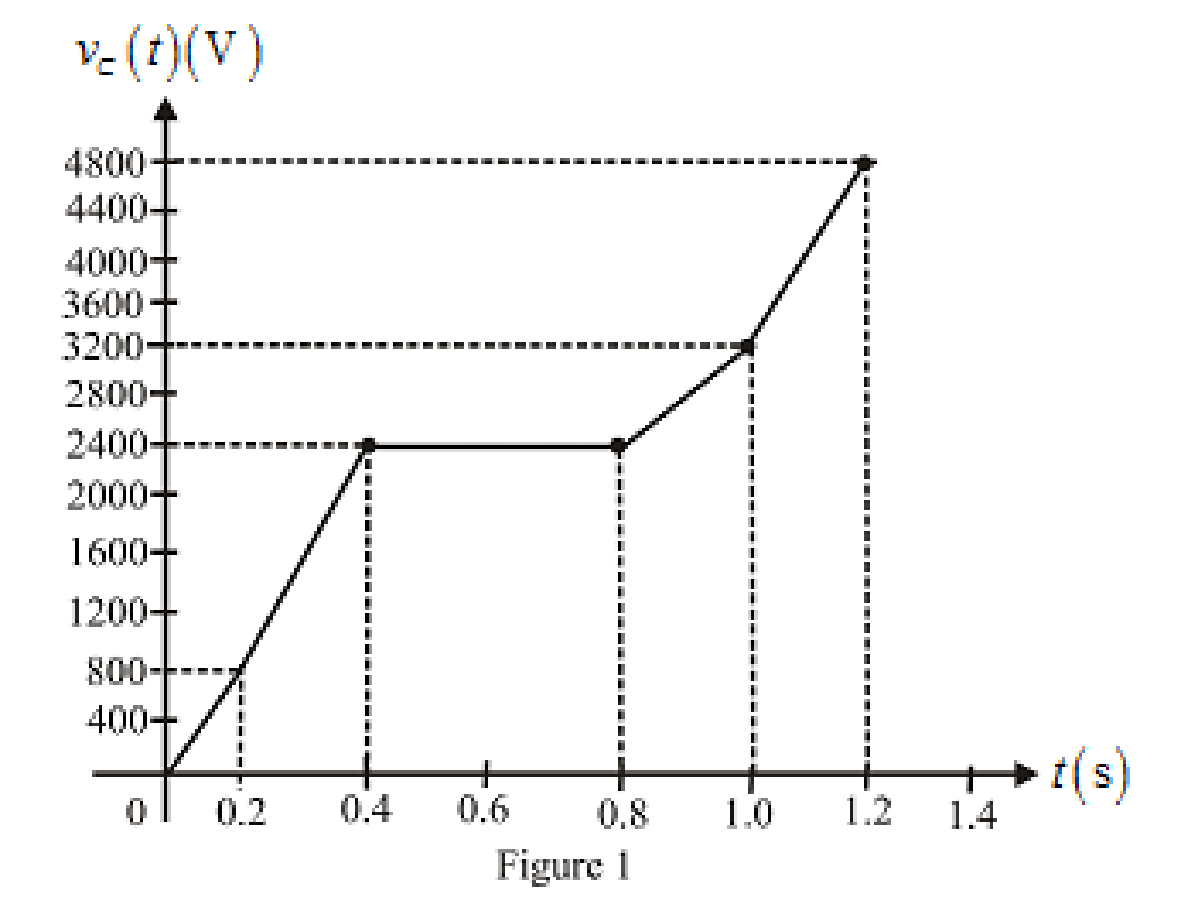
Conclusion:
Thus, the resulting voltage waveform is sketched.
(b)
Find the voltage of capacitor.
