
Concept explainers
Interpretation:
To show that each of the following fixed points has an index equal to +1.
a) stable spiral b) unstable spiral c) center d) star e) degenerate node
Concept Introduction:
Index theory provides the global information about the phase portrait.
The index of the closed curve can be defined as the net number of counter-clockwise revolutions made by
Where,
Answer to Problem 1E
Solution:
For each of the fixed points, the index is equal to +1 is proved.
Explanation of Solution
Following fixed points have an index equal to
Sketch for the stable spiral,
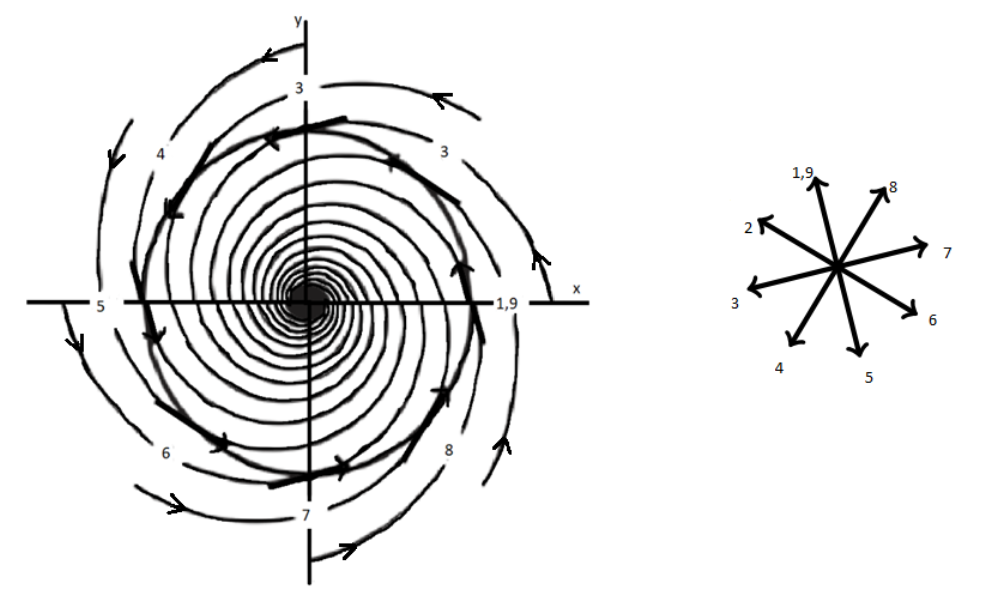
The above sketch shows that every vector is always pointing inwards. It is seen from the direction of arrow that the vector field is rotating in counter-clockwise direction. Hence, the index for the stable spiral is +1.
Sketch for an unstable spiral
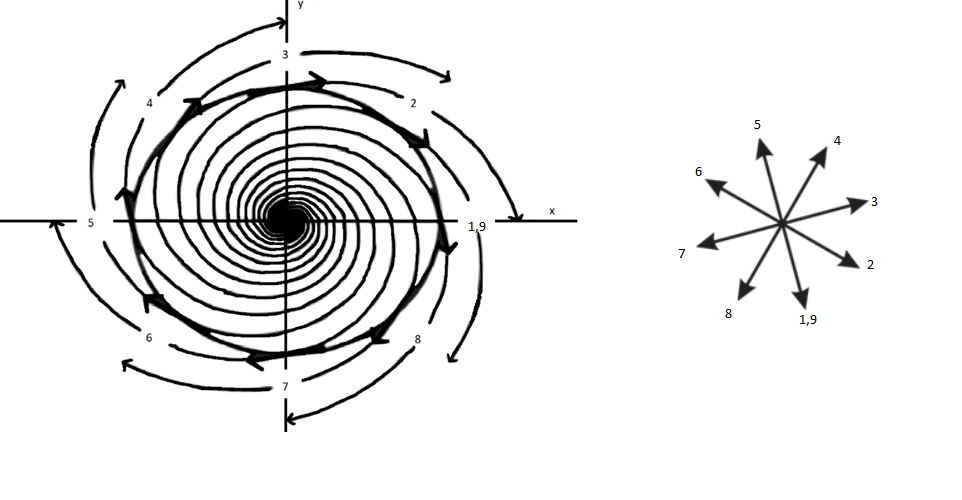
The above sketch shows that every vector is always pointing outwards. It is seen from the direction of arrow that the vector field is rotating in counter-clockwise direction. Hence, the index for the unstable spiral is +1.
