
Concept explainers
a)
To determine: The control limits for the mean and range chart and the overall means
Introduction: Control charts used to determine whether the process is under control or not. Attributes and variables are the factors under the control charts.
a)
Answer to Problem 11P
Hence, the UCL for
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The following information is given:
| Sample | Sample mean (in.) | Range (in.) |
| 1 | 10.002 | 0.011 |
| 2 | 10.002 | 0.014 |
| 3 | 9.991 | 0.007 |
| 4 | 10.006 | 0.022 |
| 5 | 9.997 | 0.013 |
| 6 | 9.999 | 0.012 |
| 7 | 10.001 | 0.008 |
| 8 | 10.005 | 0.013 |
| 9 | 9.995 | 0.004 |
| 10 | 10.001 | 0.011 |
| 11 | 10.001 | 0.014 |
| 12 | 10.006 | 0.009 |
Twelve samples that contain five parts each were taken.
Calculate the average for sample and range:
| Sample | Sample mean (in.) | Range (in.) |
| 1 | 10.002 | 0.011 |
| 2 | 10.002 | 0.014 |
| 3 | 9.991 | 0.007 |
| 4 | 10.006 | 0.022 |
| 5 | 9.997 | 0.013 |
| 6 | 9.999 | 0.012 |
| 7 | 10.001 | 0.008 |
| 8 | 10.005 | 0.013 |
| 9 | 9.995 | 0.004 |
| 10 | 10.001 | 0.011 |
| 11 | 10.001 | 0.014 |
| 12 | 10.006 | 0.009 |
| Total | 120.006 | 0.138 |
| Average | 10.0005 | 0.0115 |
Working note:
Average for sample:
It is calculated by dividing the total of sample and number of samples. Hence, the value of
Average for range:
It is calculated by dividing the total of range and number of samples. Hence, the value of
Determine the UCL and LCL for mean:
Formulae to calculate control limits:
Here, the overall mean
Substitute the values in equation (1) to determine the value of UCL as follows:
Hence, the UCL value is 10.00714.
Substitute the values in equation (2) to determine the value of LCL as follows:
Hence, the LCL value is 9.993865.
Therefore for the
Determine the UCL and LCL for range:
Formulae to calculate control limits:
Here,
The average range is
Substitute the values in equation (3) to determine the value of UCL as follows:
Hence, the UCL value is 0.024323.
Substitute the values in equation (4) to determine the value of LCL as follows:
Hence, the LCL value is 0.
Therefore, for the R-chart, the upper control limit is
b)
To plot: The values of sample means and ranges in the chart.
Introduction: Control charts used to determine whether the process is under control or not. Attributes and variables are the factors under the control charts.
b)
Answer to Problem 11P
Control chart has been plotted for sample means and ranges.
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The following information is given:
| Sample | Sample mean (in.) | Range (in.) |
| 1 | 10.002 | 0.011 |
| 2 | 10.002 | 0.014 |
| 3 | 9.991 | 0.007 |
| 4 | 10.006 | 0.022 |
| 5 | 9.997 | 0.013 |
| 6 | 9.999 | 0.012 |
| 7 | 10.001 | 0.008 |
| 8 | 10.005 | 0.013 |
| 9 | 9.995 | 0.004 |
| 10 | 10.001 | 0.011 |
| 11 | 10.001 | 0.014 |
| 12 | 10.006 | 0.009 |
Twelve samples that contain five parts each were taken.
