
Concept explainers
Interpretation:
To find the equation of the stable manifold of the system
Concept Introduction:
The equation for stable manifold can be found by introducing the new variable
The equation for stable manifold is given by
Answer to Problem 14E
Solution:
a) The equation for stable manifold is
b) With the same shape as the stable manifold shown in Figure
Explanation of Solution
a) The system is given as:
The given equations can be rewritten as:
It is given that the system has one fixed saddle point at
Introducing the new variable
Substituting
Dividing the equation
The point
The equation for stable manifold is
Differentiating both sides with respect to
From equations
Since
Substituting
Eliminating all the terms higher than the second order term in
Dividing both sides by
Simplifying it further,
To solve for equilibrium point, substituting
Since
Comparing the coefficients of
Substituting
Substituting
Thus, the equation for stable manifold for the given system is
b) The graph of the stable manifold on the phase portrait is shown below.
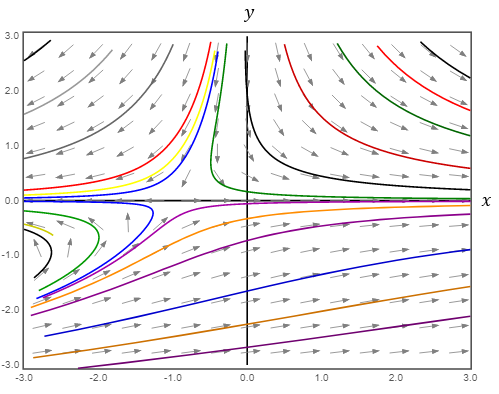
From the above graph, it is clear that with the same shape as the stable manifold shown in Figure
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 6 Solutions
Nonlinear Dynamics and Chaos
- Q/ Find the Laurent series of (2-3) cos around z = 1 2-1arrow_forward31.5. Let be the circle |+1| = 2 traversed twice in the clockwise direction. Evaluate dz (22 + 2)²arrow_forwardUsing FDF, BDF, and CDF, find the first derivative; 1. The distance x of a runner from a fixed point is measured (in meters) at an interval of half a second. The data obtained is: t 0 x 0 0.5 3.65 1.0 1.5 2.0 6.80 9.90 12.15 Use CDF to approximate the runner's velocity at times t = 0.5s and t = 1.5s 2. Using FDF, BDF, and CDF, find the first derivative of f(x)=x Inx for an input of 2 assuming a step size of 1. Calculate using Analytical Solution and Absolute Relative Error: = True Value - Approximate Value| x100 True Value 3. Given the data below where f(x) sin (3x), estimate f(1.5) using Langrage Interpolation. x 1 1.3 1.6 1.9 2.2 f(x) 0.14 -0.69 -0.99 -0.55 0.31 4. The vertical distance covered by a rocket from t=8 to t=30 seconds is given by: 30 x = Loo (2000ln 140000 140000 - 2100 9.8t) dt Using the Trapezoidal Rule, n=2, find the distance covered. 5. Use Simpson's 1/3 and 3/8 Rule to approximate for sin x dx. Compare the results for n=4 and n=8arrow_forward
- 1. A Blue Whale's resting heart rate has period that happens to be approximately equal to 2π. A typical ECG of a whale's heartbeat over one period may be approximated by the function, f(x) = 0.005x4 2 0.005x³-0.364x² + 1.27x on the interval [0, 27]. Find an nth-order Fourier approximation to the Blue Whale's heartbeat, where n ≥ 3 is different from that used in any other posts on this topic, to generate a periodic function that can be used to model its heartbeat, and graph your result. Be sure to include your chosen value of n in your Subject Heading.arrow_forward7. The demand for a product, in dollars, is p = D(x) = 1000 -0.5 -0.0002x² 1 Find the consumer surplus when the sales level is 200. [Hints: Let pm be the market price when xm units of product are sold. Then the consumer surplus can be calculated by foam (D(x) — pm) dx]arrow_forward4. Find the general solution and the definite solution for the following differential equations: (a) +10y=15, y(0) = 0; (b) 2 + 4y = 6, y(0) =arrow_forward
- 5. Find the solution to each of the following by using an appropriate formula developed in the lecture slides: (a) + 3y = 2, y(0) = 4; (b) dy - 7y = 7, y(0) = 7; (c) 3d+6y= 5, y(0) = 0arrow_forward1. Evaluate the following improper integrals: (a) fe-rt dt; (b) fert dt; (c) fi da dxarrow_forward8. Given the rate of net investment I(t) = 9t¹/2, find the level of capital formation in (i) 16 years and (ii) between the 4th and the 8th years.arrow_forward
- 9. If the marginal revenue function of a firm in the production of output is MR = 40 - 10q² where q is the level of output, and total revenue is 120 at 3 units of output, find the total revenue function. [Hints: TR = √ MRdq]arrow_forward6. Solve the following first-order linear differential equations; if an initial condition is given, definitize the arbitrary constant: (a) 2 + 12y + 2et = 0, y(0) = /; (b) dy+y=tarrow_forward4. Let A = {a, b, c, d, e, f}, B = {e, f, g, h} and C = {a, e, h,i}. Let U = {a, b, c, d, e, f, g, h, i, j, k}. • Draw a Venn Diagram to describe the relationships between these sets Find (AB) NC • Find (AC) UB Find AUBUC • Find (BC) N (A - C)arrow_forward
 Linear Algebra: A Modern IntroductionAlgebraISBN:9781285463247Author:David PoolePublisher:Cengage Learning
Linear Algebra: A Modern IntroductionAlgebraISBN:9781285463247Author:David PoolePublisher:Cengage Learning