Sketch for a Centre
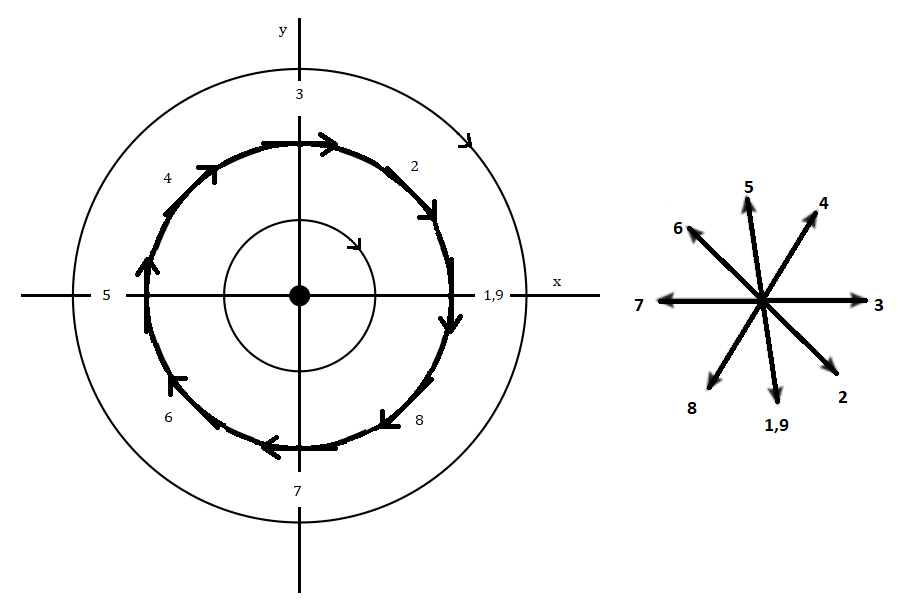
The above sketch shows that every vector is making tangent to the closed orbit. It is seen from the direction of arrow that the vector field is rotating in counter-clockwise direction by
Sketch for a star
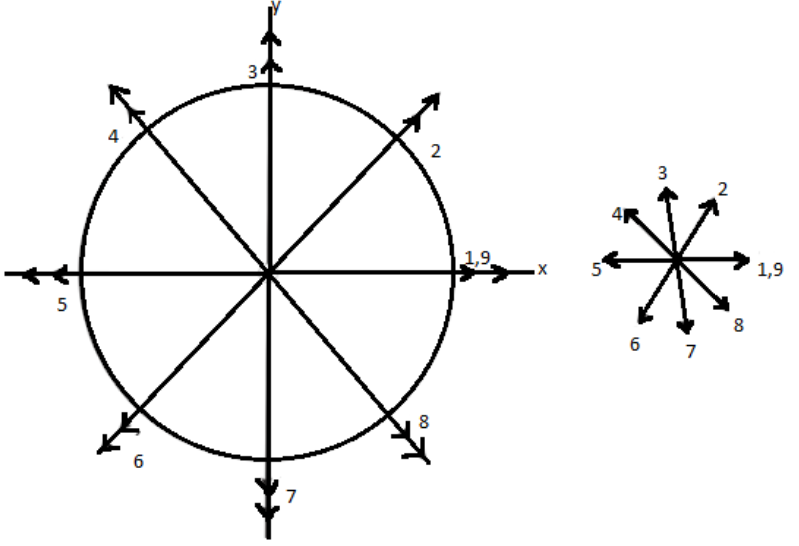
The above sketch shows that every vector is always pointing outwards. It is seen from the direction of arrow that the vector field is rotating in counter-clockwise direction by
Sketch for a degenerate node:
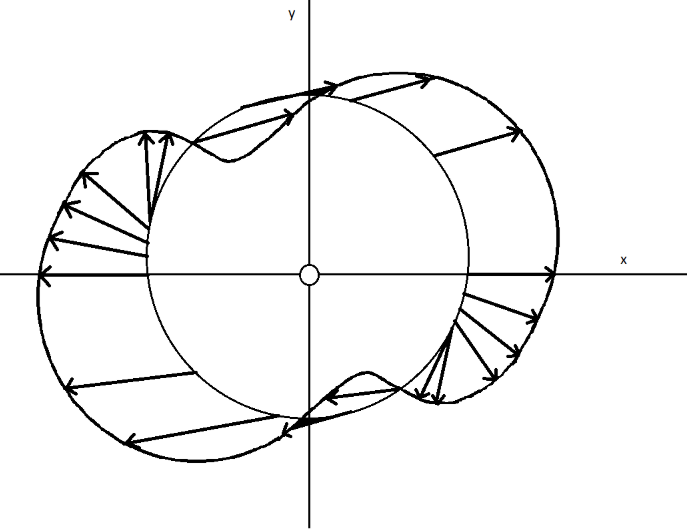
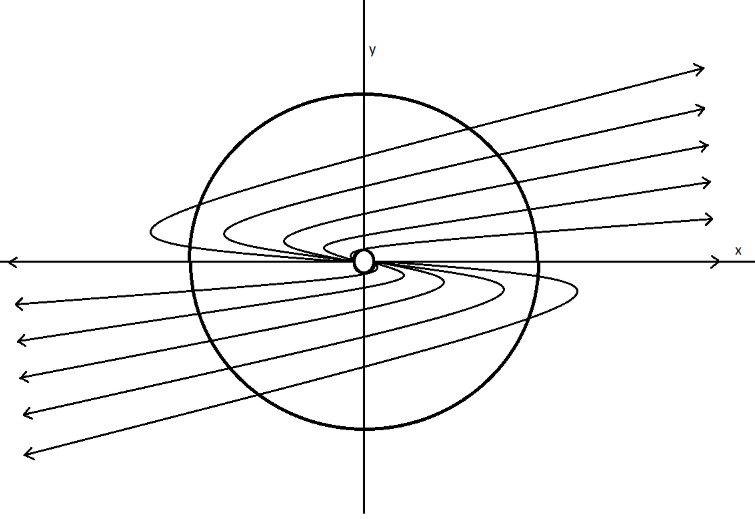
The vector field at the point is pretty fastidious where the trajectory turns around and starts moving in opposite direction. Due to this, the graph of the only vector head is plotted instead of the individual vectors. These vectors bunch around the angle
Above sketches showthat each of the fixed point have an index equal to +1.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 6 Solutions
Nonlinear Dynamics and Chaos
- 2. Sam and Deb have a weekly net income of $1500. They have a pet dog. Their monthly expenses, not related to housing, are $2875. They have savings of $32 000. They are considering two housing options: Option 1: Renting a 2-bedroom condo for $1650 a month, plus utilities averaging $210 a month Option 2: Buying a 2-bedroom condo for a down payment of $24 500, bi-weekly mortgage payments of $1100, and a monthly condo fee of $475 a) Determine the monthly cost of each housing option. Factoring in other expenses not related to housing, which one can Sam and Deb afford? b) Suppose their dog falls ill and they have to pay $85 every week to cover veterinarian and medical expenses. Calculate the additional monthly expenses. How much money would be available for savings if they choose housing option 2?arrow_forwardI bought sparrows at 3 for a penny, turtle doves at 2 for a penny, anddoves at 2 pence each. If I spent 30 pence buying 30 birds and boughtat least one of each kind of bird, how many birds of each kind did I buy?