Plot the sample mean values in the
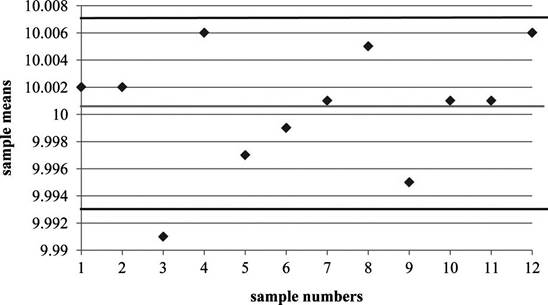
Note: Observe that sample 3 mean value is lower than the
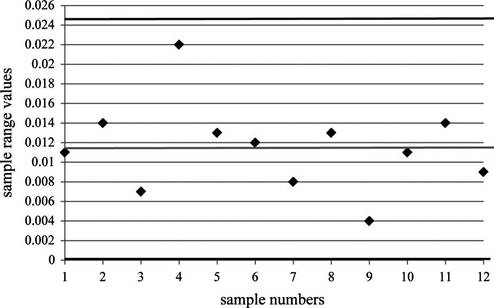
Plot the sample mean values in theR-control chart where
c)
To determine: Whether the process is in control
Introduction: Control charts used to determine whether the process is under control or not. Attributes and variables are the factors under the control charts.
c)
Answer to Problem 11P
Process is out of control during sample #3 in
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The following information is given:
| Sample | Sample mean (in.) | Range (in.) |
| 1 | 10.002 | 0.011 |
| 2 | 10.002 | 0.014 |
| 3 | 9.991 | 0.007 |
| 4 | 10.006 | 0.022 |
| 5 | 9.997 | 0.013 |
| 6 | 9.999 | 0.012 |
| 7 | 10.001 | 0.008 |
| 8 | 10.005 | 0.013 |
| 9 | 9.995 | 0.004 |
| 10 | 10.001 | 0.011 |
| 11 | 10.001 | 0.014 |
| 12 | 10.006 | 0.009 |
Twelve samples that contain five parts each were taken.
Determine whether the process is in control:
Since, the mean for sample #3 is outside the control limits of the
d)
To determine: Why the process is not in control
Introduction: Control charts used to determine whether the process is under control or not. Attributes and variables are the factors under the control charts.
d)
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The following information is given:
| Sample | Sample mean (in.) | Range (in.) |
| 1 | 10.002 | 0.011 |
| 2 | 10.002 | 0.014 |
| 3 | 9.991 | 0.007 |
| 4 | 10.006 | 0.022 |
| 5 | 9.997 | 0.013 |
| 6 | 9.999 | 0.012 |
| 7 | 10.001 | 0.008 |
| 8 | 10.005 | 0.013 |
| 9 | 9.995 | 0.004 |
| 10 | 10.001 | 0.011 |
| 11 | 10.001 | 0.014 |
| 12 | 10.006 | 0.009 |
Twelve samples that contain five parts each were taken.
Determine why the process is not in control:
Further investigations are necessary to check whether the mean value of sample #3 is a freak incident outside the three sigma limits (which has a 0.27% probability). Perhaps 12 more samples can be drawn and examined whether such an incident occurs again. In case it happens again, the process needs to be examined in detail.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 6 Solutions
EBK PRINCIPLES OF OPERATIONS MANAGEMENT
- Can you guys help me with this? Thank you! Here's the question: Compared to the CONSTRAINT model, how has the network changed? How do you plan to add contingency to your network? Please answer this thoroughly Here's the what-if scenario: Assume that the LA warehouse becomes temporarily or even indefinitely disabled since facing a large-scale labor disruption. Re-optimize the network considering this new constraint. Here's the scenario comparison analysis: Scenario Constraint Scenario vs What-if Scenario Summary The Constraint Scenario exhibits a higher total cost of $7,424,575.45 compared to the What-if Scenario's total cost of $6,611,905.60, signifying a difference of approximately $812,669.85, which indicates a more expensive operation in the Constraint Scenario. The average service time is slightly higher in the Constraint Scenario (0.72 days vs. 0.70 days), suggesting that the What-if Scenario provides a marginally quicker service. Moreover, the average end-to-end service time…arrow_forwardCan you guys help me with this? Thank you! Here's the question: Compared to the CONSTRAINT model, how has the network changed? How do you plan to add contingency to your network? Please answer this throughly Here's the what-if scenario: Assume that Dallas plant has lost power. It cannot serve the DCs anymore and has to remain locked indefinitely. Re-optimize the network considering this new constraint. Here's the scenario comparison analysis: Scenario Constraint Scenario vs What-if Scenario Summary In comparing the Constraint Scenario to the What-if Scenario, a few key differences highlight the efficiencies evident in the supply chain. Firstly, the total cost in the Constraint Scenario is lower at $7,424,575.45, while the What-if Scenario incurs a total cost of $7,486,369.12, resulting in a cost delta of $61,793.67. Additionally, although both scenarios exhibit the same average service time of 0.72 days, the What-if Scenario has a more favorable average end-to-end service time of 2.41…arrow_forwardEmployee In-Service Training ASSIGNMENT: In-Service Training. The intern is required to plan and implement two in-service training sessions for employees. Each in-service should last at least 10 but not more than 30 minutes and should be given to all employees affected. The preceptor or supervisor/unit manager must approve all in-service topics. 