(b)
Answer to Problem 11E
The voltage of capacitor for given time duration is
Explanation of Solution
Given Data:
Value of capacitor is
Value of time duration for capacitor voltage is
Formula used:
The expression for the voltage at given point of time is,
Calculation:
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Conclusion:
Thus, the voltage of capacitor for given time duration is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 7 Solutions
ENGINEERING CIRCUIT...(LL)>CUSTOM PKG.<
- Consider the following mechanical system. In the figure, y(t) denotes the displacement of the mass from its equilibrium position and u(t) denotes the force applied to the mass. k1 kz - y(t) -0000 0000 3 ► u(t) b a) Find the differential equation model of the system. b) Find the state-space model for the system. Write x, A, B, C and D clearly in your answer.arrow_forwardSee whole documentarrow_forwardC(s) a) Reduce the following system to a single transfer function G(s): R(s) G3(s) R(s) C(s) G1(s) G2(s) G4(s) b) If the input r(t) is a step signal, what will be the output C(s)? Hint: Move the block G₂(s).arrow_forward
- Consider the following electrical system. In the figure, u(t) and y(t) denote the input and output voltages, respectively. Please note that y(t) is the voltage across the resistor. с u(t) +1 y(t) R 0000 a) Find the differential equation model of the system. b) Write the transfer function H(s) = Y(s) of the system. U(s) c) If u(t) = 1 volt, what will be the steady-state output voltage?arrow_forwardQ1: A Moore model sequential network has one input (X) and two outputs (Z2 Z1). An output Z2 = 1 and Z1 =0 occurs every time the input sequence 110 is completed and An output Z2 = 0 and Z1 1 occurs every time the input sequence 010 is completed otherwise Z2 = 0 and Z1 =0. Overlap is not allowed. Use D flip-flops in your design: a) Sketch the state diagram with minimum number of states. b) Construct the state table. = c) Construct the state assigned table. d) Determine the next-state and output logic expressions. e) Sketch the logic circuit.arrow_forwardConsider the following system where two objects are separated by a thermal conductor with thermal resistance R = 1. The temperatures of the objects are denoted by T₁ (t) and T2(t) and their thermal capacities are C₁ = 1 and C2 = 2. Assume, quantities follow their respective SI units. T₁(+) C₁ = 1 12(+) C₂=2 R=1 |T,(0) = 20° -Insulator: no heat flow 5260033500 If the initial temperatures of the two objects are 20°C and 50°C respectively, what will be the steady-state values of the temperatures of these two objects? What is the impact of R in the steady-state value?arrow_forward
- 1 ΚΩ N₁ m ZL (10+j4) ks2 178/0° V N2 -202 Ω Figure P11.31 Circuit for Problem 11.31.arrow_forwardHW_#6 HW_06.pdf EE 213-01 Assignments zm Rich LTI uah.instructure.com Z (MAE 272-01) (SP25) DYNAMICS b My Questions | bartleby ✓ Download → Info Page 1 > of 2 - ZOOM + 1) (5 pts) Note have to use nodal analysis at Vp and Vn. a) Determine Vout in the following ideal op-amp circuit. The power supplies supplying power to the op-amp have voltage values of ±15 volts (Vcc = +15 Volts, -VCC = -15Volts) b) Determine the value of RĘ that makes Vo, -15 Volts. c) What value of RF makes Vo = 0 Volts? out F out = 2V 1V 25K 10K 2V 1V 30K 100K RF 12K 12K + E น out E 2) (5 pts) Find Vout in the following circuit. Perform nodal analysis at nodes VN, VP and Va 20K Va 20K 10K 10K 1 V 2 V 5K Vout 15K Note: There is no restriction on the value for Vout for this problem. 3) (5 pts) For the Thevenin equivalent circuit shown, answer the following questions: 250 Ohms a 200 V ° b a) What load resistor results in maximum power delivered to that resistor? b) What is the maximum power delivered to the resistor in…arrow_forwardA 30 kVA, single-phase transformer is rated 240/120 volts is connected as a 120 / 360 volt autotransformer. Determine the rating of the auotransformer.arrow_forward
- I just want a human answerarrow_forwardDesign a synchronous Up/Down counter to produce the following sequence (4 9 2,0,7,6,3,1,5) using T flip-flop. The counter should count up when Up/Down =1, and down when Up/Down = 0.arrow_forwardQ2: Using minimum number of D flip-flops, design a synchrounus counter. The counter counts in the sequence 0,15,2,7,0,15,....... When its enable input x is equal to 1; otherwise the counter is idle.arrow_forward
 Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON
Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON
Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,