(This is a problem from Fibonacci’s Liber Abaci, 1202.)arrow_forward2. Jacob is going to college. He has a part-time job with take-home pay of $575 every two weeks. He has received a scholarship for $5500 for the year. Determine Jacob's total monthly income.arrow_forward
- 1. Pira's expenses are $850 a month for rent and utilities, $52 a month for TV and Internet package, $90 a week for food, $110 a month for a bus pass, $25 a week for entertainment, and $85 every two weeks for miscellaneous expenses. a) Convert each expense to a monthly amount and represent each monthly amount as a percentage. b) Create a circle graph that shows the breakdown of the monthly expenses. c) Pira has an income of $1600/biweekly and is deciding whether a weeklong vacation to Florida would be within her budget. The cost of the trip is approximately $2000 per week. Would you recommend for her to take the one weeklong vacation? Explain.arrow_forward4. Mason works at a part-time job earning $985 every two weeks. Mason's expenses are $750 a month for rent and utilities, $75 a month for her cell phone, $350 a month for food, $35 a week for entertainment, $310 a month for her car loan payment, and $65 every two weeks for miscellaneous expenses. How long will it take Mason to save $2000 for a vacation? Round your answer to the nearest month.arrow_forwardPls help ASAParrow_forward
- Pls help ASAParrow_forward2. List three life events that can (not related to savings) change a person's monthly budget. Explain.arrow_forward3. Abdul works full-time in a bookstore. He earns a take-home salary of $580 a week. His expenses are $850 a month for rent and utilities, $65 a month for his cell phone, $95 a week for groceries, and $75 every two weeks for miscellaneous expenses. How much can Abdul save each month?arrow_forward