1) One presentation should be related to a policy or procedure of any kind (e.g. proper use of equipment); 2) The second presentation must be related to sanitation or safety. For each in-service presentation, the intern must develop a written class plan and a visual aid (may be a handout, poster, PowerPoint slide presentation, etc.) appropriate to the life experiences, cultural diversity and educational background of the target audience. The intern must also measure behavior change. Note, this cannot be measured by a written pre- and post- test. That would be measuring knowledge. The intern mustactually observe and document that the learners…arrow_forward
- A small furniture manufacturer produces tables and chairs. Each product must go through three stages of the manufacturing process – assembly, finishing, and inspection. Each table requires 3 hours of assembly, 2 hours of finishing, and 1 hour of inspection. The profit per table is $120 while the profit per chair is $80. Currently, each week there are 200 hours of assembly time available, 180 hours of finishing time, and 40 hours of inspection time. Linear programming is to be used to develop a production schedule. Define the variables as follows: T = number of tables produced each week C= number of chairs produced each week According to the above information, what would the objective function be? (a) Maximize T+C (b) Maximize 120T + 80C (c) Maximize 200T+200C (d) Minimize 6T+5C (e) none of the above According to the information provided in Question 17, which of the following would be a necessary constraint in the problem? (a) T+C ≤ 40 (b) T+C ≤ 200 (c) T+C ≤ 180 (d) 120T+80C ≥ 1000…arrow_forwardAs much detail as possible. Dietary Management- Nursing Home Don't add any fill-in-the-blanksarrow_forwardMenu Planning Instructions Use the following questions and points as a guide to completing this assignment. The report should be typed. Give a copy to the facility preceptor. Submit a copy in your Foodservice System Management weekly submission. 1. Are there any federal regulations and state statutes or rules with which they must comply? Ask preceptor about regulations that could prescribe a certain amount of food that must be kept on hand for emergencies, etc. Is the facility accredited by any agency such as Joint Commission? 2. Describe the kind of menu the facility uses (may include standard select menu, menu specific to station, non-select, select, room service, etc.) 3. What type of foodservice does the facility have? This could be various stations to choose from, self-serve, 4. conventional, cook-chill, assembly-serve, etc. Are there things about the facility or system that place a constraint on the menu to be served? Consider how patients/guests are served (e.g. do they serve…arrow_forward
 Practical Management ScienceOperations ManagementISBN:9781337406659Author:WINSTON, Wayne L.Publisher:Cengage,
Practical Management ScienceOperations ManagementISBN:9781337406659Author:WINSTON, Wayne L.Publisher:Cengage, Foundations of Business (MindTap Course List)MarketingISBN:9781337386920Author:William M. Pride, Robert J. Hughes, Jack R. KapoorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Foundations of Business (MindTap Course List)MarketingISBN:9781337386920Author:William M. Pride, Robert J. Hughes, Jack R. KapoorPublisher:Cengage Learning Foundations of Business - Standalone book (MindTa...MarketingISBN:9781285193946Author:William M. Pride, Robert J. Hughes, Jack R. KapoorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Foundations of Business - Standalone book (MindTa...MarketingISBN:9781285193946Author:William M. Pride, Robert J. Hughes, Jack R. KapoorPublisher:Cengage Learning