- Classify the singularities for the following functions at the given point. at a = (a) f(z) = 1 (2 sin z-1)² (b) f(z) = exp(4)-1 at 0 and at a = (c) f(z) = 1-cosh z at a=0 2 In the case of a pole, indicate the order of the pole and its residue.arrow_forwardDetermine all functions f analytic in the open unit disc || < 1 which satisfy in addition f(0) = 1 and |f(z)|≥ 1 whenever || < 1. Justify your answer.arrow_forwardDeduce the Laurent expansion for f(z) = 22(2-3)2 in the annulus 0 < |z3|< 3.arrow_forward
 Mathematics For Machine TechnologyAdvanced MathISBN:9781337798310Author:Peterson, John.Publisher:Cengage Learning,Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic GeometryAlgebraISBN:9781133382119Author:SwokowskiPublisher:Cengage
Mathematics For Machine TechnologyAdvanced MathISBN:9781337798310Author:Peterson, John.Publisher:Cengage Learning,Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic GeometryAlgebraISBN:9781133382119Author:SwokowskiPublisher:Cengage
 Elementary Geometry For College Students, 7eGeometryISBN:9781337614085Author:Alexander, Daniel C.; Koeberlein, Geralyn M.Publisher:Cengage,
Elementary Geometry For College Students, 7eGeometryISBN:9781337614085Author:Alexander, Daniel C.; Koeberlein, Geralyn M.Publisher:Cengage, Algebra for College StudentsAlgebraISBN:9781285195780Author:Jerome E. Kaufmann, Karen L. SchwittersPublisher:Cengage Learning
Algebra for College StudentsAlgebraISBN:9781285195780Author:Jerome E. Kaufmann, Karen L. SchwittersPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Linear Algebra (MindTap Course List)AlgebraISBN:9781305658004Author:Ron LarsonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Elementary Linear Algebra (MindTap Course List)AlgebraISBN:9781305658004Author:Ron LarsonPublisher:Cengage Learning





